Azure Serial Console for Windows
Applies to: ✔️ Windows VMs
Note
Was this article helpful? Your input is important to us. Please use the Feedback button on this page to let us know how well this article worked for you or how we can improve it.
The Serial Console in the Azure portal provides access to a text-based console for Windows virtual machines (VMs) and virtual machine scale set instances. This serial connection connects to the COM1 serial port of the VM or virtual machine scale set instance, providing access to it independent of the network or operating system state. The serial console can only be accessed by using the Azure portal and is allowed only for those users who have an access role of Contributor or higher to the VM or virtual machine scale set.
Serial Console works in the same manner for VMs and virtual machine scale set instances. In this doc, all mentions to VMs will implicitly include virtual machine scale set instances unless otherwise stated.
Serial Console is generally available in global Azure regions and in public preview in Azure Government. It is not yet available in the Azure China cloud.
For serial console documentation for Linux, see Azure Serial Console for Linux.
Note
Serial Console is compatible with a managed boot diagnostics storage account.
Prerequisites
Your VM or virtual machine scale set instance must use the resource management deployment model. Classic deployments aren't supported.
Your account that uses serial console must have the Virtual Machine Contributor role for the VM and the boot diagnostics storage account
Your VM or virtual machine scale set instance must have a password-based user. You can create one with the reset password function of the VM access extension. Select Reset password from the Help section.
The VM for virtual machine scale set instance must have boot diagnostics enabled.
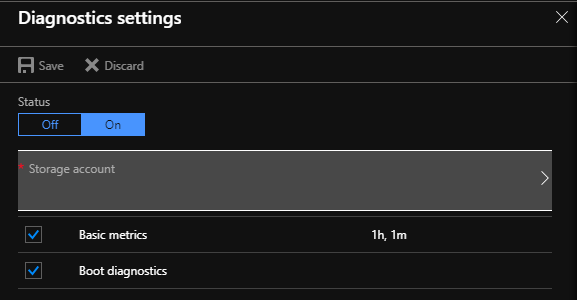
Enable Serial Console functionality for Windows Server
Note
If you are not seeing anything in the serial console, make sure that boot diagnostics is enabled on your VM or virtual machine scale set.
Enable the serial console in custom or older images
Newer Windows Server images on Azure have Special Administration Console (SAC) enabled by default. SAC is supported on server versions of Windows but isn't available on client versions (for example, Windows 10, Windows 8, or Windows 7).
For older Windows Server images (created before February 2018), you can automatically enable the serial console through the Azure portal's run command feature. In the Azure portal, select Run command, then select the command named EnableEMS from the list.
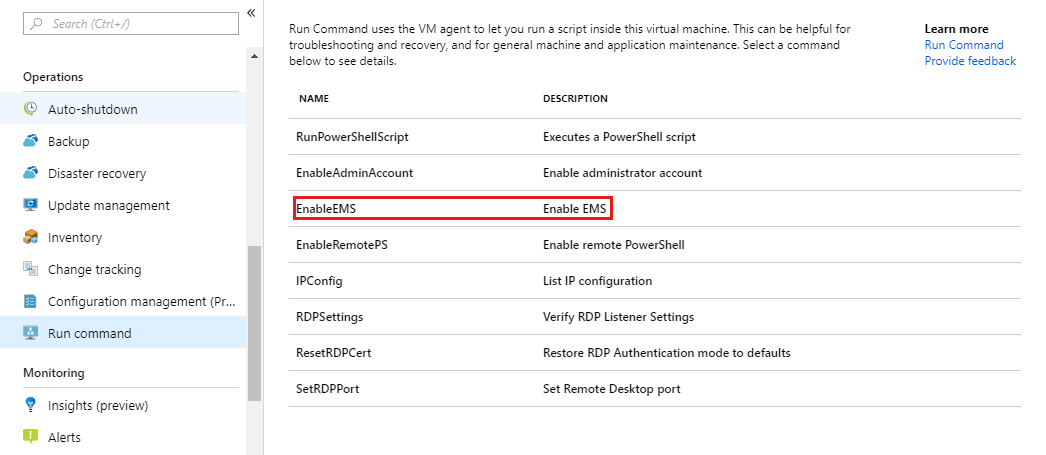
Alternatively, to manually enable the serial console for Windows VMs/virtual machine scale set created before February 2018, follow these steps:
Connect to your Windows virtual machine by using Remote Desktop
From an administrative command prompt, run the following commands:
bcdedit /ems {current} on, orbcdedit /ems '{current}' onif you are using PowerShellbcdedit /emssettings EMSPORT:1 EMSBAUDRATE:115200
Reboot the system for the SAC console to be enabled.
