Font Control
To simplify the integration and configuration of font support in applications that require word processing and text editing capabilities, the Windows Ribbon framework provides a specialized Font Control that exposes a wide range of font properties such as typeface name, style, point size, and effects.
- Introduction
- A Consistent Experience
- Easy Integration and Configuration
- Alignment with Common GDI Text Structures
- Add a FontControl
- Define a FontControl Command Handler
- Related topics
Introduction
The Font Control is a composite control that consists of buttons, toggle buttons, drop-down list boxes, and combo boxes, all of which are used to specify a particular font property or formatting option.
The following screen shot shows the Ribbon Font Control in WordPad for Windows 7.
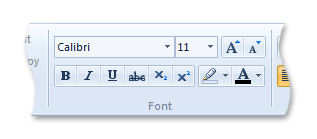
A Consistent Experience
As a built-in Ribbon control, the Font Control improves overall font management, selection and formatting functionality, and provides a rich, consistent user experience across all Ribbon applications.
This consistent experience includes
Standardized formatting and selection of fonts across Ribbon applications.
Standardized font representation across Ribbon applications.
Automatic, in Windows 7, font activation that is based on the Show or Hide setting for each font in the Fonts control panel. The Font Control only displays those fonts that are set to Show.
Note
In Windows Vista, the Fonts control panel does not offer the Show or Hide functionality, so all fonts are activated.
Font management that is available directly from the control.
The following screen shot shows that the Fonts control panel can be accessed directly from the Font Control.
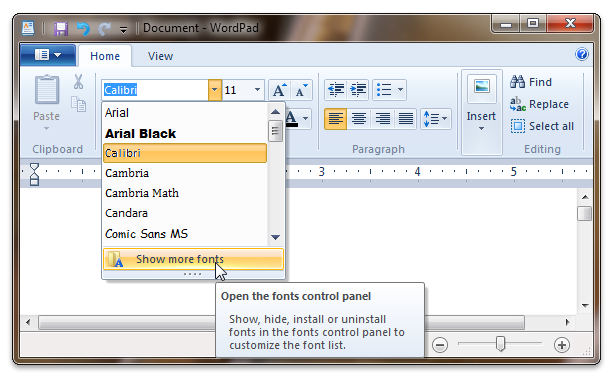
Support for auto-preview.
Exposure of fonts that are most relevant to a user, such as
- Localized font lists for international users.
- Font lists based on input device.
Note
Support for this functionality is not available on any platform older than Windows 7.
Easy Integration and Configuration
By providing standard, reusable, and easily consumed functionality, the Ribbon Font Control eases the burden of integrating font support into an application.
The details of font selection and formatting are wrapped in one, self-contained logical element that
- Eliminates the complex management of control interdependencies typical of font control implementations.
- Requires a single Command handler for all functionality exposed by the Font Control sub-controls.
This single Command handler allows the Font Control to manage the functionality of various sub-controls internally; a sub-control never interacts directly with the application, regardless of its function.
Other features of the Font Control include
Automatic, DPI-aware generation of a WYSIWYG (what you see is what you get) bitmap representation for each font in the Font family menu.
Windows Graphics Device Interface (GDI) integration.
Localized font family bitmaps and tooltips.
Font enumeration, grouping, and metadata for managing and presenting fonts.
Note
Support for this functionality is not available on any platform older than Windows 7 .
The Text color and Text highlight color drop-down color pickers that mirror the Ribbon Drop-Down Color Picker behavior.
Support of auto-previewing by all Font Control gallery-based sub-controls: Font family, Font size, Text color, and Text highlight color.
Alignment with Common GDI Text Structures
Windows Graphics Device Interface (GDI) text stack components are used to expose font selection and formatting functionality through the Ribbon Font Control. The various font features supported by the LOGFONT Structure, CHOOSEFONT Structure, and CHARFORMAT2 Structure are exposed through the sub-controls that are included in the Font Control.
The sub-controls that are displayed in the Font Control depend on the FontType template declared in the Ribbon markup. The FontType templates (discussed in further detail in the following section) are designed to align with the common Windows Graphics Device Interface (GDI) text structures.
