Prepare and deploy Active Directory Federation Services - on-premises certificate trust
This article describes Windows Hello for Business functionalities or scenarios that apply to:
- Deployment type: on-premises
- Trust type: certificate trust
- Join type: domain join
Windows Hello for Business works exclusively with the Active Directory Federation Service (AD FS) role included with Windows Server. The on-premises certificate trust deployment model uses AD FS for certificate enrollment (CRA) and device registration.
The following guidance describes the deployment of a new instance of AD FS using the Windows Information Database (WID) as the configuration database.
WID is ideal for environments with no more than 30 federation servers and no more than 100 relying party trusts. If your environment exceeds either of these factors, or needs to provide SAML artifact resolution, token replay detection, or needs AD FS to operate as a federated provider role, then the deployment requires the use of SQL as a configuration database.
To deploy AD FS using SQL as its configuration database, review the Deploying a Federation Server Farm checklist.
A new AD FS farm should have a minimum of two federation servers for proper load balancing, which can be accomplished with external networking peripherals, or with using the Network Load Balancing Role included in Windows Server.
Prepare the AD FS deployment by installing and updating two Windows Servers.
Enroll for a TLS server authentication certificate
Typically, a federation service is an edge facing role. However, the federation services and instance used with the on-premises deployment of Windows Hello for Business does not need Internet connectivity.
The AD FS role needs a server authentication certificate for the federation services, and you can use a certificate issued by your enterprise (internal) CA. The server authentication certificate should have the following names included in the certificate, if you are requesting an individual certificate for each node in the federation farm:
- Subject Name: the internal FQDN of the federation server
- Subject Alternate Name: the federation service name (e.g. sts.corp.contoso.com) or an appropriate wildcard entry (e.g. *.corp.contoso.com)
The federation service name is set when the AD FS role is configured. You can choose any name, but that name must be different than the name of the server or host. For example, you can name the host server adfs and the federation service sts. In this example, the FQDN of the host is adfs.corp.contoso.com and the FQDN of the federation service is sts.corp.contoso.com.
