End-to-end troubleshooting of Microsoft Entra Connect objects and attributes
This article is intended to establish a common practice for how to troubleshoot synchronization issues in Microsoft Entra ID.
This method is used when an object or attribute fails to synchronize with the Microsoft Entra ID directory and no errors are shown in the sync engine, Application event viewer logs, or Microsoft Entra logs. It's easy to get lost in the details if there's no obvious error. However, by using best practices, you can isolate the issue and provide insights for Microsoft Support engineers.
As you apply this troubleshooting method to your environment, over time, you'll be able to do the following steps:
- Troubleshoot the sync engine logic from end to end.
- Resolve synchronization issues more efficiently.
- Identify issues more quickly by predicting the step in which they occur.
- Identify the starting point for reviewing data.
- Determine the optimal resolution.
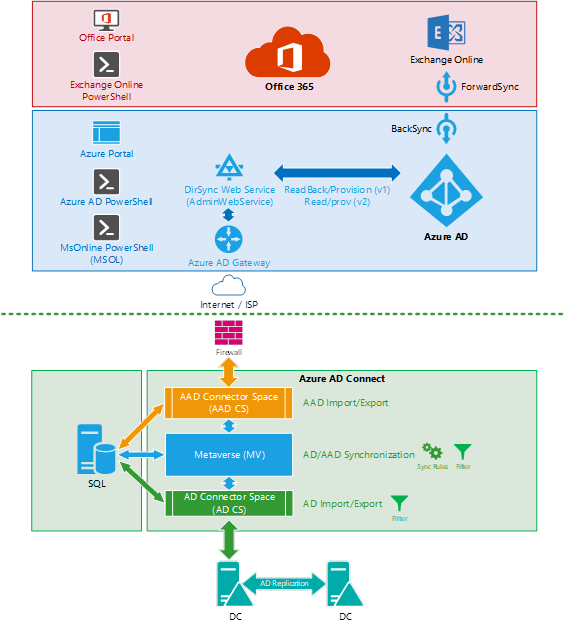
The steps that are provided here start at the local Active Directory level and progress toward Microsoft Entra ID. These steps are the most common direction of synchronization. However, the same principles apply to the inverse direction (for example, for attribute writeback).
Prerequisites
For a better understanding of this article, first read the following prerequisite articles for a better understanding of how to search for an object in different sources, and to understand how to check the connectors and lineage of an object.
- Microsoft Entra Connect: Accounts and permissions
- Troubleshoot an object that isn't synchronizing with Microsoft Entra ID
- Troubleshoot object synchronization with Microsoft Entra Connect Sync
Ineffective troubleshooting practices
The onPremisesSyncEnabled attribute in Microsoft Entra ID controls whether the tenant is prepared to accept synchronization of objects from on-premises AD DS.
It's common to disable DirSync on the tenant while troubleshooting object or attribute synchronization issues. Directory synchronization can be turned off using Graph or PowerShell. However, this process might cause disruptions.
Disabling DirSync at the tenant level triggers a complex and lengthy backend operation to transfer the Source of Authority (SoA) from local Active Directory to Microsoft Entra ID and Exchange Online for all the synced objects on the tenant. This operation is necessary to convert each object from onPremisesSyncEnabled=True to a cloud-only object (onPremisesSyncEnabled=<null>), and clean up all the shadow properties that are synced from on-premises AD DS (for example, ShadowUserPrincipalName and ShadowProxyAddresses). Depending on the tenant's size, this operation might take over 72 hours, and its completion time can't be predicted.
Don't use this method to troubleshoot a sync issue because such an operation can cause more harm and doesn't fix the root issue. You can't enable DirSync again until this disabling operation is complete. After re-enabling DirSync, the Entra Connect server must match all on-premises objects with existing Microsoft Entra ID objects.
Disabling DirSync is supported only in the following scenarios:
- You're decommissioning your on-premises synchronization server, and you want to continue managing your identities entirely from the cloud instead of from hybrid identities.
- You have some synced objects in the tenant that you want to keep as cloud-only in Microsoft Entra ID and remove from on-premises AD permanently.
- You're currently using a custom attribute as the SourceAnchor in Entra Connect (for example, employeeId), and you're re-installing AADC to start using ms-Ds-Consistency-Guid/ObjectGuid as the new SourceAnchor attribute (or vice versa).
- Certain scenarios within your mailbox migration strategy might result in potential issues.
In some situations, you might have to temporarily stop synchronization or manually control Entra Connect sync cycles. For example, you might have to pause synchronization to run one sync step at a time. Instead of disabling DirSync, you can just stop the sync scheduler by running the following cmdlet:
Set-ADSyncScheduler -SyncCycleEnabled $false
When you're ready, restore the normal sync scheduler by running the following cmdlet:
Start-ADSyncSyncCycle
Glossary
| Acronym/abbreviation | Name/description |
|---|---|
| AADC | Microsoft Entra Connect |
| AADCA | Microsoft Entra Connector Account |
| AADCS | Microsoft Entra Connector Space |
| AADCS:AttributeA | Attribute 'A' in Microsoft Entra Connector Space |
| ACLs | Access Control Lists (also known as ADDS permissions) |
| ADCA | AD Connector Account |
| ADCS | Active Directory Connector Space |
| ADCS:AttributeA | Attribute 'A' in Active Directory Connector Space |
| ADDS or AD | Active Directory Domain Services |
| CS | Connector Space |
| MV | Metaverse |
| MSOL Account | Automatically generated AD Connector Account (MSOL_########) |
| MV:AttributeA | Attribute 'A' in the Metaverse object |
| SoA | Source of Authority |
Step 1: Synchronization between ADDS and ADCS
Objective for Step 1
Determine whether the object or attribute is present and consistent in ADCS. If you can locate the object in ADCS, and all attributes have the expected values, go to Step 2.