Add a FontControl
This section outlines the basic steps for adding a Font Control to a Ribbon application.
Declaring a FontControl in Markup
Like other Ribbon controls, the Font Control is declared in markup with a FontControl element and associated with a Command declaration through a Command ID. When the application is compiled, the Command ID is used to bind the Command to a Command handler in the host application.
Note
If no Command ID is declared with the FontControl in markup, then one is generated by the framework.
Because the sub-controls of the Font Control are not exposed directly, customization of the Font Control is limited to three FontType layout templates defined by the framework.
Further customization of the Font Control can be accomplished by combining the layout template with FontControl attributes such as IsHighlightButtonVisible, IsStrikethroughButtonVisible, and IsUnderlineButtonVisible.
Note
Font functionality beyond that exposed by the standard Font Control templates and attributes requires a custom font control implementation that is outside the scope of this article.
The following table lists the Font Control templates and the edit control type that each template is aligned with.
| Template | Supports |
|---|---|
| FontOnly | LOGFONT Structure |
| FontWithColor | CHOOSEFONT Structure |
| RichFont | CHARFORMAT2 Structure |
The following table lists the controls that are associated with each template and identifies the controls that are optional for an associated template.
Controls
Templates
RichFont
FontWithColor
FontOnly
Default
Optional
Default
Optional
Default
Optional
Font size combo box
Yes
No
Yes
No
Yes
No
Font family combo box
Yes
No
Yes
No
Yes
No
Grow font button
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
-
-
Shrink font button
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
-
-
Bold button
Yes
No
Yes
No
Yes
No
Italic button
Yes
No
Yes
No
Yes
No
Underline button
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Strikethrough button
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Subscript button
Yes
No
-
-
-
-
Superscript button
Yes
No
-
-
-
-
Text highlight color button
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
-
-
Text color button
Yes
No
Yes
No
-
-
When the layout behavior of a Font Control is declared, the Ribbon framework provides an optional SizeDefinition layout template, OneFontControl, that defines two sub-control configurations based on the size of the Ribbon and the space available for the Font Control. For more information, see Customizing a Ribbon Through Size Definitions and Scaling Policies.
Adding a FontControl to a Ribbon
The following code examples demonstrate the basic markup requirements for adding a Font Control to a Ribbon:
This section of code shows the FontControl Command declaration markup, including the Tab and Group Commands that are required for displaying a control in the Ribbon.
<Command Name="cmdTab1"
Comment="These comments are optional and are inserted into the header file."
Symbol="cmdTab1" Id="10000" >
<Command.LabelTitle>Tab 1</Command.LabelTitle>
</Command>
<Command Name="cmdGroup1" Comment="Group #1" Symbol="cmdGroup1" Id="20000">
<!-- This image is used when the group scales to a pop-up. -->
<Command.SmallImages>
<Image>res/Button_Image.bmp</Image>
</Command.SmallImages>
</Command>
<Command Name="cmdFontControl" Symbol="cmdFontControl" Comment="FontControl" Id="25001" Keytip="F" />
This section of code shows the markup required to declare and associate a FontControl with a Command through a Command ID. This particular example includes the Tab and Group declarations, with scaling preferences.
<Ribbon.Tabs>
<Tab CommandName="cmdTab1">
<Tab.ScalingPolicy>
<ScalingPolicy>
<ScalingPolicy.IdealSizes>
<Scale Group="cmdGroup1" Size="Large" />
</ScalingPolicy.IdealSizes>
<!-- Describe how the FontControl group scales. -->
<Scale Group="cmdGroup1" Size="Medium" />
<Scale Group="cmdGroup1" Size="Popup" />
</ScalingPolicy>
<Group CommandName="cmdGroup1" SizeDefinition="OneFontControl">
<FontControl CommandName="cmdFontControl" FontType="RichFont" />
</Group>
</Tab>
</Ribbon.Tabs>
Adding a FontControl to a ContextPopup
Adding a Font Control to a Context Popup requires a procedure similar to that of adding a Font Control to the Ribbon. However, a Font Control in a MiniToolbar is restricted to the set of default sub-controls that are common to all Font Control templates: Font family, Font size, Bold, and Italic.