You can also issue one certificate for all hosts in the farm. If you chose this option, leave the subject name blank, and include all the names in the subject alternate name when creating the certificate request. All names should include the FQDN of each host in the farm and the federation service name.
When creating a wildcard certificate, mark the private key as exportable, so that the same certificate can be deployed across each federation server and web application proxy within the AD FS farm. Note that the certificate must be trusted (chain to a trusted root CA). Once you have successfully requested and enrolled the server authentication certificate on one node, you can export the certificate and private key to a PFX file using the Certificate Manager console. You can then import the certificate on the remaining nodes in the AD FS farm.
Be sure to enroll or import the certificate into the AD FS server's computer certificate store. Also, ensure all nodes in the farm have the proper TLS server authentication certificate.
AD FS authentication certificate enrollment
Sign-in the federation server with domain administrator equivalent credentials.
- Start the Local Computer Certificate Manager (certlm.msc)
- Expand the Personal node in the navigation pane
- Right-click Personal. Select All Tasks > Request New Certificate
- Select Next on the Before You Begin page
- Select Next on the Select Certificate Enrollment Policy page
- On the Request Certificates page, select the Internal Web Server check box
- Select the ⚠️ More information is required to enroll for this certificate. Click here to configure settings link
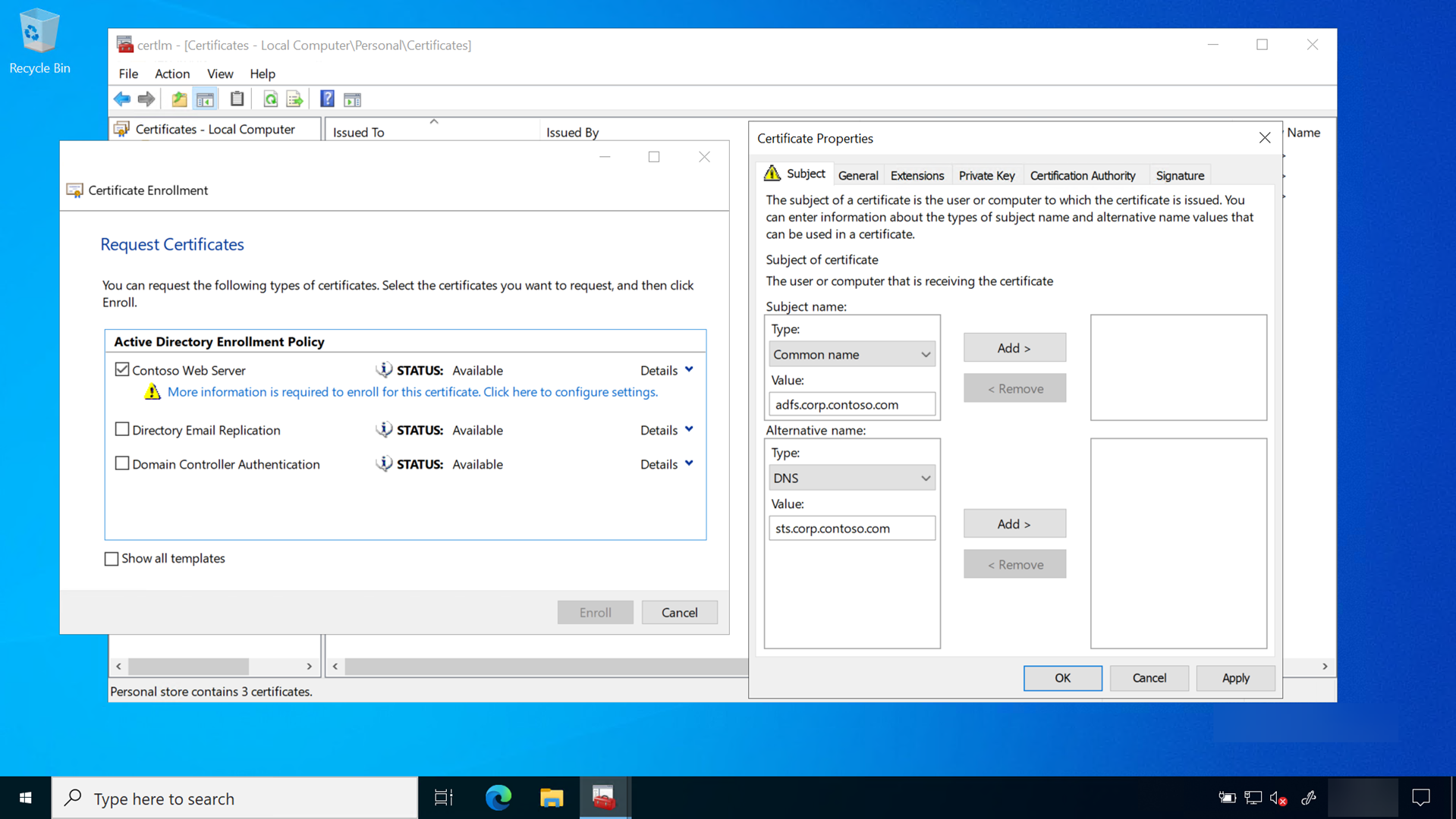
- Under Subject name, select Common Name from the Type list. Type the FQDN of the computer hosting the AD FS role and then select Add
- Under Alternative name, select DNS from the Type list. Type the FQDN of the name that you will use for your federation services (sts.corp.contoso.com). The name you use here MUST match the name you use when configuring the AD FS server role. Select Add and OK when finished
- Select Enroll
A server authentication certificate should appear in the computer's personal certificate store.
Deploy the AD FS role
Important
Finish the entire AD FS configuration on the first server in the farm before adding the second server to the AD FS farm. Once complete, the second server receives the configuration through the shared configuration database when it is added the AD FS farm.
Sign-in the federation server with Enterprise Administrator equivalent credentials.
