Set Git repository permissions
TFS 2017 | TFS 2015 | TFS 2013
You grant or restrict access to repositories to lock down who can contribute to your source code and manage other features. You can set permissions across all Git repositories by making changes to the top-level Git repositories entry. Individual repositories inherit permissions from the top-level Git Repositories entry.
Note
Branches inherit a subset of permissions from assignments made at the repository level. For branch permissions and policies, see Set branch permissions and Improve code quality with branch policies.
For guidance on who to provide greater permission levels, see Grant or restrict access using permissions.
Prerequisites
- You must have a project. If you don't have a project yet, create one in Azure DevOps or set one up in an on-premises Azure DevOps.
- You must be a member of the Project Administrators Group or have your Manage permissions set to Allow for Git repositories.
To contribute to the source code, you must be granted Basic access level or greater. Users granted Stakeholder access have no access to source code. To learn more, see About access levels.
Default repository permissions
By default, members of the project Contributors group have permissions to contribute to a repository. This includes the ability to create branches, create tags, and manage notes. For a description of each security group and permission level, see Permissions and group reference.
Permission
Readers
Contributors
Build Admins
Project Admins
Read (clone, fetch, and explore the contents of a repository); also, can create, comment on, vote, and Contribute to pull requests
✔️
✔️
✔️
✔️
Contribute, Create branches, Create tags, and Manage notes
✔️
✔️
✔️
Create repository, Delete repository, and Rename repository
✔️
Edit policies, Manage permissions, Remove others' locks
✔️
Force push (rewrite history, delete branches and tags)
✔️
Bypass policies when completing pull requests
(not set for any security group)
Set permissions for a repository
You can grant or restrict access to a repository by setting the permission state to Allow or Deny for a single user or a security group.
Open the web portal and choose the project where you want to add users or groups. To choose another project, see Switch project, repository, team.
Choose the
 gear icon to open the administrative context.
gear icon to open the administrative context.
Choose Version Control.
To set the set the permissions for all Git repositories for a project, (1) choose Git Repositories and then (2) choose the security group whose permissions you want to manage.
Note
You may not be able to find a user from a permissions page or identity field if the user hasn't been added to the project—either by adding it to a security group or to a project team. Also, when a user is added to Azure Active Directory or Active Directory, there can be a delay between the time they are added to the project and when they are searchable from an identity field. The delay can be between 5 minutes to 7 days.
Otherwise, choose a specific repository and choose the security group whose permissions you want to manage.
Choose the setting for the permission you want to change.
Here we grant permissions to the Contributors group to (3) Create repository.
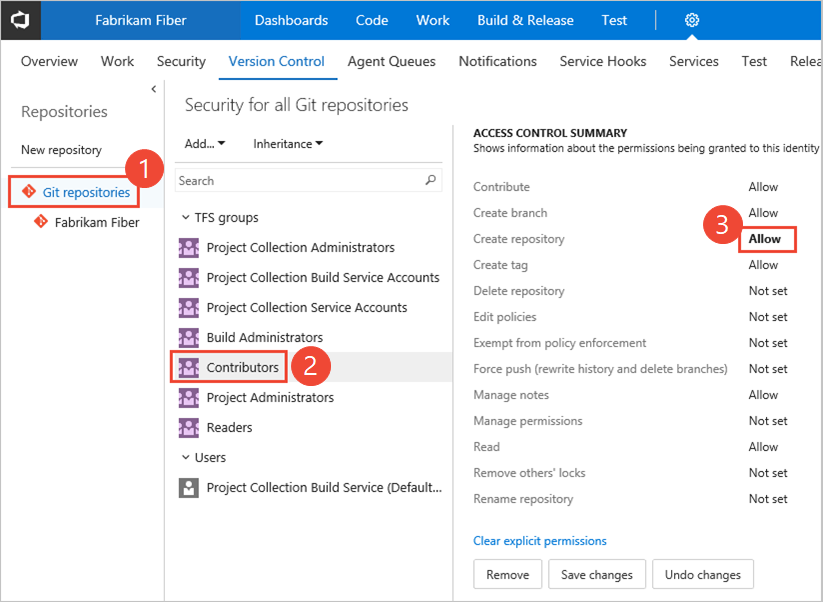
When done, choose Save changes.
Exempt from policy enforcement and bypass policy permissions
There are many scenarios where you have the occasional need to bypass a branch policy. For example, when reverting a change that caused a build break or applying a hotfix in the middle of the night. Previously, the Exempt from policy enforcement permission helped teams manage which users were granted the ability to bypass branch policies when completing a pull request. However, that permission also granted the ability to push directly to the branch, bypassing the PR process entirely.
To improve this experience, we split the Exempt from policy enforcement permission to offer more control to teams that are granting bypass permissions. The following two permissions replace the former permission:
- Bypass policies when completing pull requests. Users with this permission will be able to use the "Override" experience for pull requests.
- Bypass policies when pushing. Users with this permission will be able to push directly to branches that have required policies configured.
By granting the first permission and denying the second, a user can use the bypass option when necessary, but will still have the protection from accidentally pushing to a branch with policies.
Note
This change does not introduce any behavior changes. Users that were formerly granted Allow for Exempt from policy enforcement are granted Allow for both new permissions, so they'll be able to both override completion on PRs and push directly to branches with policies.