Extensible Key Management Using Azure Key Vault (SQL Server)
The SQL Server Connector for Microsoft Azure Key Vault enables SQL Server encryption to leverage the Azure Key Vault service as an Extensible Key Management (EKM) provider to protect its encryption keys.
Included in this topic:
Step 3: Configure SQL Server to use an EKM provider for the Key Vault
Example A: Transparent Data Encryption by Using an Asymmetric Key from the Key Vault
Example B: Encrypting Backups by Using an Asymmetric Key from the Key Vault
Example C: Column Level Encryption by Using an Asymmetric Key from the Key Vault
Uses of EKM
An organization can use SQL Server encryption to protect sensitive data. SQL Server encryption includes Transparent Data Encryption (TDE), Column Level Encryption (CLE), and Backup Encryption. In all of these cases the data is encrypted using a symmetric data encryption key. The symmetric data encryption key is further protected by encrypting it with a hierarchy of keys stored in SQL Server. Alternatively, the EKM provider architecture enables SQL Server to protect the data encryption keys by using an asymmetric key stored outside of SQL Server in an external cryptographic provider. Using EKM provider architecture adds an additional layer of security and allows organizations to separate the management of keys and data.
The SQL Server Connector for Azure Key Vault lets SQL Server leverage the scalable, high performance, and highly available key vault service as an EKM provider for encryption key protection. The key vault service can be used with SQL Server installations on Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines and for on-premises servers. The key vault service also provides the option to use tightly controlled and monitored Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) for a higher level of protection for asymmetric encryption keys. For more information about the key vault, see Azure Key Vault.
The following image summarizes the process flow of EKM using the key vault. The process step numbers in the image are not meant to match the setup step numbers that follow the image.
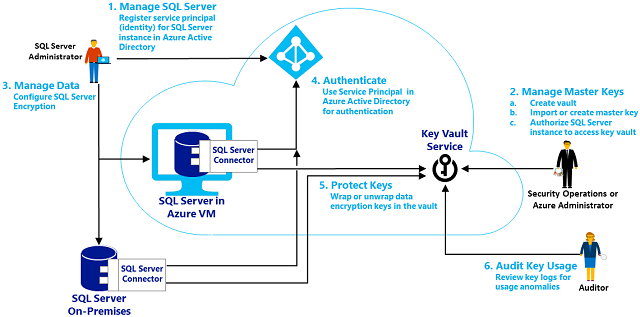
Step 1: Set up the Key Vault for use by SQL Server
Use the following steps to set up a key vault for use with the SQL Server Database Engine for encryption key protection. A vault may already be in use for the organization. When a vault does not exist, the Azure Administrator in your organization that is designated to manage encryption keys can create a vault, generate an asymmetric key in the vault, and then authorize SQL Server to use the key. To familiarize yourself with the key vault service review Get Started with Azure Key Vault, and the PowerShell Azure Key Vault Cmdlets reference.
Important
If you have multiple Azure subscriptions, you must use the subscription that contains SQL Server.
Create a vault: Create a vault by using the instructions in the Create a key vault section of Get Started with Azure Key Vault. Record the name of the vault. This topic uses ContosoKeyVault as the key vault name.
Generate an asymmetric key in the vault: The asymmetric key in the key vault is used to protect SQL Server encryption keys. Only the public portion of the asymmetric key ever leaves the vault, the private portion is never exported by the vault. All cryptographic operations using the asymmetric key are delegated to the Azure Key Vault, and are protected by the key vault security.
There are several ways that you can generate an asymmetric key and store it in the vault. You can externally generate a key, and import the key into the vault as a .pfx file. Or create the key directly in the vault by using the key vault APIs.
The SQL Server Connector requires the asymmetric keys to be 2048-bit RSA, and the key name can only use the characters "a-z", "A-Z", "0-9", and "-". In this document the name of the asymmetric key is referred to as ContosoMasterKey. Replace this with the unique name you use for the key.
Important
Importing the asymmetric key is highly recommended for production scenarios because it allows the administrator to escrow the key in a key escrow system. If the asymmetric key is created in the vault, it cannot be escrowed because the private key can never leave the vault. Keys used to protect critical data should be escrowed. The loss of an asymmetric key will result in permanently unrecoverable data.