- Start Server Manager. Select Local Server in the navigation pane
- Select Manage > Add Roles and Features
- Select Next on the Before you begin page
- On the Select installation type page, select Role-based or feature-based installation > Next
- On the Select destination server page, choose Select a server from the server pool. Select the federation server from the Server Pool list and Next
- On the Select server roles page, select Active Directory Federation Services and Next
- Select Next on the Select features page
- Select Next on the Active Directory Federation Service page
- Select Install to start the role installation
Review to validate the AD FS deployment
Before you continue with the deployment, validate your deployment progress by reviewing the following items:
- Confirm the AD FS farm uses the correct database configuration
- Confirm the AD FS farm has an adequate number of nodes and is properly load balanced for the anticipated load
- Confirm all AD FS servers in the farm have the latest updates installed
- Confirm all AD FS servers have a valid server authentication certificate
Device registration service account prerequisites
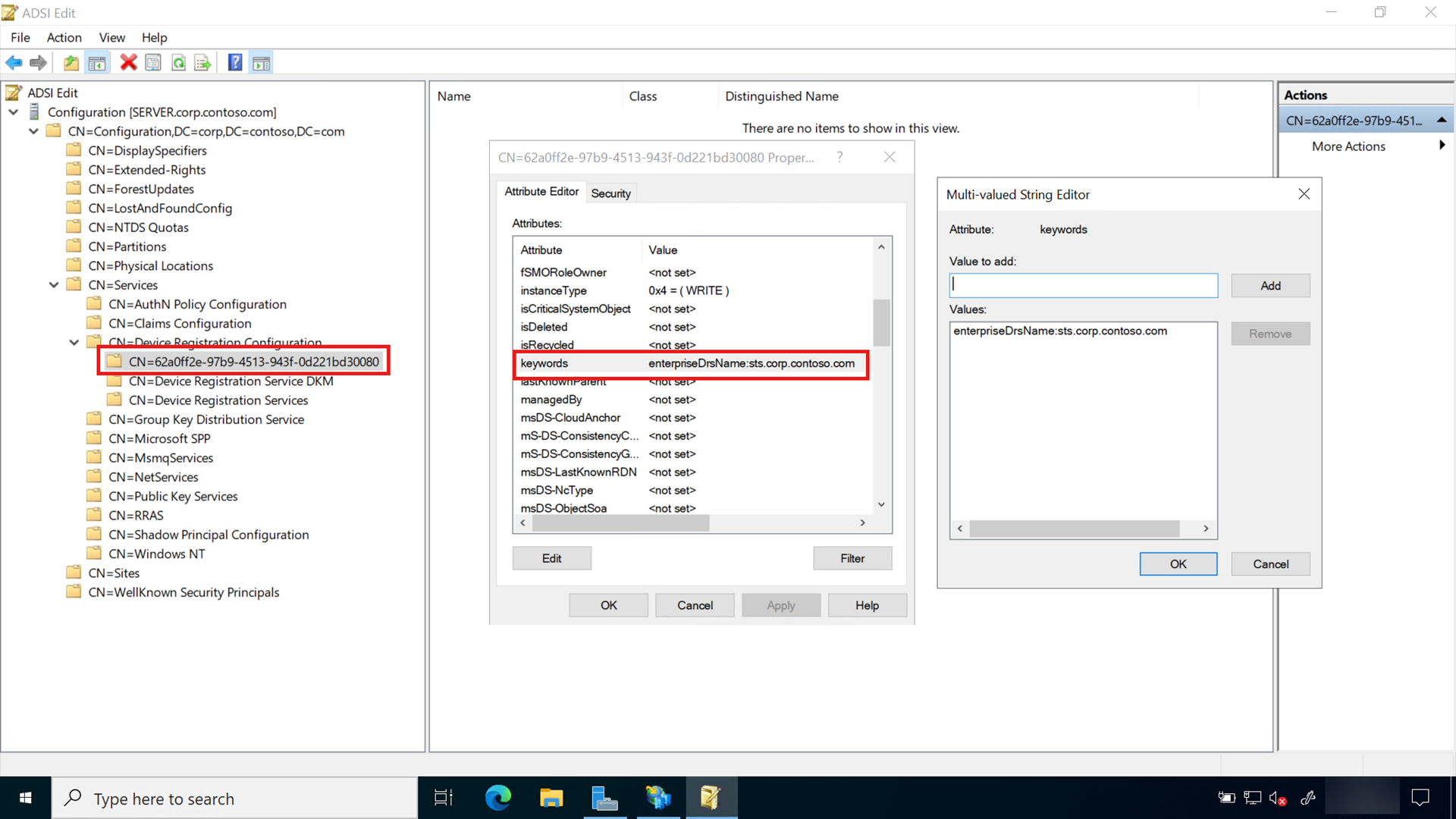
The use of Group Managed Service Accounts (GMSA) is the preferred way to deploy service accounts for services that support them. GMSAs have security advantages over normal user accounts because Windows handles password management. This means the password is long, complex, and changes periodically. AD FS supports GMSAs, and it should be configured using them for additional security.
GSMA uses the Microsoft Key Distribution Service that is located on the domain controllers. Before you can create a GSMA, you must first create a root key for the service. You can skip this if your environment already uses GSMA.
Create KDS Root Key
Sign-in a domain controller with Enterprise Administrator equivalent credentials.
Start an elevated PowerShell console and execute the following command:
Add-KdsRootKey -EffectiveTime (Get-Date).AddHours(-10)
Configure the Active Directory Federation Service Role
Use the following procedures to configure AD FS.
Sign-in to the federation server with Domain Administrator equivalent credentials. These procedures assume you are configuring the first federation server in a federation server farm.
