Filter Manager Concepts
The Filter Manager (FltMgr.sys) is a system-supplied kernel-mode driver that implements and exposes functionality commonly required in file system filter drivers. File system filter developers can use FltMgr's functionality to write minifilter drivers that are simpler to develop than legacy file system filter drivers. The end result is a shortened development process and higher-quality, more robust drivers.
FltMgr is installed with Windows, but becomes active only when a minifilter driver is loaded. It attaches to the file system stack for a target volume. A minifilter driver attaches to the file system stack indirectly, by registering with FltMgr for the I/O operations that the minifilter driver chooses to filter.
Minifilters attach in a particular order. The operating system determines the order of attachment by load order groups and altitudes. The attachment of a minifilter driver at a particular altitude on a particular volume is called an instance of the minifilter driver.
A minifilter's altitude:
- Ensures that the instance of the minifilter driver is always loaded at the appropriate location relative to other minifilter driver instances.
- Determines the order in which FltMgr calls the minifilter driver to handle I/O.
The following figure shows a simplified I/O stack with the filter manager and three minifilter drivers.
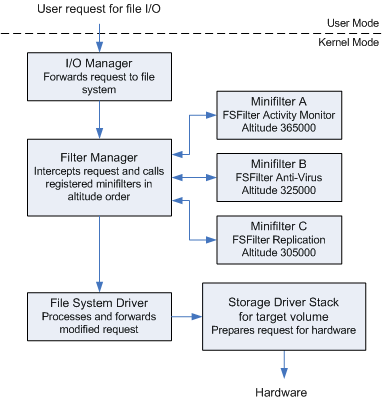
A minifilter driver can filter IRP-based I/O operations and fast I/O and file system filter (FSFilter) callback operations. For each of the I/O operations it chooses to filter, a minifilter can register a preoperation callback routine, a postoperation callback routine, or both. When FltMgr handles an I/O operation, it calls the appropriate callback routine for each minifilter driver that registered for that operation. When that callback routine returns, FltMgr calls the appropriate callback routine for the next minifilter driver that registered for the operation.
For example, assume all three minifilter drivers in this figure registered for the same I/O operation. In this situation:
- When FltMgr receives the I/O operation, it calls the minifilter preoperation callback routines in order of altitude from highest to lowest (A, B, C). FltMgr then forwards the I/O request to the next-lower driver for further processing.
- When FltMgr receives the I/O request for completion, it calls each minifilter driver's postoperation callback routines in reverse order, from lowest to highest (C, B, A).
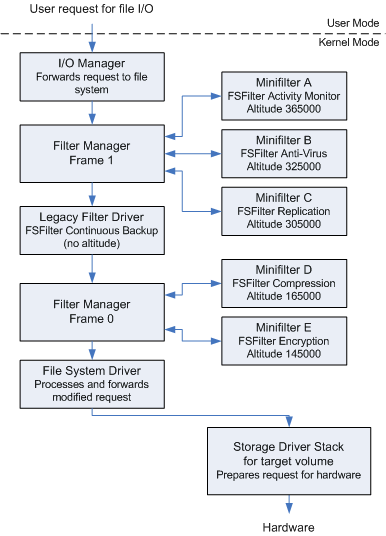
For interoperability with legacy filter drivers, FltMgr can attach filter device objects to a file system I/O stack in more than one location. Each of FltMgr's filter device objects is called a frame. From the perspective of a legacy filter driver, each filter manager frame is just another legacy filter driver.
Each filter manager frame represents a range of altitudes. FlgMgr can adjust an existing frame or create a new frame to allow minifilter drivers to attach at the correct location.
FltMgr can't attach a minifilter between two attached legacy filters unless there's already a filter manager frame between them. If a minifilter is intended to be attached above a legacy filter, it can be attached below it, depending on the existence of a second attached legacy filter. A minifilter intended to be attached below a legacy filter could, instead, be attached above that legacy filter.
Important
Always verify interoperability of legacy filters with minifilters or consider replacing legacy filters with minifilters. For more information, see Guidelines for Porting Legacy Filter Drivers.
If a minifilter driver is unloaded and reloaded, the system reloads it at the same altitude in the same frame from which it was unloaded.
The following figure shows a simplified I/O stack with a two filter manager frames, minifilter driver instances, and a legacy filter driver.