Important
The key vault supports multiple versions of the same named key. Keys to be used by SQL Server Connector should not be versioned or rolled. If the administrator wants to roll the key used for SQL Server encryption, a new key with a different name should be created in the vault and used to encrypt the DEK.
For more information on how to import a key into the key vault or to create a key in the key vault (not recommended for a production environment), see the Add a key or secret to the key vault section in Get Started with Azure Key Vault.
Get Azure Active Directory Service Principals to use for SQL Server: When the organization signs up for a Microsoft cloud service, it gets an Azure Active Directory. Create Service Principals in the Azure Active Directory for SQL Server to use (to authenticate itself to Azure Active Directory) while accessing the key vault.
One Service Principal will be needed by a SQL Server administrator to access the vault while configuring SQL Server to use encryption.
Another Service Principal will be needed by the SQL Server Database Engine to access the vault for unwrapping keys used in SQL Server encryption.
For more information about how to register an application and generate a service principal, see the Register an Application with Azure Active Directory section in Get Started with Azure Key Vault. The registration process returns an Application ID (also known as a CLIENT ID) and a Authentication Key (also known as a Secret) for each Azure Active Directory Service Principal. When used in the
CREATE CREDENTIALstatement, the hyphen must be removed from the CLIENT ID. Record these for use in the scripts below:Service Principal for a sysadmin login: CLIENTID_sysadmin_login and SECRET_sysadmin_login
Service Principal for the SQL Server Database Engine: CLIENTID_DBEngine and SECRET_DBEngine.
Grant Permission for the Service Principals to access the Key Vault: Both the CLIENTID_sysadmin_login and CLIENTID_DBEngineService Principals require the get, list, wrapKey, and unwrapKey permissions in the key vault. If you intend to create keys through SQL Server you also need to grant the create permission in key vault.
Important
Users must have at least the wrapKey and unwrapKey operations for the key vault.
For more information about granting permissions to the vault, see the Authorize the application to use the key or secret section in Get Started with Azure Key Vault.
Links to Azure Key Vault documentation
PowerShell Azure Key Vault Cmdlets reference
Step 2: Install the SQL Server Connector
The SQL Server Connector is downloaded and installed by the administrator of the SQL Server computer. The SQL Server Connector is available as a download from the Microsoft Download Center. Search for SQL Server Connector for Microsoft Azure Key Vault, review the details, system requirements and install instructions and choose to download the connector and start the installation using Run. Review the license and accept the license and continue.
By default the connector is installed at C:\Program Files\SQL Server Connector for Microsoft Azure Key Vault. This location can be changed during setup. (If changed, adjust the scripts below.)
On completing the install, the following are installed on the machine:
Microsoft.AzureKeyVaultService.EKM.dll: This is the cryptographic EKM provider DLL that needs to be registered with SQL Server by using the CREATE CRYPTOGRAPHIC PROVIDER statement.
Azure Key Vault SQL Server Connector: This is a Windows service that enables the cryptographic EKM provider to communicate with the key vault.
The SQL Server Connector installation also allows you to optionally download sample scripts for SQL Server encryption.
Step 3: Configure SQL Server to use an EKM provider for the Key Vault
Permissions
To complete this entire process requires CONTROL SERVER permission or membership in the sysadmin fixed server role. Specific actions require the following permissions:
To create a cryptographic provider, requires CONTROL SERVER permission or membership in the sysadmin fixed server role.
To change a configuration option and run the RECONFIGURE statement, you must be granted the ALTER SETTINGS server-level permission. The ALTER SETTINGS permission is implicitly held by the sysadmin and serveradmin fixed server roles.
To create a credential, requires ALTER ANY CREDENTIAL permission.
To add a credential to a login, requires ALTER ANY LOGIN permission.
To create an asymmetric key, requires CREATE ASYMMETRIC KEY permission.
To configure SQL Server to use a cryptographic provider
Configure the Database Engine to use EKM, and register (create) the cryptographic provider with SQL Server.