- Start Server Manager
- Select the notification flag in the upper right corner and select Configure the federation services on this server
- On the Welcome page, select Create the first federation server farm > Next
- On the Connect to Active Directory Domain Services page, select Next
- On the Specify Service Properties page, select the recently enrolled or imported certificate from the SSL Certificate list. The certificate is likely named after your federation service, such as sts.corp.contoso.com
- Select the federation service name from the Federation Service Name list
- Type the Federation Service Display Name in the text box. This is the name users see when signing in. Select Next
- On the Specify Service Account page, select Create a Group Managed Service Account. In the Account Name box, type adfssvc
- On the Specify Configuration Database page, select Create a database on this server using Windows Internal Database and select Next
- On the Review Options page, select Next
- On the Pre-requisite Checks page, select Configure
- When the process completes, select Close
Add the AD FS service account to the Key Admins group
During Windows Hello for Business enrollment, the public key is registered in an attribute of the user object in Active Directory. To ensure that the AD FS service can add and remove keys are part of its normal workflow, it must be a member of the Key Admins global group.
Sign-in to a domain controller or management workstation with Domain Administrator equivalent credentials.
- Open Active Directory Users and Computers
- Select the Users container in the navigation pane
- Right-click Key Admins in the details pane and select Properties
- Select the Members > Add…
- In the Enter the object names to select text box, type adfssvc. Select OK
- Select OK to return to Active Directory Users and Computers
- Change to server hosting the AD FS role and restart it
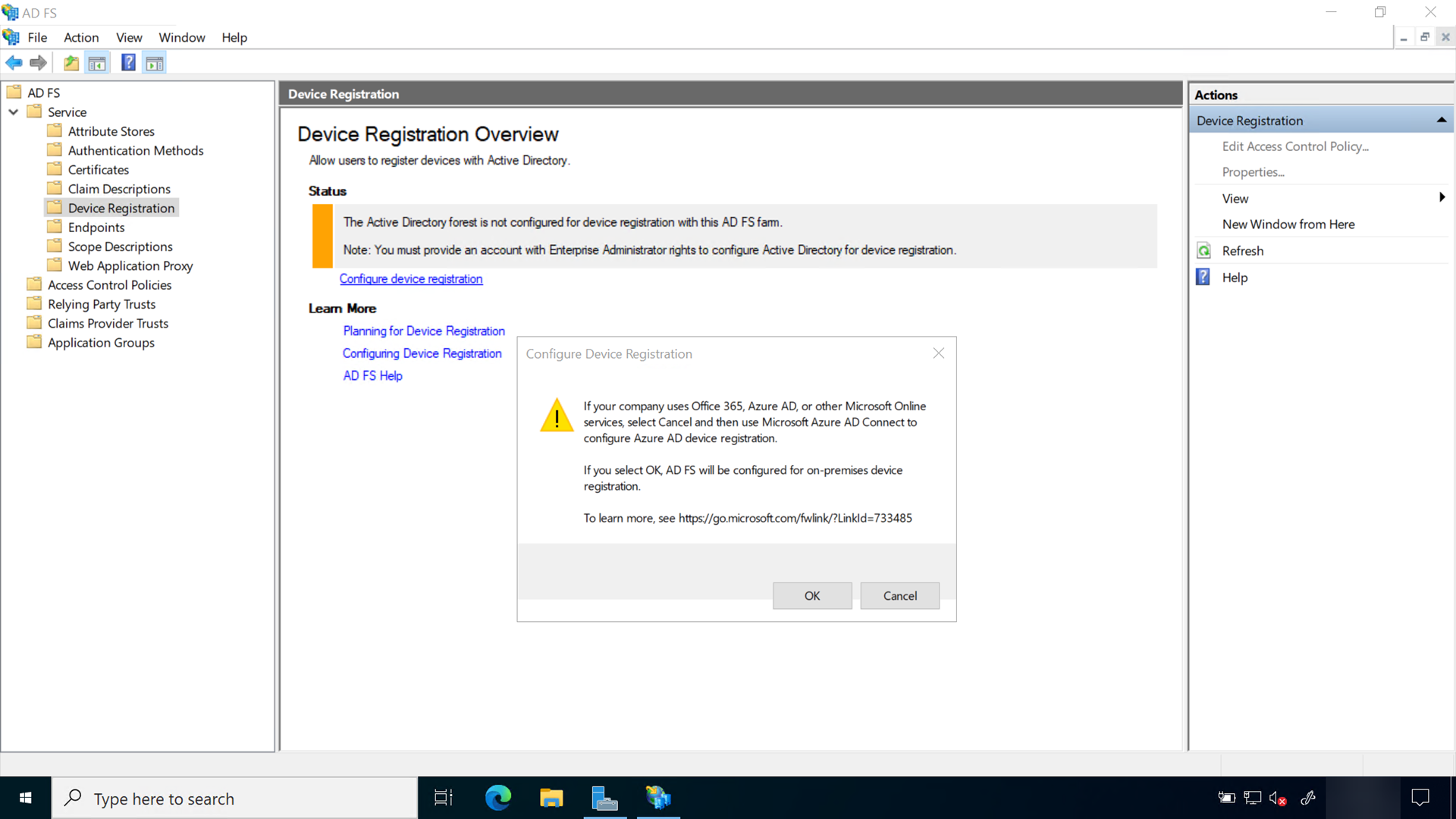
Configure the device registration service
Sign-in to the federation server with Enterprise Administrator equivalent credentials. These instructions assume you are configuring the first federation server in a federation server farm.