The following code examples demonstrate the basic markup requirements for adding a Font Control to a Context Popup:
This section of code shows the FontControl Command declaration markup that is required for displaying a FontControl in the ContextPopup.
<Command Name="cmdFontControl" Symbol="cmdFontControl" Comment="FontControl" Id="25001" />
This section of code shows the markup required to declare and associate a FontControl with a Command through a Command ID.
<ContextPopup.MiniToolbars>
<MiniToolBar Name="MiniToolbar1">
<MenuCategory Class="StandardItems">
<FontControl CommandName="cmdFontControl" />
</MenuCategory>
</MiniToolBar>
</ContextPopup.MiniToolbars>
Keytips
Each sub-control in the Ribbon Font Control is accessible through a keyboard shortcut, or keytip. This keytip is predefined and assigned to each sub-control by the framework.
If a Keytip attribute value is assigned to the FontControl element in markup, this value is added as a prefix to the framework-defined keytip.
Note
The application should enforce a single-character rule for this prefix.
The following table lists the keytips defined by the framework.
| Sub-control | Keytip |
|---|---|
| Font family | F |
| Font style | T |
| Font size | S |
| Grow font | G |
| Shrink font | K |
| Bold | B |
| Italic | I |
| Underline | U |
| Strikethrough | X |
| Superscript | Y or Z Note: If the Keytip attribute is not declared in markup, the default keytip is Y; otherwise, the default keytip is Keytip + Z. |
| Subscript | A |
| Font color | C |
| Font highlight | H |
The recommended prefix for a Multilingual User Interface (MUI) EN-US Ribbon is 'F', as shown in the following example.
<Command Name="cmdFontControl" Symbol="cmdFontControl" Comment="FontControl" Id="25001" Keytip="F" />
The following screen shot illustrates the Font Control keytips as they are defined in the previous example.
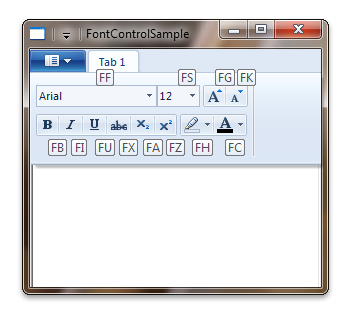
The Ribbon Resource File
When the markup file is compiled, a resource file that contains all resource references for the Ribbon application is generated.
Example of a simple resource file:
// ******************************************************************************
// * This is an automatically generated file containing the ribbon resource for *
// * your application. *
// ******************************************************************************
#include ".\ids.h"
STRINGTABLE
BEGIN
cmdTab1_LabelTitle_RESID L"Tab 1"
/* LabelTitle cmdTab1_LabelTitle_RESID: These comments are optional and are
inserted into the header file. */
END
cmdGroup1_SmallImages_RESID BITMAP "res\\Button_Image.bmp"
/* SmallImages cmdGroup1_SmallImages_RESID: Group #1 */
STRINGTABLE
BEGIN
cmdFontControl_Keytip_RESID L"F" /* Keytip cmdFontControl_Keytip_RESID: FontControl */
END
FCSAMPLE_RIBBON UIFILE "Debug\\FCSample.bml"
Font Control Properties
The Ribbon framework defines a collection of property keys for the Font Control and its constituent sub-controls.
Typically, a Font Control property is updated in the ribbon UI by invalidating the Command associated with the control through a call to the IUIFramework::InvalidateUICommand method. The invalidation event is handled, and the property updates defined, by the IUICommandHandler::UpdateProperty callback method.
The IUICommandHandler::UpdateProperty callback method is not executed, and the application queried for an updated property value, until the property is required by the framework. For example, when a tab is activated and a control revealed in the ribbon UI, or when a tooltip is displayed.
Note
In some cases, a property can be retrieved through the IUIFramework::GetUICommandProperty method and set with the IUIFramework::SetUICommandProperty method.
