Ověření zrcadlení portů
Platí pro: Advanced Threat Analytics verze 1.9
Poznámka
Tento článek je relevantní jenom v případě, že místo ATA Lightweight Gateway nasadíte KOMPONENTY ATA Gateway. Pokud chcete zjistit, jestli potřebujete používat KOMPONENTY ATA Gateway, přečtěte si téma Volba správných bran pro vaše nasazení.
Následující kroky vás provedou procesem ověření správné konfigurace zrcadlení portů. Aby ATA fungovala správně, musí ata gateway vidět provoz do a z řadiče domény. Hlavním zdrojem dat, který ATA používá, je hloubková kontrola paketů síťového provozu do a z vašich řadičů domény. Aby ATA viděla síťový provoz, je potřeba nakonfigurovat zrcadlení portů. Zrcadlení portů kopíruje provoz z jednoho portu (zdrojového portu) do jiného (cílového portu).
Ověření zrcadlení portů pomocí skriptu Windows PowerShell
- Uložte text tohoto skriptu do souboru s názvem ATAdiag.ps1.
- Spusťte tento skript na ATA Gateway, kterou chcete ověřit. Skript vygeneruje provoz PROTOKOLU ICMP z ATA Gateway do řadiče domény a vyhledá ho na síťové kartě pro zachytávání na řadiči domény. Pokud ATA Gateway uvidí provoz PROTOKOLU ICMP s cílovou IP adresou stejnou jako IP adresa řadiče domény, kterou jste zadali v konzole ATA, považuje zrcadlení portů za nakonfigurované.
Ukázka spuštění skriptu:
# ATAdiag.ps1 -CaptureIP n.n.n.n -DCIP n.n.n.n -TestCount n
param([parameter(Mandatory=$true)][string]$CaptureIP, [parameter(Mandatory=$true)][string]$DCIP, [int]$PingCount = 10)
# Set variables
$ErrorActionPreference = "stop"
$starttime = get-date
$byteIn = new-object byte[] 4
$byteOut = new-object byte[] 4
$byteData = new-object byte[] 4096 # size of data
$byteIn[0] = 1 # for promiscuous mode
$byteIn[1-3] = 0
$byteOut[0-3] = 0
# Convert network data to host format
function NetworkToHostUInt16 ($value)
{
[Array]::Reverse($value)
[BitConverter]::ToUInt16($value,0)
}
function NetworkToHostUInt32 ($value)
{
[Array]::Reverse($value)
[BitConverter]::ToUInt32($value,0)
}
function ByteToString ($value)
{
$AsciiEncoding = new-object system.text.asciiencoding
$AsciiEncoding.GetString($value)
}
Write-Host "Testing Port Mirroring..." -ForegroundColor Yellow
Write-Host ""
Write-Host "Here is a summary of the connection we will test." -ForegroundColor Yellow
# Initialize a first ping connection
Test-Connection -Count 1 -ComputerName $DCIP -ea SilentlyContinue
Write-Host ""
Write-Host "Press any key to continue..." -ForegroundColor Red
[void][System.Console]::ReadKey($true)
Write-Host ""
Write-Host "Sending ICMP and Capturing data..." -ForegroundColor Yellow
# Open a socket
$socket = new-object system.net.sockets.socket([Net.Sockets.AddressFamily]::InterNetwork,[Net.Sockets.SocketType]::Raw,[Net.Sockets.ProtocolType]::IP)
# Include the IP header
$socket.setsocketoption("IP","HeaderIncluded",$true)
$socket.ReceiveBufferSize = 10000
$ipendpoint = new-object system.net.ipendpoint([net.ipaddress]"$CaptureIP",0)
$socket.bind($ipendpoint)
# Enable promiscuous mode
[void]$socket.iocontrol([net.sockets.iocontrolcode]::ReceiveAll,$byteIn,$byteOut)
# Initialize test variables
$tests = 0
$TestResult = "Noise"
$OneSuccess = 0
while ($tests -le $PingCount)
{
if (!$socket.Available) # see if any packets are in the queue
{
start-sleep -milliseconds 500
continue
}