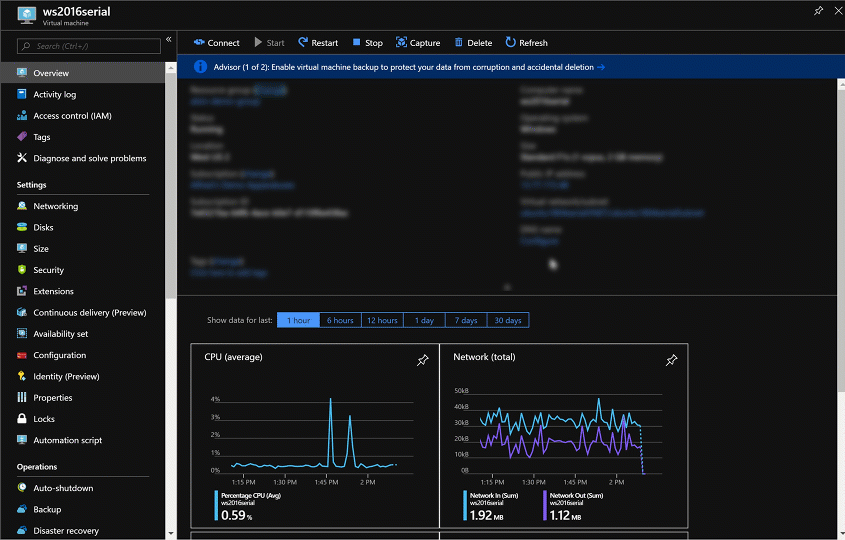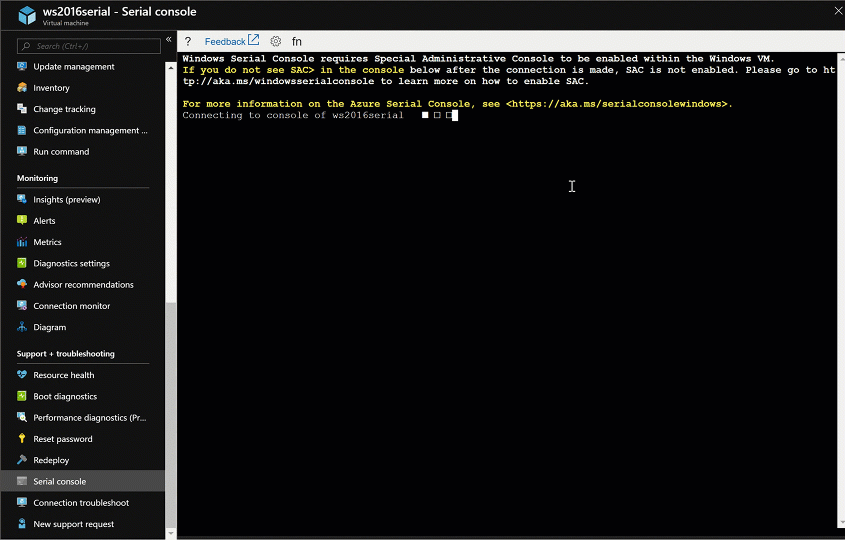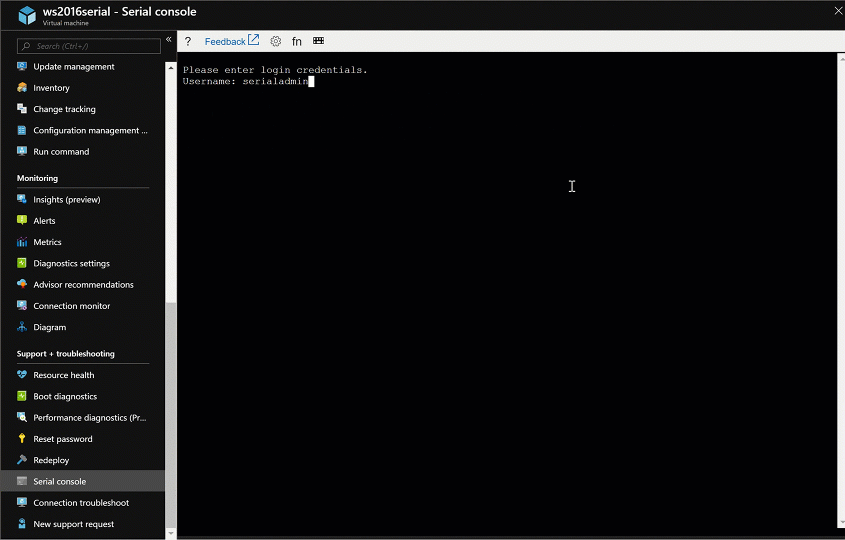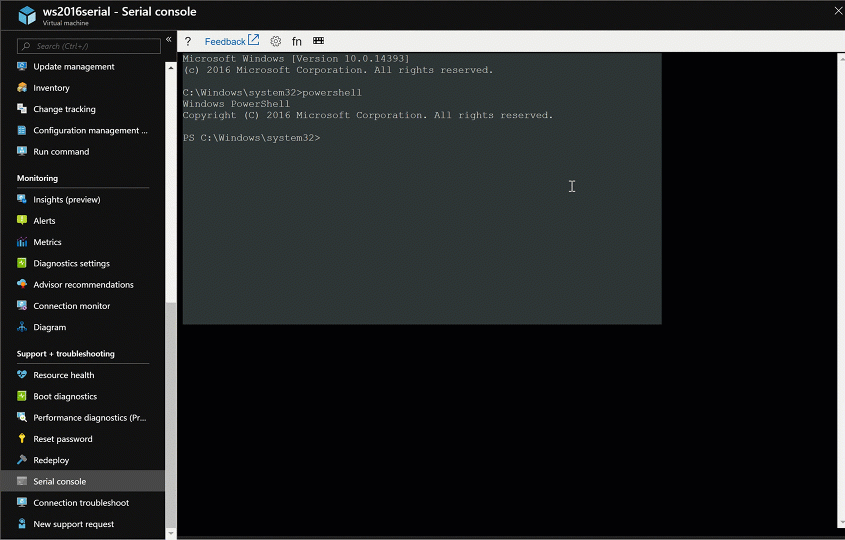
If needed, the SAC can be enabled offline as well:
Attach the windows disk for which you want SAC configured as a data disk to the existing VM.
From an administrative command prompt, run the following commands:
bcdedit /store <mountedvolume>\boot\bcd /ems {default} onbcdedit /store <mountedvolume>\boot\bcd /emssettings EMSPORT:1 EMSBAUDRATE:115200
How do I know if SAC is enabled?
If SAC isn't enabled, the serial console won't display the SAC prompt. In some cases, VM health information is shown, and in other cases it's blank. If you're using a Windows Server image created before February 2018, SAC probably won't be enabled.
Enable the Windows boot menu in the serial console
If you need to enable Windows boot loader prompts to display in the serial console, you can add the following additional options to your boot configuration data. For more information, see bcdedit.
