Obslužné rutiny schématu a obslužné rutiny Byte-Stream
Toto téma popisuje interní podrobnosti o tom, jak zdrojový překladač vytváří zdroj médií. Toto téma si přečtěte, pokud implementujete vlastní zdroj médií pro Media Foundation a chcete, aby byl zdroj médií dostupný pro aplikace prostřednictvím překladače zdroje.
Zdrojový překladač může vytvořit zdroj médií z adresy URL nebo z bajtového datového proudu (to znamená MMFByteStream ukazatel). K tomu používá pomocné objekty označované jako obslužné rutiny . Pro adresy URL používá zdrojový překladač obslužné rutiny schématu . Pro bajtové datové proudy používá obslužné rutiny bajtového datového proudu.
Obslužná rutina schématu přebírá jako vstup adresu URL a vytváří zdroj médií nebo datový proud bajtů. Pokud vytvoří datový proud bajtů, přeloží ho obslužné rutině bajtového streamu, která vytvoří zdroj médií. Tento proces znázorňuje následující obrázek.
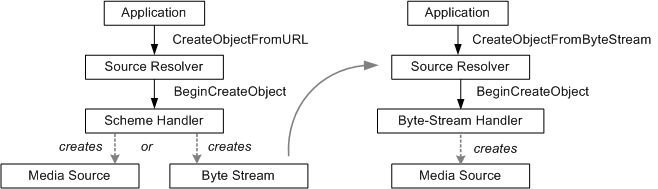
Obslužné rutiny schématu
Obslužné rutiny schématu se používají při volání aplikace MMFSourceResolver::CreateObjectFromURL nebo jeho asynchronní ekvivalent, BeginCreateObjectFromURL.
Zdrojový překladač vyhledá obslužné rutiny schématu v registru. Obslužné rutiny schématu jsou uvedeny podle schématu adres URL pod následujícími klíči:
HKEY_CURRENT_USER
Software
Microsoft
Windows Media Foundation
SchemeHandlers
<scheme>
{00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000} = REG_SZ
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE
Software
Microsoft
Windows Media Foundation
SchemeHandlers
<scheme>
{00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000} = REG_SZ
kde <schéma> je schéma adresy URL, které je obslužná rutina navržena k analýze. Schéma zahrnuje koncový znak ":"; například http:.
Chcete-li zaregistrovat novou obslužnou rutinu schématu, přidejte položku, jejíž název je CLSID obslužné rutiny schématu, v kanonickém řetězcovém formátu: {xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx}. Hodnota položky je řetězec (REG_SZ), který obsahuje stručný popis obslužné rutiny, například "My Scheme Handler" (Obslužná rutina schématu). Důležitou součástí položky je CLSID. Zdrojový překladač vytvoří obslužnou rutinu voláním CoCreateInstance s tímto CLSID.
Obslužné rutiny schématu zpřístupňují rozhraní MMFSchemeHandler. Pokud zdrojový překladač najde obslužnou rutinu schématu, která odpovídá schématu adresy URL, volá zdrojový překladač MMFSchemeHandler::BeginCreateObjecta předává původní adresu URL. Obslužná rutina schématu otevře adresu URL a pokusí se analyzovat obsah. V tomto okamžiku má obslužná rutina schématu dvě možnosti:
- Vytvořte zdroj médií.
- Vytvoření bajtového datového proudu
Pokud se vytvoří zdroj médií, vrátí překladač zdrojového média zdroj do aplikace. Pokud vytvoří datový proud bajtů, pokusí se překladač zdroje najít odpovídající obslužnou rutinu bajtového datového proudu, jak je popsáno v další části.
obslužné rutiny Byte-Stream
Obslužné rutiny byte-stream se používají při volání aplikace MMFSourceResolver::CreateObjectFromByteStream nebo jeho asynchronní ekvivalent, BeginCreateObjectFromByteStream. Používají se také v případě, že obslužná rutina schématu vrací bajtový datový proud, jak je popsáno výše.
Stejně jako u obslužných rutin schématu jsou obslužné rutiny bajtů-stream uvedeny v registru. Jsou uvedeny buď podle přípony názvu souboru, nebo typu MIME (nebo obojího) pod následujícími klíči:
HKEY_CURRENT_USER
Software
Microsoft
Windows Media Foundation
ByteStreamHandlers
<ExtensionOrMimeType>
{00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000} = REG_SZ
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE
Software
Microsoft
Windows Media Foundation
ByteStreamHandlers
<ExtensionOrMimeType>
{00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000} = REG_SZ
where <ExtensionOrMimeType> je přípona názvu souboru nebo typ MIME. Přípony souborů zahrnují počáteční znak "."; například ".wmv".
Přípona názvu souboru je součástí adresy URL, kterou poskytuje aplikace. Typ MIME může být k dispozici prostřednictvím atributu MF_BYTESTREAM_CONTENT_TYPE v bajtovém streamu.
Pokud chcete zaregistrovat novou obslužnou rutinu bajtového streamu, přidejte položku, jejíž název je CLSID obslužné rutiny, ve formuláři kanonického řetězce. Hodnota položky je řetězec (REG_SZ), který obsahuje stručný popis obslužné rutiny, například "My Byte-Stream Handler" (Obslužná rutina my Byte-Stream). Zdrojový překladač volá CoCreateInstance vytvořit obslužnou rutinu z CLSID. Stejnou obslužnou rutinu můžete zaregistrovat pod více než jedním rozšířením nebo typem MIME.
Obslužné rutiny byte-stream zpřístupňují rozhraní MMFByteStreamHandler. Pokud zdrojový překladač najde odpovídající obslužnou rutinu byte-stream, volá MMFByteStreamHandler::BeginCreateObject. Vstupem této metody je ukazatel na bajtový stream a původní adresa URL, pokud je k dispozici. Obslužná rutina bajtového streamu čte z bajtového datového proudu, dokud neanalyduje dostatek dat k vytvoření zdroje médií.
Související témata