- Open the AD FS management console
- In the navigation pane, expand Service. Select Device Registration
- In the details pane, select Configure device registration
- In the Configure Device Registration dialog, Select OK
Triggering device registration from AD FS, creates the service connection point (SCP) in the Active Directory configuration partition. The SCP is used to store the device registration information that Windows clients will automatically discover.
Note
For AD FS 2019 and later in a certificate trust model, a known PRT issue exists. You may encounter this error in AD FS Admin event logs: Received invalid Oauth request. The client 'NAME' is forbidden to access the resource with scope 'ugs'. For more information about the isse and its resolution, see Certificate trust provisioning with AD FS broken on windows server 2019.
Review to validate the AD FS and Active Directory configuration
Before you continue with the deployment, validate your deployment progress by reviewing the following items:
- Record the information about the AD FS certificate, and set a renewal reminder at least six weeks before it expires. Relevant information includes: certificate serial number, thumbprint, common name, subject alternate name, name of the physical host server, the issued date, the expiration date, and issuing CA vendor (if a non-Microsoft certificate)
- Confirm you added the AD FS service account to the KeyAdmins group
- Confirm you enabled the Device Registration service
Configure an enrollment agent certificate template
A certificate registration authority (CRA) is a trusted authority that validates certificate request. Once it validates the request, it presents the request to the certification authority (CA) for issuance. The CA issues the certificate, returns it to the CRA, which returns the certificate to the requesting user. Windows Hello for Business certificate trust deployments use AD FS as the CRA.
The CRA enrolls for an enrollment agent certificate. Once the CRA verifies the certificate request, it signs the certificate request using its enrollment agent certificate and sends it to the CA. The Windows Hello for Business Authentication certificate template is configured to only issue certificates to certificate requests that have been signed with an enrollment agent certificate. The CA only issues a certificate for that template if the registration authority signs the certificate request.
Important
Follow the procedures below based on the AD FS service account used in your environment.
Create an enrollment agent certificate for Group Managed Service Accounts (GMSA)
Sign in to a CA or management workstations with Domain Administrator equivalent credentials.
Open the Certification Authority management console
Right-click Certificate Templates and select Manage
In the Certificate Template Console, right-click on the Exchange Enrollment Agent (Offline request) template details pane and select Duplicate Template
Use the following table to configure the template:
Tab Name Configurations Compatibility - Clear the Show resulting changes check box
- Select Windows Server 2016 from the Certification Authority list
- Select Windows 10 / Windows Server 2016 from the Certification Recipient list
General - Specify a Template display name, for example WHFB Enrollment Agent
- Set the validity period to the desired value
Subject Name Select Supply in the request
Note: Group Managed Service Accounts (GMSA) don't support the Build from this Active Directory information option and will result in the AD FS server failing to enroll the enrollment agent certificate. You must configure the certificate template with Supply in the request to ensure that AD FS servers can perform the automatic enrollment and renewal of the enrollment agent certificate.Cryptography - Set the Provider Category to Key Storage Provider
- Set the Algorithm name to RSA
- Set the minimum key size to 2048
- Set the Request hash to SHA256
Security - Select Add
- Select Object Types and select the Service Accounts check box
- Select OK
- Type
adfssvcin the Enter the object names to select text box and select OK - Select the adfssvc from the Group or users names list. In the Permissions for adfssvc section:
- In the Permissions for adfssvc section, select the Allow check box for the Enroll permission
- Excluding the adfssvc user, clear the Allow check box for the Enroll and Autoenroll permissions for all other items in the Group or users names list
- Select OK
Select OK to finalize your changes and create the new template
Close the console
Create an enrollment agent certificate for a standard service account
Sign in to a CA or management workstations with Domain Administrator equivalent credentials.