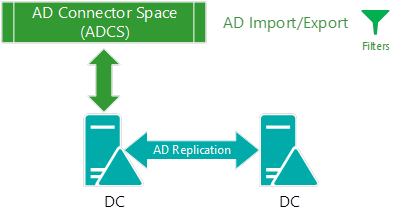
Description for Step 1
Synchronization between ADDS and ADCS occurs at the import step, and is the moment when AADC reads from the source directory and stores data in the database. That is, when data is staged in the connector space. During a delta import from AD, AADC requests all the new changes that occurred after a given directory watermark. This call is initiated by AADC by using the Directory Services DirSync Control against the Active Directory Replication Service. This step provides the last watermark as the last successful AD import, and gives AD the point-in-time reference from when all the (delta) changes should be retrieved. A full import is different because AADC imports from ADCS all the data in sync scope, and then marks as obsolete (and deletes) all the objects that are still in ADCS but weren't imported from AD. All the data between AD and AADC is transferred through LDAP and is encrypted by default.
If the connection with AD is successful, but the object or attribute isn't present in ADCS (assuming the domain or object is in sync scope), the issue most likely involves ADDS permissions. The ADCA requires ay least read permissions on the object in AD in order to import data to ADCS. By default, the MSOL account has explicit read/write permissions for all user, group, and computer properties. However, this situation might still be problematic if the following conditions are true:
- AADC uses a custom ADCA, but it wasn't provided sufficient permissions in AD.
- A parent OU has blocked inheritance, which prevents propagation of permissions from the root of the domain.
- The object or attribute itself has blocked inheritance, which prevents propagation of permissions.
- The object or attribute has an explicit Deny permission that prevents ADCA from reading it.
Troubleshooting Active Directory
Connectivity with AD
In the Synchronization Service Manager, the "Import from AD" step shows which domain controller is contacted under Connection Status. You'll most likely see an error here when there is a connectivity issue that affects AD.
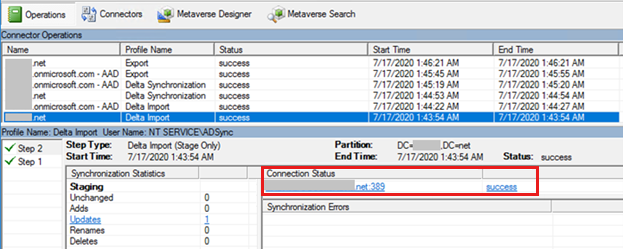
If you have to further troubleshoot connectivity for AD, especially if no errors surfaced in Microsoft Entra Connect server or if you're still in the process of installing the product, start by using the ADConnectivityTool.
Connection issues to ADDS have the following causes:
- Invalid AD credentials. For example, the ADCA has expired or the password has changed.
- A "failed-search" error, which occurs when DirSync Control doesn't communicate with the AD Replication Service, typically because of high-network packet fragmentation.
- A "no-start-ma" error, which occurs when there are name resolution issues (DNS) in AD.
- Other problems that can be caused by name resolution issues, network routing problems, blocked network ports, high network packet fragmentation, no writable DCs available, and so on. In such cases, you will likely have to involve the Directory Services or networking support teams to help troubleshoot.
Troubleshooting summary:
- Identify which domain controller is used.
- Use preferred domain controllers to target the same domain controller.
- Correctly identify the ADCA.
- Use the ADConnectivityTool to identify the problem.
- Use the LDP tool to try to bind against the domain controller with the ADCA.
- Contact Directory Services or a networking support team to help you troubleshoot.
Run the Synchronization Troubleshooter
After you troubleshoot AD connectivity, run the Troubleshoot Object Synchronization tool because this alone can detect the most obvious reasons for an object or attribute not to synchronize.
AD Permissions
A lack of AD permissions can affect both directions of the synchronization:
- When you import from ADDS to ADCS, a lack of permissions can cause AADC to skip objects or attributes so that AADC can't get ADDS updates in the import stream. This error occurs because the ADCA doesn't have enough permissions to read the object.
- When you export from ADCS to ADDS, a lack of permissions generates a "permission-issue" export error.
To check permissions, open the Properties window of an AD object, select Security > Advanced, and then examine the object's allow/deny ACLs by selecting the Disable Inheritance button (if inheritance is enabled). You can sort the column contents by Type to locate all the "deny" permissions. AD permissions can vary widely. However, by default, you might only see one "Deny ACL" for "Exchange Trusted Subsystem." Most permissions will be marked as Allow.
The following default permissions are the most relevant:
Authenticated Users

Everyone

Custom ADCA or MSOL account

Pre-Windows 2000 Compatible Access

SELF
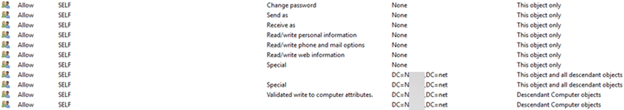
The best way to troubleshoot permissions is to use the "Effective Access" feature in AD Users and Computers console. This feature checks the effective permissions for a given account (the ADCA) on the target object or attribute that you want to troubleshoot.
Important
Troubleshooting AD permissions can be difficult because a change in ACLs doesn't take immediate effect. Always consider that such changes are subject to AD replication.