The following table lists the property keys that are associated with the Font Control.
| Property Key | Notes |
|---|---|
| UI_PKEY_FontProperties | Exposes, in aggregate as an IPropertyStore object, all Font Control sub-control properties. The framework queries this property when UI_INVALIDATIONS_VALUE is passed as the value of flags in the call to IUIFramework::InvalidateUICommand. |
| UI_PKEY_FontProperties_ChangedProperties | Exposes, in aggregate as an IUISimplePropertySet object, only Font Control sub-control properties that have changed. |
| UI_PKEY_Keytip | Can only be updated through invalidation. |
| UI_PKEY_Enabled | Supports IUIFramework::GetUICommandProperty and IUIFramework::SetUICommandProperty. |
In addition to the properties supported by the Font Control itself, the Ribbon framework also defines a property key for each Font Control sub-control. These property keys and their values are exposed by the framework through an IPropertyStore interface implementation that defines the methods for managing a collection, also called a property bag, of name and value pairs.
The application translates the font structures to properties that are accessible through the IPropertyStore interface methods. This model emphasizes the distinction between the Font Control and the Windows Graphics Device Interface (GDI) text stack components (LOGFONT Structure, CHOOSEFONT Structure, and CHARFORMAT2 Structure) that are supported by the framework.
The following table lists the individual controls and their associated property keys.
| Controls | Property Key | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Font size | UI_PKEY_FontProperties_Size | When a run of heterogeneously sized text is highlighted, the Ribbon framework sets the Font size control to blank and the value of UI_PKEY_FontProperties_Size to 0. When the Grow font or Shrink font button is clicked, all highlighted text is resized but the relative difference in text sizes is preserved. |
| Font family | UI_PKEY_FontProperties_Family | GDI font family names vary with system locale. As such, if the value of UI_PKEY_FontProperties_Family is preserved across application sessions, that value should be retrieved on each new session. |
| Grow font | UI_PKEY_FontProperties_Size | See Font size. |
| Shrink font | UI_PKEY_FontProperties_Size | See Font size. |
| Bold | UI_PKEY_FontProperties_Bold | |
| Italic | UI_PKEY_FontProperties_Italic | |
| Underline | UI_PKEY_FontProperties_Underline | |
| Strikethrough | UI_PKEY_FontProperties_Strikethrough | |
| Subscript | UI_PKEY_FontProperties_VerticalPositioning | If the Subscript button is set, then the Superscript cannot also be set. |
| Superscript | UI_PKEY_FontProperties_VerticalPositioning | If the Superscript button is set, then the Subscript cannot also be set. |
| Text highlight color | UI_PKEY_FontProperties_BackgroundColor, UI_PKEY_FontProperties_BackgroundColorType | Provides the same functionality as the HighlightColors template of the DropDownColorPicker element.We highly recommend that only an initial Text highlight color value be set by the application. The last selected value should be preserved and not set when the cursor is repositioned within a document. This allows quick access to the user's last selection, and the color picker does not have to be reopened. Color swatches cannot be customized. |
| Text color | UI_PKEY_FontProperties_ForegroundColor, UI_PKEY_FontProperties_ForegroundColorType | Provides the same functionality as the StandardColors template of the DropDownColorPicker element.We highly recommend that only an initial Text color value be set by the application. The last selected value should be preserved and not set when the cursor is repositioned within a document. This allows quick access to the user's last selection, and the color picker does not have to be reopened. Color swatches cannot be customized. |
Define a FontControl Command Handler
This section describes the steps required to bind a Font Control to a Command handler.
Warning
Any attempt to select a color swatch from the color picker of a Font Control may result in an access violation if no Command handler is associated with the control.
The following code example demonstrates how to bind Commands that are declared in markup to a Command handler.
//
// FUNCTION: OnCreateUICommand(UINT, UI_COMMANDTYPE, IUICommandHandler)
//
// PURPOSE: Called by the Ribbon framework for each command specified in markup, to allow
// the host application to bind a command handler to that command.
//
STDMETHODIMP CApplication::OnCreateUICommand(
UINT nCmdID,
__in UI_COMMANDTYPE typeID,
__deref_out IUICommandHandler** ppCommandHandler)
{
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER(typeID);
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER(nCmdID);
if (NULL == m_pCommandHandler)
{
HRESULT hr = CCommandHandler::CreateInstance(&m_pCommandHandler);
if (FAILED(hr))
{
return hr;
}
}
return m_pCommandHandler->QueryInterface(IID_PPV_ARGS(ppCommandHandler));
}
The following code example illustrates how to implement the IUICommandHandler::Execute method for a Font Control.
