Attach to Running Processes with the Visual Studio Debugger
Note
This article applies to Visual Studio 2015. If you're looking for the latest Visual Studio documentation, see Visual Studio documentation. We recommend upgrading to the latest version of Visual Studio. Download it here
You can attach the Visual Studio debugger to a running process on a local or remote computer. After the process is running, click Debug / Attach to Process (or press CTRL+ALT+P) to open the Attach to Process dialog box.
You can use this capability to debug apps that are running on a local or remote computer, debug multiple processes simultaneously, or debug an application that was not created in Visual Studio. It is often useful when you want to debug an app, but (for whatever reason) you did not start the app from Visual Studio with the debugger attached. For example, if you are running the app without the debugger and hit an exception, you might then attach to the process running the app to begin debugging.
Tip
Not sure whether you need to use Attach to Process for your debugging scenario? See Common debugging scenarios. If you want to debug ASP.NET applications that have been deployed to IIS, see Remote Debugging ASP.NET on a remote IIS computer.
Attach to a running process on the local machine
In order to attach to a process, you must know the name of the process (see Common debugging scenarios for a few common process names).
In Visual Studio, select Debug / Attach to Process (or press CTRL+ALT+P).
In the Attach to Process dialog box, find the program that you want to attach to from the Available Processes list.
To quickly select the process you want, type the first letter of the process name. If you don't know the process name, see Common debugging scenarios.
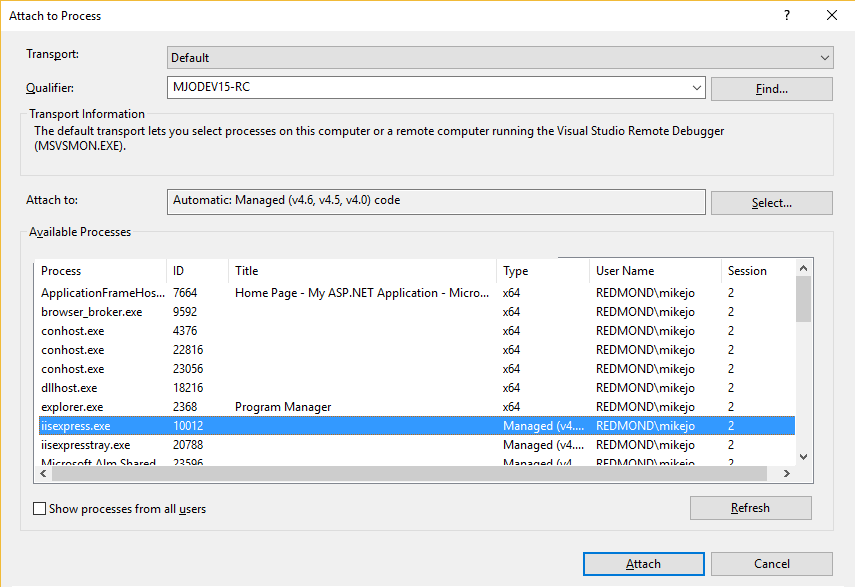
If the process is running under a different user account, select the Show processes from all users check box.
In the Attach to box, make sure that the type of code you will debug is listed. The default Automatic setting tries to determine what type of code you want to debug. To set the type of code manually, do the following
In the Attach to box, click Select.
In the Select Code Type dialog box, click Debug these code types and select the types to debug.
Click OK.
Click Attach.
Attach to a process on a remote computer
In order to attach to a process, you must know the name of the process (see Common debugging scenarios for a few common process names). For more complete guidance for ASP.NET apps that have been deployed to IIS, see Remote Debugging ASP.NET on a remote IIS computer. For other apps, you may be able to find the name of the process in the Task Manager.
When you use the Attach to Process dialog box, you can select another computer that has been set up for remote debugging. For more information, see Remote Debugging. When you have selected a remote computer, you can view a list of available processes running on that computer and attach to one or more of the processes for debugging.
To select a remote computer:
In Visual Studio, select Debug / Attach to Process (or press CTRL+ALT+P).
In the Attach to Process dialog box, select the appropriate connection type from the Transport list. Default is the correct setting for most cases.
The Transport setting persists between debugging sessions.
Use the Qualifier list box to choose the remote computer name by one of the following methods:
Type the name in the Qualifier list box.
Note
If, in later steps, you can't connect using the remote computer name, use the IP address. (The port number may appear automatically after selecting the process. You can also enter it manually. In the illustration below, 4020 is the default port for the remote debugger.)
Click the drop-down arrow attached to the Qualifier list box and select the computer name from the drop-down list.
Click the Find button next to the Qualifier list to open the Select Remote Debugger Connection dialog box. The Select Remote Debugger Connection dialog box lists all the devices that are on your local sub-net, and any device that is directly attached to your computer through an Ethernet cable. Click the computer or device that you want, and then click Select.
The Qualifier setting persists between debugging sessions only if a successful debugging connection occurs with that qualifier.
Click Refresh.
The Available Processes list is displayed automatically when you open the Processes dialog box. Processes can start and stop in the background while the dialog box is open. However, the contents are not always current. You can refresh the list at any time to see the current list of processes by clicking Refresh.
In the Attach to Process dialog box, find the program that you want to attach to from the Available Processes list.
If the process is running under a different user account, select the Show processes from all users check box.
Click Attach.