Troubleshooting summary:
- Identify which domain controller is used.
- Use preferred domain controllers to target the same domain controller.
- Correctly identify the ADCA.
- Use the Configure AD DS Connector Account Permissions tool.
- Use the "Effective Access" feature in AD Users and Computers.
- Use the LDP tool to bind against the domain controller that has the ADCA, and try to read the failing object or attribute.
- Temporarily add the ADCA to the Enterprise admins or Domain admins, and restart the ADSync service.
Warning
Don't use this as a permanent solution to permission issues. After determining the permission issue, remove the ADCA from any highly privileged groups, and grant the required AD permissions directly to the ADCA.
Note
Engage Directory Services or a network support team to help you troubleshoot the situation.
AD replications
This issue is less likely to affect Microsoft Entra Connect because it causes greater problems. However, when Microsoft Entra Connect is importing data from a domain controller by using delayed replication, it will not import the latest information from AD, which causes sync issues in which an object or attribute that was recently created or changed in AD doesn't sync to Microsoft Entra ID because it wasn't replicated to the domain controller that Microsoft Entra Connect is contacting. To verify that this is the issue, check the domain controller that AADC uses for import (see "Connectivity to AD"), and use the AD Users and Computers console to directly connect to this server (see Change Domain Controller in the next image). Then, verify that the data on this server corresponds to the latest data, and whether it's consistent with the respective ADCS data. At this stage, AADC will generate a greater load on the domain controller and networking layer.
Another approach is to use the RepAdmin tool to check the object's replication metadata on all domain controllers, get the value from all domain controllers, and check replication status between domain controllers:
Attribute value from all domain controllers:
RepAdmin /showattr * "DC=contoso,DC=com" /subtree /filter:"sAMAccountName=User01" /attrs:pwdLastSet,UserPrincipalName
Object metadata from all DCs:
RepAdmin /showobjmeta * "CN=username,DC=contoso,DC=com" > username-ObjMeta.txt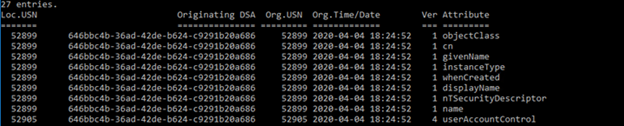
AD Replication Summary
RepAdmin /replsummary
Troubleshooting summary:
- Identify which domain controller is used.
- Compare data between domain controllers.
- Analyze the RepAdmin results.
- Contact Directory Services or the network support team to help troubleshoot the issue.
Domain and OU changes, and object types or attributes filtered or excluded in ADDS Connector
Changing domain or OU filtering requires a full import
Keep in mind that even if the domain or OU filtering is confirmed, any changes to domain or OU filtering take effect only after running a full import step.
Attribute filtering with Microsoft Entra app and attribute filtering
An easy-to-miss scenario for attributes not synchronizing is when Microsoft Entra Connect is configured with the Microsoft Entra app and attribute filtering feature. To check whether the feature is enabled, and for which attributes, get a General Diagnostics Report from the Troubleshooting Task, or run
(Get-ADSyncGlobalSettings).Parameters | where Name -eq 'Microsoft.OptionalFeature.FilterAAD' | select Name, Valuefrom PowerShell.Object type excluded in ADDS Connector configuration
This situation doesn't occur as commonly for users and groups. However, if all the objects of a specific object type are missing in ADCS, it might be useful to examine which object types enabled in ADDS Connector configuration.
Use the Get-ADSyncConnector cmdlet to retrieve the object types that are enabled on the Connector, as shown in the next image.
$connectorName = "Contoso.com"
(Get-ADSyncConnector | where Name -eq $connectorName).ObjectInclusionList`
The following list shows the object types that should be enabled by default (The publicFolder object type exists only when the Mail Enabled Public Folder feature is enabled.):

Attribute excluded in ADCS
In the same manner, if the attribute is missing for all objects, check whether the attribute is selected on the AD Connector.
To check for enabled attributes in ADDS Connector, use the Synchronization Manager, as shown in the next image, or run the following PowerShell cmdlet:
$connectorName = "Contoso.com" (Get-ADSyncConnector | where Name -eq $connectorName).AttributeInclusionList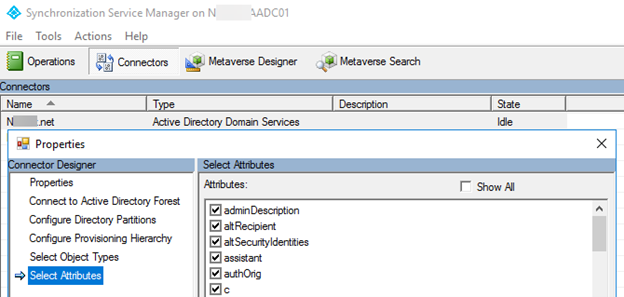
Important
Including or excluding object types or attributes in the Synchronization Service Manager isn't supported.
Troubleshooting summary:
- Check the Microsoft Entra app and attribute filtering feature
- Verify that the object type is included in ADCS.
- Verify that the attribute is included in ADCS.
- Run a full import.