Connect to your Windows VM or virtual machine scale set instance by using Remote Desktop.
From an administrative command prompt, run the following commands:
bcdedit /set {bootmgr} displaybootmenu yesbcdedit /set {bootmgr} timeout 10bcdedit /set {bootmgr} bootems yes
Reboot the system for the boot menu to be enabled
Note
The timeout that you set for the boot manager menu to display will impact your OS boot time. If you think the 10-second timeout value is too short or too long, set it to a different value.
Use Serial Console
Use CMD or PowerShell in Serial Console
Connect to the serial console. If you successfully connect, the prompt is SAC>:
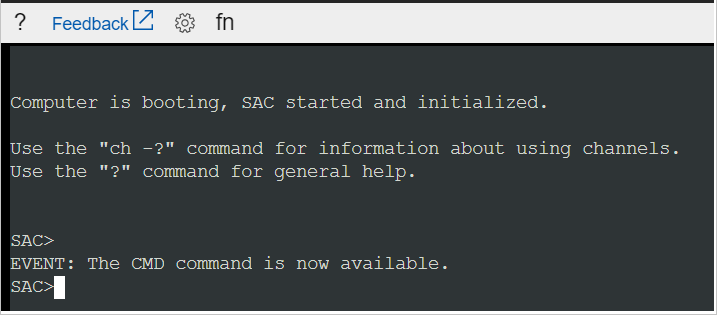
Enter
cmdto create a channel that has a CMD instance.Enter
ch -si 1or press the<esc>+<tab>shortcut keys to switch to the channel that's running the CMD instance.Press Enter, and then enter sign-in credentials with administrative permissions.