-- Enable advanced options. USE master; GO sp_configure 'show advanced options', 1 ; GO RECONFIGURE ; GO -- Enable EKM provider sp_configure 'EKM provider enabled', 1 ; GO RECONFIGURE ; GO -- Create a cryptographic provider, using the SQL Server Connector -- which is an EKM provider for the Azure Key Vault. This example uses -- the name AzureKeyVault_EKM_Prov. CREATE CRYPTOGRAPHIC PROVIDER AzureKeyVault_EKM_Prov FROM FILE = 'C:\Program Files\SQL Server Connector for Microsoft Azure Key Vault\Microsoft.AzureKeyVaultService.EKM.dll'; GOSetup a SQL Server credential for a SQL Server administrator login to use the key vault in order to setup and manage SQL Server encryption scenarios.
Important
The IDENTITY argument of
CREATE CREDENTIALrequires the key vault name. The SECRET argument ofCREATE CREDENTIALrequires the <Client ID> (without hyphens) and <Secret> to be passed together without a space between them.In the following example, the Client ID (
EF5C8E09-4D2A-4A76-9998-D93440D8115D) is stripped of the hyphens and entered as the stringEF5C8E094D2A4A769998D93440D8115Dand the Secret is represented by the string SECRET_sysadmin_login.USE master; CREATE CREDENTIAL sysadmin_ekm_cred WITH IDENTITY = 'ContosoKeyVault', SECRET = 'EF5C8E094D2A4A769998D93440D8115DSECRET_sysadmin_login' FOR CRYPTOGRAPHIC PROVIDER AzureKeyVault_EKM_Prov ; -- Add the credential to the SQL Server administrators domain login ALTER LOGIN [<domain>/<login>] ADD CREDENTIAL sysadmin_ekm_cred;For an example of using variables for the
CREATE CREDENTIALarguments and programmatically removing the hyphens from the Client ID, see CREATE CREDENTIAL (Transact-SQL).If you imported an asymmetric key as described earlier in step 1, section 3, open the key by providing your key name in the following example.
CREATE ASYMMETRIC KEY CONTOSO_KEY FROM PROVIDER [AzureKeyVault_EKM_Prov] WITH PROVIDER_KEY_NAME = 'ContosoMasterKey', CREATION_DISPOSITION = OPEN_EXISTING;Though not recommended for production (because the key cannot be exported), it is possible to create an asymmetric key directly in the vault from SQL Server. If you did not import a key earlier, then create an asymmetric key in the key vault for testing by using the following script. Execute the script, using a login provisioned with the sysadmin_ekm_cred credential.
CREATE ASYMMETRIC KEY CONTOSO_KEY FROM PROVIDER [AzureKeyVault_EKM_Prov] WITH ALGORITHM = RSA_2048, PROVIDER_KEY_NAME = 'ContosoMasterKey';
Tip
Users receiving the error Cannot export public key from the provider. Provider error code: 2053. should check their get, list, wrapKey, and unwrapKey permissions in the key vault.
For more information, see the following:
Examples
Example A: Transparent Data Encryption by Using an Asymmetric Key from the Key Vault
After completing the steps above, create a credential and a login, create a database encryption key protected by the asymmetric key in the key vault. Use the database encryption key to encrypt a database with TDE.
To encrypt a database requires CONTROL permission on the database.
To enable TDE using EKM and the Key Vault
Create a SQL Server credential for the Database Engine to use when accessing the key vault EKM during database load.
Important
The IDENTITY argument of
CREATE CREDENTIALrequires the key vault name. The SECRET argument ofCREATE CREDENTIALrequires the <Client ID> (without hyphens) and <Secret> to be passed together without a space between them.In the following example, the Client ID (
EF5C8E09-4D2A-4A76-9998-D93440D8115D) is stripped of the hyphens and entered as the stringEF5C8E094D2A4A769998D93440D8115Dand the Secret is represented by the string SECRET_DBEngine.USE master; CREATE CREDENTIAL Azure_EKM_TDE_cred WITH IDENTITY = 'ContosoKeyVault', SECRET = 'EF5C8E094D2A4A769998D93440D8115DSECRET_DBEngine' FOR CRYPTOGRAPHIC PROVIDER AzureKeyVault_EKM_Prov ;Create a SQL Server login to be used by the Database Engine for TDE, and add the credential to it. This example uses the CONTOSO_KEY asymmetric key stored in the key vault, which was imported or created earlier for the master database, as described in Step 3, section 3 above.