Resources for Step 1
Main resources:
Get-ADSyncConnectorAccount - Identify the correct Connector account used by AADC
Identify connectivity problems with ADDS
Trace-ADSyncToolsADImport (ADSyncTools) - Trace data being imported from ADDS
LDIFDE - Dump object from ADDS to compare data between ADDS and ADCS
LDP - Test AD Bind connectivity and permissions to read object in the security context of ADCA
DSACLS - Compare and evaluate ADDS permissions
Set-ADSync< Feature >Permissions - Apply default AADC permissions in ADDS
RepAdmin - Check AD object metadata and AD replication status
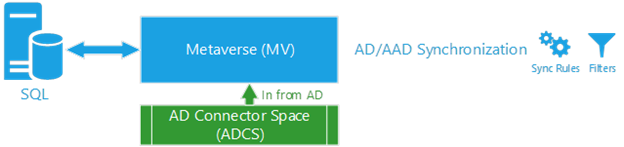
Step 2: Synchronization between ADCS and MV
Objective for Step 2
This step checks whether the object or attribute flows from CS to MV (in other words, whether the object or attribute is projected to the MV). At this stage, make sure that the object is present, or that the attribute is correct in ADCS (covered in Step 1), and then start looking at the synchronization rules and lineage of the object.
Description for Step 2
The synchronization between ADCS and MV occurs on the delta/full synchronization step. At this point, AADC reads the staged data in ADCS, processes all sync rules, and updates the respective MV object. This MV object will contain CS links (or connectors) pointing to the CS objects that contribute to its properties and the lineage of sync rules that were applied in the synchronization step. During this stage, AADC generates more load on the SQL Server (or LocalDB) and networking layers.
Troubleshooting ADCS > MV for objects
Check the inbound sync rules for provisioning
An object that is present in ADCS but missing in MV indicates that there were no scoping filters on any of the provisioning sync rules that applied to that object. Therefore, the object wasn't projected to MV. This issue might occur if there are disabled or customized sync rules.
To get a list of inbound provisioning sync rules, run the following command:
Get-ADSyncRule | where {$_.Name -like "In From AD*" -and $_.LinkType -eq "Provision"} | select Name,Direction,LinkType,Precedence,Disabled | ft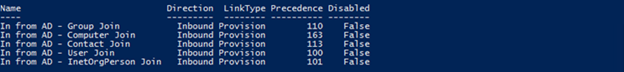
Check the lineage of the ADCS object
You can retrieve the failing object from the ADCS by searching on "DN or Anchor" in "Search Connector Space." On the Lineage tab, you will probably see that the object is a Disconnector (no links to MV), and the lineage is empty. Also, check whether the object has any errors, in case there is a sync error tab.
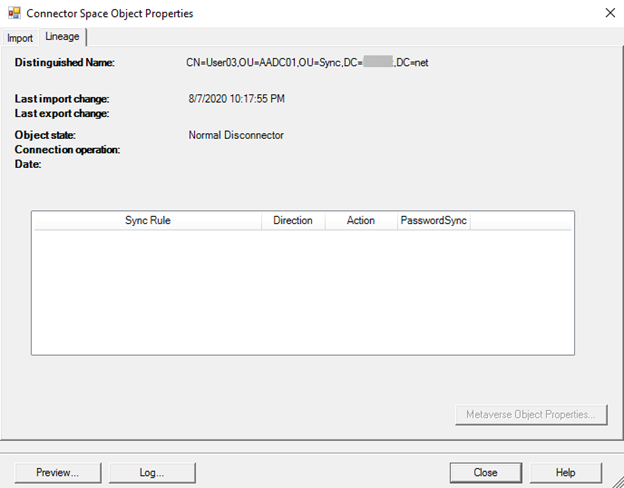
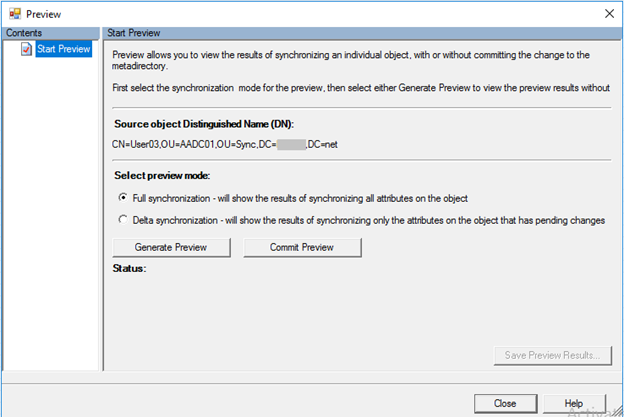
Run a preview on the ADCS object
Select Preview > Generate Preview > Commit Preview to see whether the object is projected to MV. If that's the case, then a full sync cycle should fix the issue for other objects in the same situation.
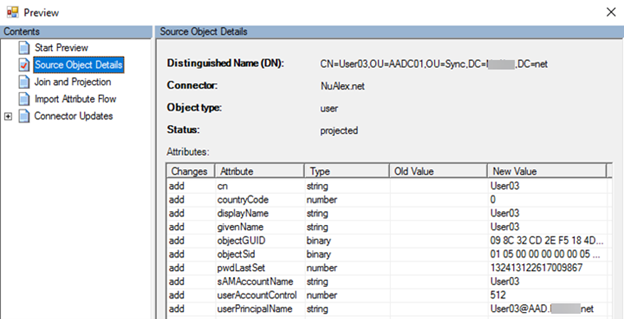
Export the object to XML
For a more detailed analysis (or for offline analysis), you can collect all the database data that's related to the object by using the
Export-ADSyncToolsObjectscmdlet. This exported information will help determine which rule is filtering out the object. In other words, which Inbound Scoping Filter in the Provisioning Sync Rules is preventing the object from being projected to the MV.Here are some examples of the
Export-ADSyncToolsObjectssyntax:[Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [Net.SecurityProtocolType]::Tls12 Install-Module ADSyncTools Import-Module ADSyncTools Export-ADSyncToolsObjects -DistinguishedName 'CN=TestUser,OU=Sync,DC=Contoso,DC=com' -ConnectorName 'Contoso.com' -ExportSerialized Export-ADSyncToolsObjects -ObjectId '{46EBDE97-7220-E911-80CB-000D3A3614C0}' -Source Metaverse -ExportSerializedTip
To read the exported data, use the
Import-Clixml <filename>.xmlcmdlet.