After you've entered valid credentials, the CMD instance opens.
To start a PowerShell instance, enter
PowerShellin the CMD instance, and then press Enter.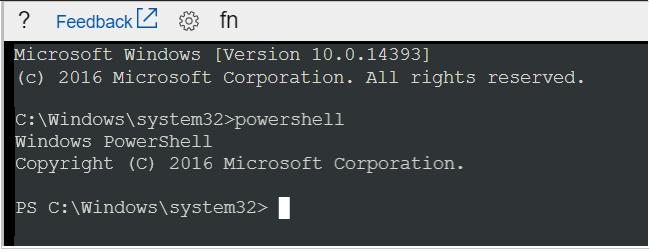
Use the serial console for NMI calls
A non-maskable interrupt (NMI) is designed to create a signal that software on a virtual machine won't ignore. Historically, NMIs have been used to monitor for hardware issues on systems that required specific response times. Today, programmers and system administrators often use NMI as a mechanism to debug or troubleshoot systems that are not responding.
The serial console can be used to send an NMI to an Azure virtual machine by using the keyboard icon in the command bar. After the NMI is delivered, the virtual machine configuration will control how the system responds. Windows can be configured to crash and create a memory dump file when receiving an NMI.
For information on configuring Windows to create a crash dump file when it receives an NMI, see How to generate a crash dump file by using an NMI.
Use function keys in serial console
Function keys are enabled for usage for serial console in Windows VMs. The F8 in the serial console dropdown provides the convenience of easily entering the Advanced Boot Settings menu, but serial console is compatible with all other function keys. You may need to press Fn + F1 (or F2, F3, etc.) on your keyboard depending on the computer you are using serial console from.
Use WSL in serial console
The Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) has been enabled for Windows Server 2019 or later, so it is also possible to enable WSL for use within the serial console if you are running Windows Server 2019 or later. This may be beneficial for users that also have a familiarity with Linux commands. For instructions to enable WSL for Windows Server, see the Installation guide.
Restart your Windows VM/virtual machine scale set instance within Serial Console
You can initiate a restart within the serial console by navigating to the power button and clicking "Restart VM". This will initiate a VM restart, and you will see a notification within the Azure portal regarding the restart.
This is useful in situations where you may want to access the boot menu without leaving the serial console experience.

Disable the Serial Console
By default, all subscriptions have serial console access enabled. You can disable the serial console at either the subscription level or VM/virtual machine scale set level. For detailed instructions, visit Enable and disable the Azure Serial Console.
Serial Console security
Use Serial Console with custom boot diagnostics storage account firewall enabled
Serial Console uses the storage account configured for boot diagnostics in its connection workflow. When a firewall is enabled on this storage account, the Serial Console service IPs must be added as exclusions. To do this, follow these steps:
Navigate to the settings of the custom boot diagnostics storage account firewall you have enabled.
Note
To determine which storage account is enabled for your VM, from the Support + troubleshooting section, select Boot diagnostics > Settings.
Add Serial Console service IPs as firewall exclusions based on the VM's geography.
The following table lists the IPs that need to be permitted as firewall exclusions based on the region or geography where the VM is located. This is a subset of the complete list of Serial Console IP addresses used in the SerialConsole service tag. You can limit access to boot diagnostics storage accounts via the SerialConsole service tag. The service tag isn't regionally separated. Traffic on the service tag is inbound only, and the Serial Console doesn't generate traffic to Customer Controllable Destinations. Although Azure storage account firewalls don't currently support service tags, the SerialConsole service tag can be programmatically consumed to determine the IP list. For more information about service tags, see Virtual network service tags.
Note
Storage account firewalls for the Serial Console aren't supported for VMs in geographies with only one region, such as Italy North in Italy.