Open the Certification Authority management console
Right-click Certificate Templates and select Manage
In the Certificate Template Console, right-click on the Exchange Enrollment Agent (Offline request) template details pane and select Duplicate Template
Use the following table to configure the template:
Tab Name Configurations Compatibility - Clear the Show resulting changes check box
- Select Windows Server 2016 from the Certification Authority list
- Select Windows 10 / Windows Server 2016 from the Certificate Recipient list
General - Specify a Template display name, for example WHFB Enrollment Agent
- Set the validity period to the desired value
Subject Name - Select Build from this Active Directory information
- Select Fully distinguished name from the Subject name format list
- Select the User Principal Name (UPN) check box under Include this information in alternative subject name
Cryptography - Set the Provider Category to Key Storage Provider
- Set the Algorithm name to RSA
- Set the minimum key size to 2048
- Set the Request hash to SHA256
Security - Select Add
- Select Object Types and select the Service Accounts check box
- Select OK
- Type
adfssvcin the Enter the object names to select text box and select OK - Select the adfssvc from the Group or users names list. In the Permissions for adfssvc section:
- In the Permissions for adfssvc section, select the Allow check box for the Enroll permission
- Excluding the adfssvc user, clear the Allow check box for the Enroll and Autoenroll permissions for all other items in the Group or users names list
- Select OK
Select OK to finalize your changes and create the new template
Close the console
Publish the certificate template to the CA
Sign in to the CA or management workstations with Enterprise Admin equivalent credentials.
- Open the Certification Authority management console.
- Expand the parent node from the navigation pane.
- Select Certificate Templates in the navigation pane.
- Right-click the Certificate Templates node. Select New > Certificate Template to issue.
- In the Enable Certificates Templates window, select the WHFB Enrollment Agent template you created in the previous step. Select OK to publish the selected certificate templates to the certification authority.
- If you published the Domain Controller Authentication (Kerberos) certificate template, then unpublish the certificate templates you included in the superseded templates list.
- To unpublish a certificate template, right-click the certificate template you want to unpublish and select Delete. Select Yes to confirm the operation.
- Close the console.
Configure the certificate registration authority
The Windows Hello for Business on-premises certificate-based deployment uses AD FS as the certificate registration authority (CRA). The registration authority is responsible for issuing certificates to users and devices. The registration authority is also responsible for revoking certificates when users or devices are removed from the environment.
Sign-in the AD FS server with domain administrator equivalent credentials.
Open a Windows PowerShell prompt and type the following command:
Set-AdfsCertificateAuthority -EnrollmentAgent -EnrollmentAgentCertificateTemplate WHFBEnrollmentAgent -WindowsHelloCertificateTemplate WHFBAuthentication
Note
If you gave your Windows Hello for Business Enrollment Agent and Windows Hello for Business Authentication certificate templates different names, then replace WHFBEnrollmentAgent and WHFBAuthentication in the above command with the name of your certificate templates. It's important that you use the template name rather than the template display name. You can view the template name on the General tab of the certificate template by using the Certificate Template management console (certtmpl.msc). Or, you can view the template name by using the Get-CATemplate PowerShell cmdlet on a CA.
Enrollment agent certificate lifecycle management
AD FS performs its own certificate lifecycle management. Once the registration authority is configured with the proper certificate template, the AD FS server attempts to enroll the certificate on the first certificate request or when the service first starts.
Approximately 60 days prior to enrollment agent certificate's expiration, the AD FS service attempts to renew the certificate until it is successful. If the certificate fails to renew, and the certificate expires, the AD FS server will request a new enrollment agent certificate. You can view the AD FS event logs to determine the status of the enrollment agent certificate.
Additional federation servers
Organizations should deploy more than one federation server in their federation farm for high-availability. You should have a minimum of two federation services in your AD FS farm, however most organizations are likely to have more. This largely depends on the number of devices and users using the services provided by the AD FS farm.
Server authentication certificate
Each server you add to the AD FS farm must have a proper server authentication certificate. Refer to the Enroll for a TLS Server Authentication Certificate section of this document to determine the requirements for your server authentication certificate. As previously stated, AD FS servers used exclusively for on-premises deployments of Windows Hello for Business can use enterprise server authentication certificates rather than server authentication certificates issued by public certificate authorities.
Install additional servers
Adding federation servers to the existing AD FS farm begins with ensuring the server are fully patched, to include Windows Server 2016 Update needed to support Windows Hello for Business deployments (https://aka.ms/whfbadfs1703). Next, install the Active Directory Federation Service role on the additional servers and then configure the server as an additional server in an existing farm.