Troubleshooting summary (objects)
- Check the scoping filters on the "In From AD" inbound provisioning rules.
- Create a preview of the object.
- Run a full sync cycle.
- Export the object data by using the
Export-ADSyncToolsObjectscmdlet.
Troubleshooting ADCS > MV for attributes
Identify the inbound sync rules and transformation rules of the attribute
Each attribute has its own set of transformations rules that are responsible for directing the value from ADCS to MV. The first step is to identify which sync rules contain the transformation rule for the attribute that you're troubleshooting.
The best way to identify which sync rules have a transformation rule for a given attribute is to use the built-in filtering capabilities of the Synchronization Rules Editor.
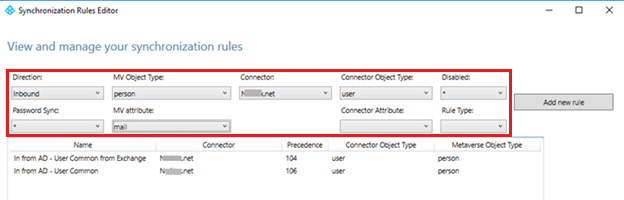
Check the Lineage of the ADCS Object
Each connector (or link) between the CS and MV will have a lineage that contains information about the sync rules that are applied to that CS object. The previous step will tell you which set of inbound sync rules (whether provisioning or joining sync rules) must be present in the object's lineage to flow the correct value from ADCS to MV. By examining the lineage on the ADCS object, you'll be able to determine whether that sync rule was applied to the object.
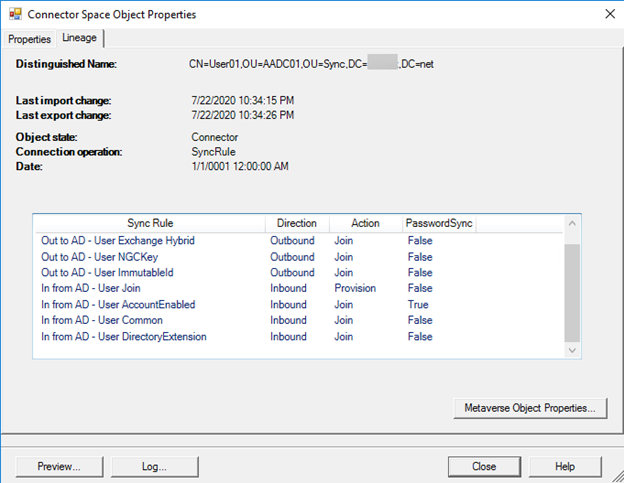
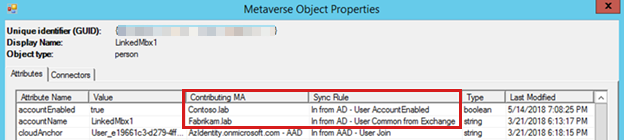
If there are multiple connectors (multiple AD forests) linked to the MV object, you might have to examine the Metaverse Object Properties to determine which connector is contributing the attribute value to the attribute that you're trying to troubleshoot. After you've identified the connector, examine the lineage of that ADCS object.
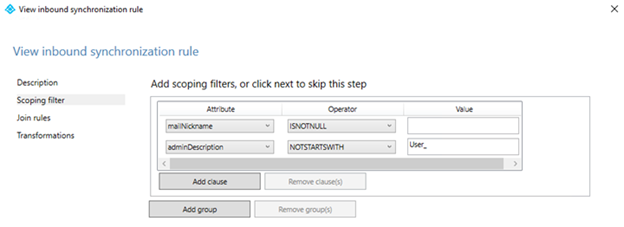
Check the scoping filters on the inbound sync rule
If a sync rule is enabled but not present in the object's lineage, the object should be filtered out by the sync rule's scoping filter. By checking the sync rule's scoping filters, the data on the ADCS object, and whether the sync rule is enabled or disabled, you should be able to determine why that sync rule wasn't applied to the ADCS object.
Here is an example of a common troublesome scoping filter from a sync rule responsible for synchronizing Exchange properties. If the object has a null value for mailNickName, then none of the Exchange attributes in the transformation rules will flow to Microsoft Entra ID.
Run a preview on ADCS object
If you can't determine why the sync rule missing in the ADCS object's lineage, run a preview by using Generate Preview and Commit Preview for a full synchronization of the object. If the attribute is updated in the MV and has a preview, then a full sync cycle should fix the issue for other objects in the same situation.
Export the object to XML
For a more detailed analysis or offline analysis, you can collect all the database data that's related to the object by using
Export-ADSyncToolsObjectscmdlet. This exported information can help you determine which sync rule or transformation rule is missing on the object that's preventing the attribute from being projected to the MV (see theExport-ADSyncToolsObjectsexamples earlier in this article).
Troubleshooting summary (for attributes)
- Identify the correct sync rules and transformation rules responsible for flowing the attribute to the MV.
- Check the lineage of the object.
- Check whether sync rules have been enabled.