USE master; -- Create a SQL Server login associated with the asymmetric key -- for the Database engine to use when it loads a database -- encrypted by TDE. CREATE LOGIN TDE_Login FROM ASYMMETRIC KEY CONTOSO_KEY; GO -- Alter the TDE Login to add the credential for use by the -- Database Engine to access the key vault ALTER LOGIN TDE_Login ADD CREDENTIAL Azure_EKM_TDE_cred ; GOCreate the database encryption key (DEK) that will be used for TDE. The DEK can be created using any SQL Server supported algorithm or key length. The DEK will be protected by the asymmetric key in the key vault.
This example uses the CONTOSO_KEY asymmetric key stored in the key vault, which was imported or created earlier, as described in Step 3, section 3 above.
USE ContosoDatabase; GO CREATE DATABASE ENCRYPTION KEY WITH ALGORITHM = AES_128 ENCRYPTION BY SERVER ASYMMETRIC KEY CONTOSO_KEY; GO -- Alter the database to enable transparent data encryption. ALTER DATABASE ContosoDatabase SET ENCRYPTION ON ; GOFor more information, see the following:
Example B: Encrypting Backups by Using an Asymmetric Key from the Key Vault
Encrypted backups are supported starting with SQL Server 2014. The following example creates and restores a backup encrypted a data encryption key protected by the asymmetric key in the key vault.
USE master;
BACKUP DATABASE [DATABASE_TO_BACKUP]
TO DISK = N'[PATH TO BACKUP FILE]'
WITH FORMAT, INIT, SKIP, NOREWIND, NOUNLOAD,
ENCRYPTION(ALGORITHM = AES_256, SERVER ASYMMETRIC KEY = [CONTOSO_KEY]);
GO
Sample restore code.
RESTORE DATABASE [DATABASE_TO_BACKUP]
FROM DISK = N'[PATH TO BACKUP FILE]' WITH FILE = 1, NOUNLOAD, REPLACE;
GO
For more information about backup options, see BACKUP (Transact-SQL).
Example C: Column Level Encryption by Using an Asymmetric Key from the Key Vault
The following example creates a symmetric key protected by the asymmetric key in the key vault. Then the symmetric key is used to encrypt data in the database.
This example uses the CONTOSO_KEY asymmetric key stored in the key vault, which was imported or created earlier, as described in Step 3, section 3 above. To use this asymmetric key in the ContosoDatabase database, you must execute the CREATE ASYMMETRIC KEY statement again, to provide the ContosoDatabase database with a reference to the key.
USE [ContosoDatabase];
GO
-- Create a reference to the key in the key vault
CREATE ASYMMETRIC KEY CONTOSO_KEY
FROM PROVIDER [AzureKeyVault_EKM_Prov]
WITH PROVIDER_KEY_NAME = 'ContosoMasterKey',
CREATION_DISPOSITION = OPEN_EXISTING;
-- Create the data encryption key.
-- The data encryption key can be created using any SQL Server
-- supported algorithm or key length.
-- The DEK will be protected by the asymmetric key in the key vault
CREATE SYMMETRIC KEY DATA_ENCRYPTION_KEY
WITH ALGORITHM=AES_256
ENCRYPTION BY ASYMMETRIC KEY CONTOSO_KEY;
DECLARE @DATA VARBINARY(MAX);
--Open the symmetric key for use in this session
OPEN SYMMETRIC KEY DATA_ENCRYPTION_KEY
DECRYPTION BY ASYMMETRIC KEY CONTOSO_KEY;
--Encrypt syntax
SELECT @DATA = ENCRYPTBYKEY(KEY_GUID('DATA_ENCRYPTION_KEY'), CONVERT(VARBINARY,'Plain text data to encrypt'));
-- Decrypt syntax
SELECT CONVERT(VARCHAR, DECRYPTBYKEY(@DATA));
--Close the symmetric key
CLOSE SYMMETRIC KEY DATA_ENCRYPTION_KEY;
See Also
CREATE CRYPTOGRAPHIC PROVIDER (Transact-SQL) CREATE CREDENTIAL (Transact-SQL) CREATE ASYMMETRIC KEY (Transact-SQL) CREATE SYMMETRIC KEY (Transact-SQL) Extensible Key Management (EKM) Enable TDE Using EKM Backup Encryption Create an Encrypted Backup