Load balance AD FS
Many environments load balance using hardware devices. Environments without hardware load-balancing capabilities can take advantage the network load-balancing feature included in Windows Server to load balance the AD FS servers in the federation farm. Install the Windows Network Load Balancing feature on all nodes participating in the AD FS farm that should be load balanced.
Install Network Load Balancing Feature on AD FS Servers
Sign-in the federation server with Enterprise Administrator equivalent credentials.
- Start Server Manager. Select Local Server in the navigation pane
- Select Manage and then select Add Roles and Features
- Select Next On the Before you begin page
- On the Select installation type page, select Role-based or feature-based installation and select Next
- On the Select destination server page, choose Select a server from the server pool. Select the federation server from the Server Pool list. Select Next
- On the Select server roles page, select Next
- Select Network Load Balancing on the Select features page
- Select Install to start the feature installation
Configure Network Load Balancing for AD FS
Before you can load balance all the nodes in the AD FS farm, you must first create a new load balance cluster. Once you have created the cluster, then you can add new nodes to that cluster.
Sign-in a node of the federation farm with Administrator equivalent credentials.
- Open Network Load Balancing Manager from Administrative Tools
- Right-click Network Load Balancing Clusters, and then select New Cluster
- To connect to the host that is to be a part of the new cluster, in the Host text box, type the name of the host, and then select Connect
- Select the interface that you want to use with the cluster, and then select Next (the interface hosts the virtual IP address and receives the client traffic to load balance)
- In Host Parameters, select a value in Priority (Unique host identifier). This parameter specifies a unique ID for each host. The host with the lowest numerical priority among the current members of the cluster handles all of the cluster's network traffic that is not covered by a port rule. Select Next
- In Cluster IP Addresses, select Add and type the cluster IP address that is shared by every host in the cluster. NLB adds this IP address to the TCP/IP stack on the selected interface of all hosts that are chosen to be part of the cluster. Select Next
- In Cluster Parameters, select values in IP Address and Subnet mask (for IPv6 addresses, a subnet mask value is not needed). Type the full Internet name that users will use to access this NLB cluster
- In Cluster operation mode, select Unicast to specify that a unicast media access control (MAC) address should be used for cluster operations. In unicast mode, the MAC address of the cluster is assigned to the network adapter of the computer, and the built-in MAC address of the network adapter is not used. We recommend that you accept the unicast default settings. Select Next
- In Port Rules, select Edit to modify the default port rules to use port 443
Additional AD FS Servers
- To add more hosts to the cluster, right-click the new cluster, and then select Add Host to Cluster
- Configure the host parameters (including host priority, dedicated IP addresses, and load weight) for the additional hosts by following the same instructions that you used to configure the initial host. Because you are adding hosts to an already configured cluster, all the cluster-wide parameters remain the same
Configure DNS for Device Registration
Sign-in the domain controller or administrative workstation with domain administrator equivalent credentials.
You'll need the federation service name to complete this task. You can view the federation service name by selecting Edit Federation Service Properties from the Action pan of the AD FS management console, or by using (Get-AdfsProperties).Hostname. (PowerShell) on the AD FS server.
- Open the DNS Management console
- In the navigation pane, expand the domain controller name node and Forward Lookup Zones
- In the navigation pane, select the node that has the name of your internal Active Directory domain name
- In the navigation pane, right-click the domain name node and select New Host (A or AAAA)
- In the name box, type the name of the federation service. In the IP address box, type the IP address of your federation server. Select Add Host
- Right-click the
<domain_name>node and select New Alias (CNAME) - In the New Resource Record dialog box, type
enterpriseregistrationin the Alias name box - In the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the target host box, type
federation_service_farm_name.<domain_name_fqdn, and select OK - Close the DNS Management console
Note
If your forest has multiple UPN suffixes, please make sure that enterpriseregistration.<upnsuffix_fqdn> is present for each suffix.
Configure the Intranet Zone to include the federation service
The Windows Hello provisioning presents web pages from the federation service. Configuring the intranet zone to include the federation service enables the user to authenticate to the federation service using integrated authentication. Without this setting, the connection to the federation service during Windows Hello provisioning prompts the user for authentication.