- Check the scoping filters of the sync rules that are missing in the object's lineage.
Advanced troubleshooting of the sync rule pipeline
If you have to further debug the ADSync engine (also known as the MiiServer) in terms of sync rule processing, you can enable ETW tracing on the .config file (C:\Program Files\Microsoft Azure AD Sync\Bin\miiserver.exe.config). This method generates an extensive verbose text file that shows all the processing of sync rules. However, it might be difficult to interpret all the information. Use this method as a last resort or if it's indicated by Microsoft Support.
Resources for Step 2
- Synchronization Service Manager UI
- Synchronization Rules Editor
- Export-ADSyncToolsObjects cmdlet
- Start-ADSyncSyncCycle -PolicyType Initial
- ETW tracing SyncRulesPipeline (miiserver.exe.config)
Step 3: Synchronization between MV and AADCS
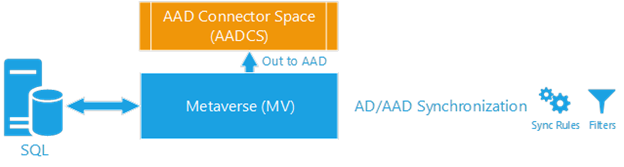
Objective for Step 3
This step checks whether the object or attribute flows from MV to AADCS. At this point, make sure that the object is present, or that the attribute is correct in ADCS and MV (covered in Steps 1 and 2). Then, examine the synchronization rules and lineage of the object. This step is similar to Step 2, in which the inbound direction from ADCS to MV was examined, However, at this stage, we'll concentrate on the outbound sync rules and attribute that flows from MV to AADCS.
Description for Step 3
The synchronization between MV and AADCS occurs in the delta/full synchronization step, when AADC reads the data in MV, processes all sync rules, and updates the respective AADCS object. This MV object will contain CS links (also known as connectors) that point to the CS objects that contribute to its properties and the lineage of the sync rules that were applied in the synchronization step. At this point, AADC generates more load on SQL Server (or localDB) and the networking layer.
Troubleshooting MV to AADCS for objects
Check the outbound sync rules for provisioning
An object that is present in MV but missing in AADCS indicates that there were no scoping filters on any of the provisioning sync rules that applied to that object. For example, see the "Out to Microsoft Entra ID" sync rules shown in the next image. Therefore, the object wasn't provisioned in AADCS. This error can occur if there are disabled or customized sync rules.
To get a list of inbound provisioning sync rules, run the following command:
Get-ADSyncRule | where {$_.Name -like "Out to AAD*" -and $_.LinkType -eq "Provision"} | select Name,Direction,LinkType,Precedence,Disabled | ft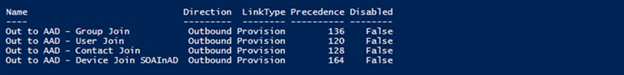
Check the lineage of the ADCS object
To retrieve the failing object from the MV, use a Metaverse Search, and then examine the connectors tab. On this tab, you can determine whether the MV object is linked to an AADCS object. Also, check whether the object has any errors, in case a sync error tab is present.
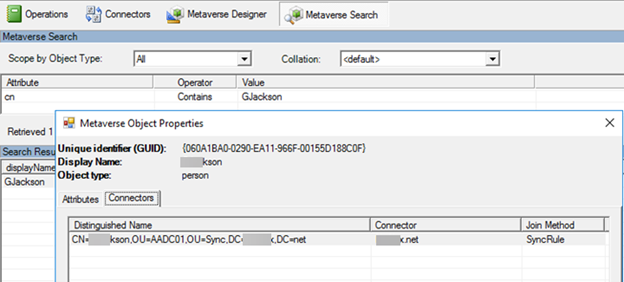
If no AADCS connector is present, the object is most likely set to cloudFiltered=True. You can verify whether the object is cloud-filtered by examining the MV attributes for which sync rule is contributing with the cloudFiltered value.
Run a Preview on AADCS object
Select Preview > Generate Preview > Commit a Preview to determine whether the object connects to AADCS. If so, then a full sync cycle should fix the issue for other objects in the same situation.
Export the object to XML
For a more detailed analysis or offline analysis, you can collect all the database data that's related to the object by using
Export-ADSyncToolsObjectscmdlet. This exported information, together with the (outbound) sync rules configuration, can help determine which rule is filtering out the object, and can determine which outbound scoping filter in the provisioning sync rules is preventing the object from connecting with the AADCS.Here are some examples of the
Export-ADSyncToolsObjectssyntax:
[Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [Net.SecurityProtocolType]::Tls12
Install-Module ADSyncTools
Import-Module ADSyncTools
Export-ADSyncToolsObjects -DistinguishedName 'CN=TestUser,OU=Sync,DC=Contoso,DC=com' -ConnectorName 'Contoso.com' -ExportSerialized
Export-ADSyncToolsObjects -ObjectId '{46EBDE97-7220-E911-80CB-000D3A3614C0}' -Source Metaverse -ExportSerialized
Tip
To read the exported data, use Import-Clixml <filename>.xml
Troubleshooting summary for objects
- Check the scoping filters on the "Out to Microsoft Entra ID" outbound provisioning rules.
- Create a preview of the object.
- Run a full sync cycle.
- Export the object data by using the
Export-ADSyncToolsObjectscmdlet.
Troubleshooting MV to AADCS for attributes
Identify the outbound sync rules and transformation rules of the attribute
Each attribute has its own set of transformation rules that are responsible to flow the value from MV to AADCS. Begin by identifying which sync rules contain the transformation rule for the attribute that you're troubleshooting.