Geography Regions IP addresses Asia Asia East, Asia Southeast 4.145.74.168, 20.195.85.180, 20.195.85.181, 20.205.68.106, 20.205.68.107, 20.205.69.28, 23.97.88.117, 23.98.106.151 Australia Australia Central, Australia Central 2, Australia East, Australia Southeast 4.198.45.55, 4.200.251.224, 20.167.131.228, 20.53.52.250, 20.53.53.224, 20.53.55.174, 20.70.222.112, 20.70.222.113, 68.218.123.133 Brazil Brazil South, Brazil Southeast 20.206.0.192, 20.206.0.193, 20.206.0.194, 20.226.211.157, 108.140.5.172, 191.234.136.63, 191.238.77.232, 191.238.77.233 Canada Canada Central, Canada East 20.175.7.183, 20.48.201.78, 20.48.201.79, 20.220.7.246, 52.139.106.74, 52.139.106.75, 52.228.86.177, 52.242.40.90 Canary (EUAP) US Central EUAP, US East 2 EUAP 20.45.242.18, 20.45.242.19, 20.45.242.20, 20.47.232.186, 20.47.232.187, 20.51.21.252, 68.220.123.194, 168.61.232.59 China China North 3, China East 3 163.228.102.122, 163.228.102.123, 52.131.192.182, 52.131.192.183, 159.27.255.76, 159.27.253.236, 163.228.102.122, 163.228.102.123, 52.131.192.182, 52.131.192.183 Europe Europe North, Europe West 4.210.131.60, 20.105.209.72, 20.105.209.73, 40.113.178.49, 52.146.137.65, 52.146.139.220, 52.146.139.221, 98.71.107.78 France France Central, France South 20.111.0.244, 40.80.103.247, 51.138.215.126, 51.138.215.127, 52.136.191.8, 52.136.191.9, 52.136.191.10, 98.66.128.35 Germany Germany North, Germany West Central 20.52.94.114, 20.52.94.115, 20.52.95.48, 20.113.251.155, 51.116.75.88, 51.116.75.89, 51.116.75.90, 98.67.183.186 India India Central, India South, India West 4.187.107.68, 20.192.47.134, 20.192.47.135, 20.192.152.150, 20.192.152.151, 20.192.153.104, 20.207.175.96, 52.172.82.199, 98.70.20.180 Japan Japan East, Japan West 20.18.7.188, 20.43.70.205, 20.89.12.192, 20.89.12.193, 20.189.194.100, 20.189.228.222, 20.189.228.223, 20.210.144.254 Korea Korea Central, Korea South 20.200.166.136, 20.200.194.238, 20.200.194.239, 20.200.196.96, 20.214.133.81, 52.147.119.28, 52.147.119.29, 52.147.119.30 Norway Norway East, Norway West 20.100.1.154, 20.100.1.155, 20.100.1.184, 20.100.21.182, 51.13.138.76, 51.13.138.77, 51.13.138.78, 51.120.183.54 South Africa South Africa North, South Africa West 20.87.80.28, 20.87.86.207, 40.117.27.221, 102.37.86.192, 102.37.86.193, 102.37.86.194, 102.37.166.222, 102.37.166.223 Sweden Sweden Central, Sweden South 20.91.100.236, 51.12.22.174, 51.12.22.175, 51.12.22.204, 51.12.72.222, 51.12.72.223, 51.12.73.92, 172.160.216.6 Switzerland Switzerland North, Switzerland West 20.199.207.188, 20.208.4.98, 20.208.4.99, 20.208.4.120, 20.208.149.229, 51.107.251.190, 51.107.251.191, 51.107.255.176 UAE UAE Central, UAE North 20.38.141.5, 20.45.95.64, 20.45.95.65, 20.45.95.66, 20.203.93.198, 20.233.132.205, 40.120.87.50, 40.120.87.51 United Kingdom UK South, UK West 20.58.68.62, 20.58.68.63, 20.90.32.180, 20.90.132.144, 20.90.132.145, 51.104.30.169, 172.187.0.26, 172.187.65.53 United States US Central, US East, US East 2, US East 2 EUAP, US North, US South, US West, US West 2, US West 3 4.149.249.197, 4.150.239.210, 20.14.127.175, 20.40.200.175, 20.45.242.18, 20.45.242.19, 20.45.242.20, 20.47.232.186, 20.51.21.252, 20.69.5.160, 20.69.5.161, 20.69.5.162, 20.83.222.100, 20.83.222.101, 20.83.222.102, 20.98.146.84, 20.98.146.85, 20.98.194.64, 20.98.194.65, 20.98.194.66, 20.168.188.34, 20.241.116.153, 52.159.214.194, 57.152.124.244, 68.220.123.194, 74.249.127.175, 74.249.142.218, 157.55.93.0, 168.61.232.59, 172.183.234.204, 172.191.219.35 USGov All US Government Cloud regions 20.140.104.48, 20.140.105.3, 20.140.144.58, 20.140.144.59, 20.140.147.168, 20.140.53.121, 20.141.10.130, 20.141.10.131, 20.141.13.121, 20.141.15.104, 52.127.55.131, 52.235.252.252, 52.235.252.253, 52.243.247.124, 52.245.155.139, 52.245.156.185, 62.10.196.24, 62.10.196.25, 62.10.84.240, 62.11.6.64, 62.11.6.65 Important