Create an Intranet Zone Group Policy
Sign-in the domain controller or administrative workstation with Domain Admin equivalent credentials:
- Start the Group Policy Management Console (
gpmc.msc) - Expand the domain and select the Group Policy Object node in the navigation pane
- Right-click Group Policy object and select New
- Type Intranet Zone Settings in the name box and select OK
- In the content pane, right-click the Intranet Zone Settings Group Policy object and select Edit
- In the navigation pane, expand Policies under Computer Configuration
- Expand Administrative Templates > Windows Component > Internet Explorer > Internet Control Panel >Security Page. Open Site to Zone Assignment List
- Select Enable > Show. In the Value Name column, type the url of the federation service beginning with https. In the Value column, type the number 1. Select OK twice, then close the Group Policy Management Editor
Deploy the Intranet Zone Group Policy object
- Start the Group Policy Management Console (gpmc.msc)
- In the navigation pane, expand the domain and right-click the node that has your Active Directory domain name and select Link an existing GPO…
- In the Select GPO dialog box, select Intranet Zone Settings or the name of the Windows Hello for Business Group Policy object you previously created and select OK
Event Logs
Use the event logs on the AD FS service to confirm the service account enrolled for an enrollment agent certificate. First, look for the AD FS event ID 443 that confirms certificate enrollment cycle has finished. Once confirmed the AD FS certificate enrollment cycle completed review the CertificateLifecycle-User event log. In this event log, look for event ID 1006, which indicates a new certificate was installed. Details of the event log should show:
- The account name under which the certificate was enrolled
- The action, which should read enroll
- The thumbprint of the certificate
- The certificate template used to issue the certificate
You cannot use the Certificate Manager to view enrolled certificates for group managed service accounts. Use the event log information to confirm the AD FS service account enrolled a certificate. Use certutil.exe to view the details of the certificate shown in the event log.
Group managed service accounts use user profiles to store user information, which included enrolled certificates. On the AD FS server, use a command prompt and navigate to %systemdrive%\users\<adfsGMSA_name>\appdata\roaming\Microsoft\systemcertificates\my\certificates.
Each file in this folder represents a certificate in the service account's Personal store (You may need to use dir.exe /A to view the files in the folder). Match the thumbprint of the certificate from the event log to one of the files in this folder. That file is the certificate. Use the Certutil -q <certificateThumbprintFileName> to view the basic information about the certificate.
For detailed information about the certificate, use Certutil -q -v <certificateThumbprintFileName>.
Validate and deploy multifactor authentication (MFA)
Windows Hello for Business requires users perform multifactor authentication (MFA) prior to enroll in the service. On-premises deployments can use, as MFA option:
- certificates
Note
When using this option, the certificates must be deployed to the users. For example, users can use their smart card or virtual smart card as a certificate authentication option.
- non-Microsoft authentication providers for AD FS
- custom authentication provider for AD FS
Important
As of July 1, 2019, Microsoft will no longer offer MFA Server for new deployments. New customers who would like to require multifactor authentication from their users should use cloud-based Microsoft Entra multifactor authentication. Existing customers who have activated MFA Server prior to July 1 will be able to download the latest version, future updates and generate activation credentials as usual.
For information on available non-Microsoft authentication methods see Configure Additional Authentication Methods for AD FS. For creating a custom authentication method see Build a Custom Authentication Method for AD FS in Windows Server
Follow the integration and deployment guide for the authentication provider you select to integrate and deploy it to AD FS. Make sure that the authentication provider is selected as a multifactor authentication option in the AD FS authentication policy. For information on configuring AD FS authentication policies see Configure Authentication Policies.
Tip
When you validate the AD FS configuration, verify if you need to update the configuration of user agent strings to support Windows Integrated Authentication (WIA). For more information, see Change WIASupportedUserAgent settings.
Review to validate the configuration
Before you continue with the deployment, validate your deployment progress by reviewing the following items:
- Configure an enrollment agent certificate template.
- Confirm only the AD FS service account has the allow enroll permission for the enrollment agent certificate template.
- Consider using an HSM to protect the enrollment agent certificate; however, understand the frequency and quantity of signature operations the enrollment agent server makes and understand the impact it has on overall performance.
- Confirm you properly configured the Windows Hello for Business authentication certificate template.
- Confirm all certificate templates were properly published to the appropriate issuing certificate authorities.
- Confirm the AD FS service account has the allow enroll permission for the Windows Hello Business authentication certificate template.
- Confirm the AD FS certificate registration authority is properly configured using the
Get-AdfsCertificateAuthorityWindows PowerShell cmdlet. - Confirm you restarted the AD FS service.
- Confirm you properly configured load-balancing (hardware or software).
- Confirm you created a DNS A Record for the federation service and the IP address used is the load-balanced IP address.
- Confirm you created and deployed the Intranet Zone settings to prevent double authentication to the federation server.
- Confirm you have deployed a MFA solution for AD FS.