The best way to identify which sync rules have a transformation rule for a given attribute is to use the built-in filtering capabilities of the Synchronization Rules Editor.
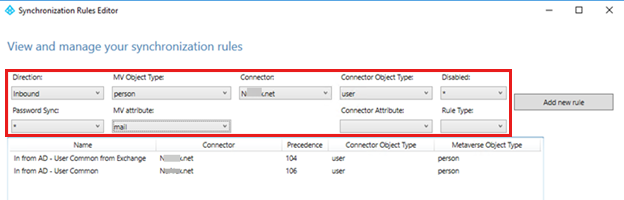
Check the lineage of the ADCS object
Each connector (or link) between the CS and MV will have a lineage that contains information about the sync rules applied to that CS object. The previous step will tell you which set of outbound sync rules (whether provisioning or joining sync rules) must be present in the object's lineage to flow the correct value from MV to AADCS. By examining the lineage on the AADCS object, you can determine whether that sync rule has been applied to the object.
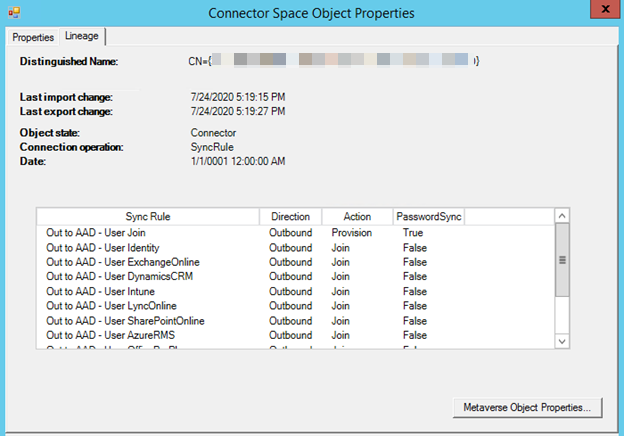
Check the scoping filters on the outbound sync rule
If a sync rule is enabled but not present in the object's lineage, it should be filtered out by the sync rule's scoping filter. By checking the presence of the sync rule's scoping filters, and the data on the MV object, and whether the sync rule is enabled or disabled, you should be able to determine why that sync rule wasn't applied to the AADCS object.
Run a preview on AADCS object
If you determine why the sync rule is missing from the ADCS object's lineage, run a preview that uses Generate Preview and Commit Preview for a full synchronization of the object. If the attribute is updated in the MV by having a preview, then a full sync cycle should fix the issue for other objects in the same situation.
Export the object to XML
For a more detailed analysis or offline analysis, you can collect all the database data that's related to the object by using the
Export-ADSyncToolsObjectscmdlet. This exported information, together with the (outbound) sync rules configuration, can help you determine which sync rule or transformation rule is missing from the object that's preventing the attribute from flowing to AADCS (see theExport-ADSyncToolsObjectsexamples earlier).
Troubleshooting summary for attributes
- Identify the correct sync rules and transformation rules that are responsible to flow the attribute to AADCS.
- Check the lineage of the object.
- Check that the sync rules are enabled.
- Check the scoping filters of the sync rules that are missing in the object's lineage.
Troubleshoot the sync rule pipeline
If you have to further debug the ADSync engine (also known as the MiiServer) in terms of sync rule processing, you can enable ETW tracing on the .config file (C:\Program Files\Microsoft Azure AD Sync\Bin\miiserver.exe.config). This method generates an extensive verbose text file that shows all the processing of sync rules. However, it might be difficult to interpret all the information. Use this method only as a last resort or if it's indicated by Microsoft Support.
Resources
Synchronization Service Manager
Synchronization Rules Editor
Export-ADSyncObjects cmdlet
Start-ADSyncSyncCycle -PolicyType Initial
ETW tracing SyncRulesPipeline (miiserver.exe.config)
Step 4: Synchronization between AADCS and Entra ID
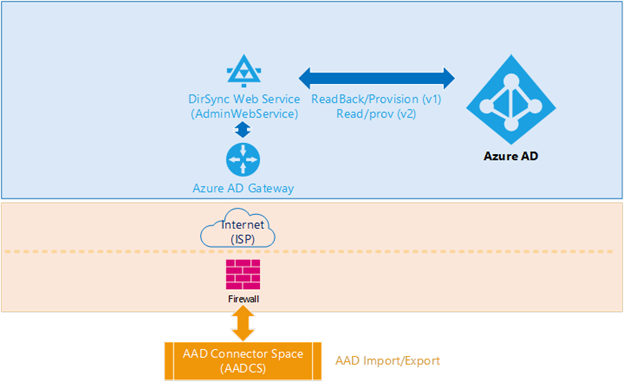
Objective for Step 4
This stage compares the AADCS object with the respective object that's provisioned in Microsoft Entra ID.
Description for Step 4
Multiple components and processes that are involved in importing and exporting data to and from Microsoft Entra ID can cause the following issues:
- Connectivity to the internet
- Internal firewalls and ISP connectivity (for example, blocked network traffic)
- The Microsoft Entra Gateway in front of DirSync Webservice (also known as AdminWebService)
- The DirSync Webservice API
- The Microsoft Entra Core directory service
Fortunately, the issues that affect these components usually generate an error in event logs that can be traced by Microsoft Support. Therefore, these issues are out of scope for this article. Nevertheless, there are still some "silent" issues that can be examined.