- The IPs that need to be permitted are specific to the region where the VM is located. For example, a virtual machine deployed in the North Europe region needs to add the following IP exclusions to the storage account firewall for the Europe geography: 52.146.139.220 and 20.105.209.72. View the table above to find the correct IPs for your region and geography.
- In the current serial console operation, the web socket is opened to an endpoint like
<region>.gateway.serialconsole.azure.com. Ensure the endpointserialconsole.azure.comis allowed for browser clients in your organization. In the US Government (Fairfax) cloud, the endpoint suffix isserialconsole.azure.us.
For more information about how to add IPs to the storage account firewall, see Configure Azure Storage firewalls and virtual networks: Managing IP network rules.
After the IP addresses are successfully added to the storage account firewall, retry the Serial Console connection to the VM. If you still have connection problems, verify that the correct IP addresses are excluded from the storage account firewall for the region of the VM.
Access security
Access to the serial console is limited to users who have an access role of Virtual Machine Contributor or higher to the virtual machine. If your Microsoft Entra tenant requires multi-factor authentication (MFA), then access to the serial console will also need MFA because the serial console's access is through the Azure portal.
Channel security
All data that is sent back and forth is encrypted in transit with TLS 1.2 or a later version.
Data storage and encryption
Azure Serial Console doesn't review, inspect, or store any data that's transmitted in and out of the virtual machine serial port. Therefore, there's no data to encrypt at rest.
To ensure that any in-memory data that's paged to disks by virtual machines running Azure Serial Console is encrypted, use the host-based encryption. The host-based encryption is enabled by default for all Azure Serial Console connections.
Data residency
The Azure portal or Azure CLI act as remote terminals to the virtual machine serial port. As these terminals can't directly connect to the servers which host the virtual machine over the network, an intermediate service gateway is used to proxy the terminal traffic. Azure Serial Console doesn't store or process this customer data. The intermediate service gateway that transfers the data will reside in the geography of the virtual machine.
Audit logs
All access to the serial console is currently logged in the boot diagnostics logs of the virtual machine. Access to these logs are owned and controlled by the Azure virtual machine administrator.
Caution
No access passwords for the console are logged. However, if commands run within the console contain or output passwords, secrets, user names, or any other form of personally identifiable information (PII), those will be written to the VM boot diagnostics logs. They will be written along with all other visible text, as part of the implementation of the serial console's scroll back function. These logs are circular and only individuals with read permissions to the diagnostics storage account have access to them. However, we recommend following the best practice of using the Remote Desktop for anything that may involve secrets and/or PII.
Concurrent usage
If a user is connected to the serial console and another user successfully requests access to that same virtual machine, the first user will be disconnected and the second user connected to the same session.
Caution
This means that a user who's disconnected won't be logged out. The ability to enforce a logout upon disconnect (by using SIGHUP or similar mechanism) is still in the roadmap. For Windows, there's an automatic timeout enabled in SAC; for Linux, you can configure the terminal timeout setting.
Accessibility
Accessibility is a key focus for the Azure serial console. To that end, we've ensured that the serial console is accessible for the people with vision impairment, or who are hard of hearing, as well as people who might not be able to use a mouse.