//
// FUNCTION: Execute()
//
// PURPOSE: Called by the Ribbon framework when a command is executed
// by the user. For example, when a button is pressed.
//
STDMETHODIMP CCommandHandler::Execute(
UINT nCmdID,
UI_EXECUTIONVERB verb,
__in_opt const PROPERTYKEY* key,
__in_opt const PROPVARIANT* ppropvarValue,
__in_opt IUISimplePropertySet* pCommandExecutionProperties)
{
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER(nCmdID);
HRESULT hr = E_NOTIMPL;
if ((key) && (*key == UI_PKEY_FontProperties))
{
// Font properties have changed.
switch (verb)
{
case UI_EXECUTIONVERB_EXECUTE:
{
hr = E_POINTER;
if (pCommandExecutionProperties != NULL)
{
// Get the changed properties.
PROPVARIANT varChanges;
hr = pCommandExecutionProperties->GetValue(UI_PKEY_FontProperties_ChangedProperties, &varChanges);
if (SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
IPropertyStore *pChanges;
hr = UIPropertyToInterface(UI_PKEY_FontProperties, varChanges, &pChanges);
if (SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
// Using the changed properties, set the new font on the selection on RichEdit control.
g_pFCSampleAppManager->SetValues(pChanges);
pChanges->Release();
}
PropVariantClear(&varChanges);
}
}
break;
}
case UI_EXECUTIONVERB_PREVIEW:
{
hr = E_POINTER;
if (pCommandExecutionProperties != NULL)
{
// Get the changed properties for the preview event.
PROPVARIANT varChanges;
hr = pCommandExecutionProperties->GetValue(UI_PKEY_FontProperties_ChangedProperties, &varChanges);
if (SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
IPropertyStore *pChanges;
hr = UIPropertyToInterface(UI_PKEY_FontProperties, varChanges, &pChanges);
if (SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
// Set the previewed values on the RichEdit control.
g_pFCSampleAppManager->SetPreviewValues(pChanges);
pChanges->Release();
}
PropVariantClear(&varChanges);
}
}
break;
}
case UI_EXECUTIONVERB_CANCELPREVIEW:
{
hr = E_POINTER;
if (ppropvarValue != NULL)
{
// Cancel the preview.
IPropertyStore *pValues;
hr = UIPropertyToInterface(UI_PKEY_FontProperties, *ppropvarValue, &pValues);
if (SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
g_pFCSampleAppManager->CancelPreview(pValues);
pValues->Release();
}
}
break;
}
}
}
return hr;
}
The following code example illustrates how to implement the IUICommandHandler::UpdateProperty method for a Font Control.
//
// FUNCTION: UpdateProperty()
//
// PURPOSE: Called by the Ribbon framework when a command property (PKEY) needs to be updated.
//
// COMMENTS:
//
// This function is used to provide new command property values, such as labels, icons, or
// tooltip information, when requested by the Ribbon framework.
//
//
STDMETHODIMP CCommandHandler::UpdateProperty(
UINT nCmdID,
__in REFPROPERTYKEY key,
__in_opt const PROPVARIANT* ppropvarCurrentValue,
__out PROPVARIANT* ppropvarNewValue)
{
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER(nCmdID);
HRESULT hr = E_NOTIMPL;
if (key == UI_PKEY_FontProperties)
{
hr = E_POINTER;
if (ppropvarCurrentValue != NULL)
{
// Get the font values for the selected text in the font control.
IPropertyStore *pValues;
hr = UIPropertyToInterface(UI_PKEY_FontProperties, *ppropvarCurrentValue, &pValues);
if (SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
g_pFCSampleAppManager->GetValues(pValues);
// Provide the new values to the font control.
hr = UIInitPropertyFromInterface(UI_PKEY_FontProperties, pValues, ppropvarNewValue);
pValues->Release();
}
}
}
return hr;
}