Troubleshooting AADCS
Multiple Active AADC servers exporting to Microsoft Entra ID
In a common scenario in which objects in Microsoft Entra ID flip attribute values back and forth, there are more than one active Microsoft Entra Connect servers, and one of these servers loses contact with the local AD but is still connected to the internet and able to export data to Microsoft Entra ID. Therefore, every time that this "stale" server imports a change from Microsoft Entra ID on a synchronized object that's made by the other active server, the sync engine reverts that change based on the stale AD data that's in the ADCS. A typical symptom in this scenario is that you make a change in AD that's synced to Microsoft Entra ID, but the change reverts to the original value a few minutes later (up to 30 minutes). To quickly mitigate this issue, return to any old servers or virtual machines that have been decommissioned, and check whether the ADSync service is still running.
Mobile attribute with DirSyncOverrides
When the Admin uses the legacy MSOnline or AzureAD PowerShell modules, or if the user goes to the Office Portal and updates the
Mobileattribute, the updated phone number will be overwritten in Microsoft Entra ID despite the object being synced from on-premises AD (onPremisesSyncEnabled=true).Together with this update, Microsoft Entra ID also sets a
DirSyncOverrideson the object to flag that this user has the mobile phone number "overwritten" in Microsoft Entra ID. From this point on, any update to the mobile attribute that originates from on-premises will be ignored because this attribute will no longer be managed by on-premises AD.For more information about the BypassDirSyncOverrides feature and how to restore synchronization of
MobileandotherMobileattributes from Microsoft Entra ID to on-premises Active Directory, see How to use the BypassDirSyncOverrides feature of a Microsoft Entra tenant.UserPrincipalName changes don't update in Microsoft Entra ID
If the
UserPrincipalNameattribute isn't updated in Microsoft Entra ID, while other attributes synchronize as expected, it's possible that a feature called SynchronizeUpnForManagedUsers isn't enabled on the tenant.Before this feature is added, any updates to the UPN from on-premises are silently ignored after the user is provisioned in Microsoft Entra ID and assigned a license. An admin must use the legacy MSOnline or AzureAD PowerShell to update the UPN directly in Microsoft Entra ID. After this feature is added, any updates to UPN will flow to Microsoft Entra regardless of whether the user is licensed (managed).
Note
After it's enabled, this feature can't be disabled.
UserPrincipalName updates will work if the user isn't licensed. However, without the SynchronizeUpnForManagedUsers feature, UserPrincipalName changes after the user is provisioned and is assigned a licensed that won't be updated in Microsoft Entra ID. Notice that Microsoft doesn't disable this feature on behalf of customers.
Invalid characters and ProxyCalc internals
Issues that involve invalid characters that don't produce any sync error are more troublesome in UserPrincipalName and ProxyAddresses attributes because of the cascading effect in ProxyCalc processing that will silently discard the value synchronized from on-premises AD. This situation occurs as follows:
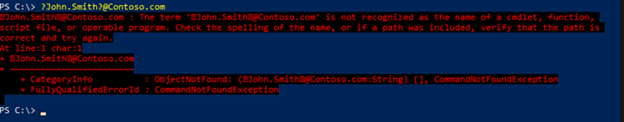
The resulting UserPrincipalName in Microsoft Entra ID will be the MailNickName or CommonName @ (at) initial domain. For example, instead of John.Smith@Contoso.com, the UserPrincipalName in Microsoft Entra ID might become smithj@Contoso.onmicrosoft.com because there's an invisible character in the UPN value from on-premises AD.
If a ProxyAddress contains a space character, ProxyCalc will discard it and autogenerate an email address based on MailNickName at Initial Domain. For example, "SMTP: John.Smith@Contoso.com" will not appear in Microsoft Entra ID because it contains a space character after the colon.
Either a UserPrincipalName that includes a space character or a ProxyAddress that includes an invisible character will cause the same issue.
To troubleshoot an invalid character in the UserPrincipalName or ProxyAddress, examine the value that's stored in the local AD from an LDIFDE or PowerShell exported to a file. An easy trick to detect an invisible character is to copy the contents of the exported file, and then paste it into a PowerShell window. The invisible character will be replaced by a question mark (?), as shown in the following example.
ThumbnailPhoto attribute (KB4518417)
There's a general misconception that after you sync ThumbnailPhoto from AD for the first time, you can no longer update it, which is only partly true.
Usually, the ThumbnailPhoto in Microsoft Entra ID is continually updated. However, an issue occurs if the updated picture is no longer retrieved from Microsoft Entra ID by the respective workload or partner (for example, EXO or SfBO). This issue causes the false impression that the picture wasn't synced from on-premises AD to Microsoft Entra ID.
Basic steps to troubleshoot ThumbnailPhoto:
Make sure that the image is correctly stored in AD and doesn't exceed the size limit of 100 KB.
Check the image in the Accounts Portal or call Get profilePhoto via Graph.
If the ADDS (or Entra ID) thumbnailPhoto has the correct image but it's not the correct image on other online services, the following conditions might apply:
- The user's mailbox contains an HD image and isn't accepting low-resolution images from Microsoft Entra thumbnailPhoto. The solution is to directly update the user's mailbox image.
- The user's mailbox image was updated correctly, but you're still seeing the original image. The solution is to wait at least six hours to see the updated image in the Office 365 User Portal or the Azure portal.
Additional resources
Troubleshoot object synchronization with Microsoft Entra Connect Sync
Troubleshoot an object that isn't synchronizing with Microsoft Entra ID
Contact us for help
If you have questions or need help, create a support request, or ask Azure community support. You can also submit product feedback to Azure feedback community.