Additional info
You can be attached to multiple programs when you are debugging, but only one program is active in the debugger at any time. You can set the active program in the Debug Location toolbar or the Processes window. For more information, see How to: Set the Current Program.
If you try to attach to a process owned by an untrusted user account, a security warning dialog box confirmation will appear. For more information see Security Warning: Attaching to a process owned by an untrusted user can be dangerous. If the following information looks suspicious or you are unsure, do not attach to this process.
In some cases, when you debug in a Remote Desktop (Terminal Services) session, the Available Processes list will not display all available processes. If you are running Visual Studio as a user who has a limited user account, the Available Processes list will not show processes that are running in Session 0, which is used for services and other server processes, including w3wp.exe. You can solve the problem by running Visual Studio under an administrator account or by running Visual Studio from the server console instead of a Terminal Services session. If neither of those workarounds is possible, a third option is to attach to the process by running vsjitdebugger.exe -p ProcessId from the Windows command line. You can determine the process id using tlist.exe. To obtain tlist.exe, download and install Debugging Tools for Windows, available at WDK and WinDbg downloads.
Common debugging scenarios
To help you identify whether you need to use Attach to process and what process to attach to, a few common debugging scenarios are shown here (the list is not exhaustive). Where more instructions are available, we provide links.
For some app types (like Windows Store apps), you don't attach directly to a process name, but use the Debug Installed App Package menu option instead (see table).
Note
For information about basic debugging in Visual Studio, see Getting started with the debugger.
| Scenario | Debug Method | Process Name | Notes and Links |
|---|---|---|---|
| Debug a managed or native app on the local machine | Use attach to process or standard debugging | appname.exe | To quickly access the dialog box, use CTRL+ALT+P and then type the first letter of the process name. |
| Debug ASP.NET apps on the local machine after starting the app without the debugger | Use attach to process | iiexpress.exe | This may be helpful to make your app load faster, such as (for example) when profiling. |
| Remote debug ASP.NET 4 or 4.5 on an IIS server | Use remote tools and attach to process | w3wp.exe | See Remote Debugging ASP.NET on a remote IIS computer |
| Remote debug ASP.NET Core on an IIS server | Use remote tools and attach to process | dnx.exe | For app deployment, see Publish to IIS. For debugging, see Remote Debugging ASP.NET on a remote IIS computer |
| Debug other supported app types on a server process | Use remote tools (if server is remote) and attach to process | iexplore.exe or other processes | If necessary, use Task Manager to help identify the process. See Remote Debugging and later sections in this topic |
| Remote debug a Windows desktop app | Remote Tools and F5 | N/A | See Remote Debugging |
| Remote debug a Windows Universal (UWP), OneCore, HoloLens, or IoT app | Debug installed app package | N/A | Use Debug / Other Debug Targets / Debug Installed App Package instead of Attach to process |
| Debug a Windows Universal (UWP), OneCore, HoloLens, or IoT app that you didn't start from Visual Studio | Debug installed app package | N/A | Use Debug / Other Debug Targets / Debug Installed App Package instead of Attach to process |
Warning
To attach to a Windows Universal app that is written in JavaScript, you must first enable debugging for the app. See Attach the debugger in the Windows Dev Center.
Note
For the debugger to attach to code written in C++, the code needs to emit DebuggableAttribute. You can add this to your code automatically by linking with the /ASSEMBLYDEBUG linker option.
What debugger features can I use?
To use the full features of the Visual Studio debugger (like hitting breakpoints) when attaching to a process, the executable must exactly match your local source and symbols (that is, the debugger must be able to load the correct symbol (.pbd) files). By default, this requires a debug build.
For remote debugging scenarios, you must have the source code (or a copy of the source code) already open in Visual Studio. The compiled app binaries on the remote machine must come from the same build as on the local machine.
In some local debugging scenarios, you can debug in Visual Studio with no access to the source if the correct symbol files are present with the app (by default, this requires a debug build). For more info, see Specify Symbol and Source Files.
Troubleshoot attach errors
When the debugger attaches to a running process, the process can contain one or more types of code. The code types the debugger can attach to are displayed and selected in the Select Code Type dialog box.
Sometimes, the debugger can successfully attach to one code type, but not to another code type. This might occur if you are trying to attach to a process that is running on a remote computer. The remote computer might have remote debugging components installed for some code types but not for others. It can also occur if you try to attach to two or more processes for direct database debugging. SQL debugging supports attaching to a single process only.
If the debugger is able to attach to some, but not all, code types, you will see a message identifying which types failed to attach.
If the debugger successfully attaches to at least one code type, you can proceed to debug the process. You will be able to debug only the code types that were successfully attached. The preceding example message shows that the script code type failed to attach. Therefore, you would not be able to debug script code within the process. The script code in the process would still run, but you would not be able to set breakpoints, view data, or perform other debugging operations in the Script.
If you want more specific information about why the debugger failed to attach to a code type, you can try to reattach to only that code type.
To obtain specific information about why a code type failed to attach
Detach from the process. On the Debug menu, click Detach All.
Reattach to the process, selecting only a single code type.
In the Attach to Process dialog box, select the process in the Available Processes list.
Click Select.
In the Select Code Type dialog box, select Debug these code types and the code type that failed to attach. Clear any other code.
Click OK. The Select Code Type dialog box closes.
In the Attach to Process dialog box, click Attach.
This time, the attach will fail completely, and you will get a specific error message.
See Also
Debug Multiple Processes Just-In-Time Debugging Remote Debugging