Keyboard navigation
Use the Tab key on your keyboard to navigate in the serial console interface from the Azure portal. Your location will be highlighted on screen. To leave the focus of the serial console window, press Ctrl+F6 on your keyboard.
Use the serial console with a screen reader
The serial console has screen reader support built in. Navigating around with a screen reader turned on will allow the alt text for the currently selected button to be read aloud by the screen reader.
Common scenarios for accessing the serial console
| Scenario | Actions in the serial console |
|---|---|
| Incorrect firewall rules | Access serial console and fix Windows firewall rules. |
| Filesystem corruption/check | Access the serial console and recover the filesystem. |
| RDP configuration issues | Access the serial console and change the settings. For more information, see the RDP documentation. |
| Network lock down system | Access the serial console from the Azure portal to manage the system. Some network commands are listed in Windows commands: CMD and PowerShell. |
| Interacting with bootloader | Access BCD through the serial console. For information, see Enable the Windows boot menu in the serial console. |
Known issues
We're aware of some issues with the serial console and the VM's operating system. Here's a list of these issues and steps for mitigation for Windows VMs. These issues and mitigations apply for both VMs and virtual machine scale set instances. If these don't match the error you're seeing, see the common serial console service errors at Common Serial Console errors.
| Issue | Mitigation |
|---|---|
| Pressing Enter after the connection banner does not cause a sign-in prompt to be displayed. | This error can occur if you're running a custom VM, hardened appliance, or boot config that causes Windows to fail to properly connect to the serial port. This error will also occur if you're running a Windows 10 VM, because only Windows Server VMs are configured to have EMS enabled. |
| Only health information is shown when connecting to a Windows VM | This error occurs if the Special Administration Console has not been enabled for your Windows image. See Enable the serial console in custom or older images for instructions on how to manually enable SAC on your Windows VM. |
| SAC does not take up the entire Serial Console area in the browser | This is a known issue with Windows and the terminal emulator. We are tracking this issue with both teams but for now there is no mitigation. |
| Unable to type at SAC prompt if kernel debugging is enabled. | RDP to VM and run bcdedit /debug {current} off from an elevated command prompt. If you can't RDP, you can instead attach the OS disk to another Azure VM and modify it while attached as a data disk by running bcdedit /store <drive letter of data disk>:\boot\bcd /debug <identifier> off, then swapping the disk back. |
| Pasting into PowerShell in SAC results in a third character if the original content had a repeating character. | For a workaround, run Remove-Module PSReadLine to unload the PSReadLine module from the current session. This action will not delete or uninstall the module. |
| Some keyboard inputs produce strange SAC output (for example, [A, [3~). | VT100 escape sequences aren't supported by the SAC prompt. |
| Pasting long strings doesn't work. | The serial console limits the length of strings pasted into the terminal to 2048 characters to prevent overloading the serial port bandwidth. |
Frequently asked questions
Q. How can I send feedback?
A. Provide feedback by creating a GitHub issue at https://aka.ms/serialconsolefeedback. Alternatively (less preferred), you can send feedback via azserialhelp@microsoft.com or in the virtual machine category of https://feedback.azure.com.
Q. Does the serial console support copy/paste?
A. Yes. Use Ctrl+Shift+C and Ctrl+Shift+V to copy and paste into the terminal.
Q. Who can enable or disable the serial console for my subscription?
A. To enable or disable the serial console at a subscription-wide level, you must have write permissions to the subscription. Roles that have write permission include administrator or owner roles. Custom roles can also have write permissions.
Q. Who can access the serial console for my VM?
A. You must have the Virtual Machine Contributor role or higher for a VM to access the VM's serial console.
Q. My serial console isn't displaying anything, what do I do?
A. Your image is likely misconfigured for serial console access. For information about configuring your image to enable the serial console, see Enable the serial console in custom or older images.
Q. Is the serial console available for virtual machine scale sets?
A. Yes, it is! See Get started with Serial Console.
Next steps
- For an in-depth guide to CMD and PowerShell commands you can use in the Windows SAC, see Windows commands: CMD and PowerShell.
- The serial console is also available for Linux VMs.
- Learn more about boot diagnostics.
Contact us for help
If you have questions or need help, create a support request, or ask Azure community support. You can also submit product feedback to Azure feedback community.