# Capture traffic
$rcv = $socket.receive($byteData,0,$byteData.length,[net.sockets.socketflags]::None)
# Decode the header so we can read ICMP
$MemoryStream = new-object System.IO.MemoryStream($byteData,0,$rcv)
$BinaryReader = new-object System.IO.BinaryReader($MemoryStream)
# Set IP version & header length
$VersionAndHeaderLength = $BinaryReader.ReadByte()
# TOS
$TypeOfService= $BinaryReader.ReadByte()
# More values, and the Protocol Number for ICMP traffic
# Convert network format of big-endian to host format of little-endian
$TotalLength = NetworkToHostUInt16 $BinaryReader.ReadBytes(2)
$Identification = NetworkToHostUInt16 $BinaryReader.ReadBytes(2)
$FlagsAndOffset = NetworkToHostUInt16 $BinaryReader.ReadBytes(2)
$TTL = $BinaryReader.ReadByte()
$ProtocolNumber = $BinaryReader.ReadByte()
$Checksum = [Net.IPAddress]::NetworkToHostOrder($BinaryReader.ReadInt16())
# The source and destination IP addresses
$SourceIPAddress = $BinaryReader.ReadUInt32()
$DestinationIPAddress = $BinaryReader.ReadUInt32()
# The source and destimation ports
$sourcePort = [uint16]0
$destPort = [uint16]0
# Close the stream reader
$BinaryReader.Close()
$memorystream.Close()
# Cast DCIP into an IPaddress type
$DCIPP = [ipaddress] $DCIP
$DestinationIPAddressP = [ipaddress] $DestinationIPAddress
#Ping the DC at the end after starting the capture
Test-Connection -Count 1 -ComputerName $DCIP -ea SilentlyContinue | Out-Null
# This is the match logic - check to see if Destination IP from the Ping sent matches the DCIP entered by in the ATA Console
# The only way the ATA Gateway should see a destination of the DC is if Port Spanning is configured
if ($DestinationIPAddressP -eq $DCIPP) # is the destination IP eq to the DC IP?
{
$TestResult = "Port Spanning success!"
$OneSuccess = 1
} else {
$TestResult = "Noise"
}
# Put source, destination, test result in Powershell object
new-object psobject | add-member -pass noteproperty CaptureSource $([system.net.ipaddress]$SourceIPAddress) | add-member -pass noteproperty CaptureDestination $([system.net.ipaddress]$DestinationIPAddress) | Add-Member -pass NoteProperty Result $TestResult | Format-List | Out-Host
#Count tests
$tests ++
}
if ($OneSuccess -eq 1)
{
Write-Host "Port Spanning Success!" -ForegroundColor Green
Write-Host ""
Write-Host "At least one packet which was addressed to the DC, was picked up by the Gateway." -ForegroundColor Yellow
Write-Host "A little noise is OK, but if you don't see a majority of successes, you might want to re-run." -ForegroundColor Yellow
} else {
Write-Host "No joy, all noise. You may want to re-run, increase the number of Ping Counts, or check your config." -ForegroundColor Red
}
Write-Host ""
Write-Host "Press any key to continue..." -ForegroundColor Red
[void][System.Console]::ReadKey($true)
Ověření zrcadlení portů pomocí Net Mon
Nainstalujte Microsoft Network Monitor 3.4 na ATA Gateway, kterou chcete ověřit.
Důležité
Na ATA Gateway neinstalujte Microsoft Message Analyzer ani žádný jiný software pro zachytávání provozu.
Otevřete nástroj Sledování sítě a vytvořte novou kartu zachycení.
Vyberte pouze síťový adaptér Capture nebo síťový adaptér, který je připojený k portu přepínače, který je nakonfigurovaný jako cíl zrcadlení portů.
Ujistěte se, že je povolený režim P.
Klikněte na Nový záznam.
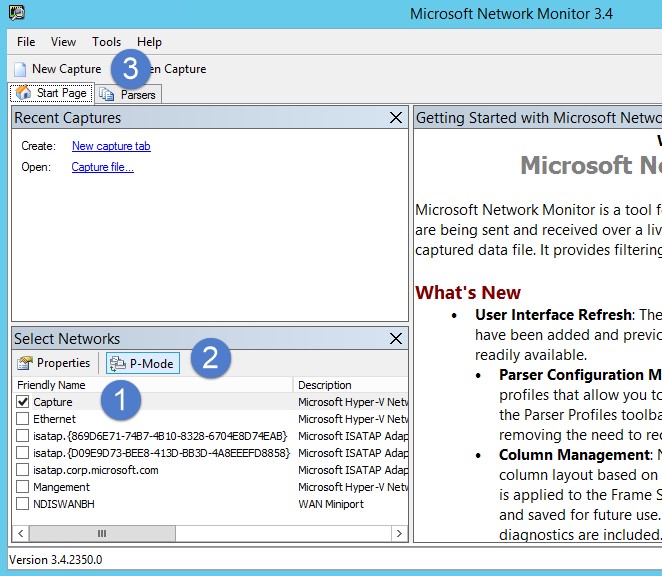
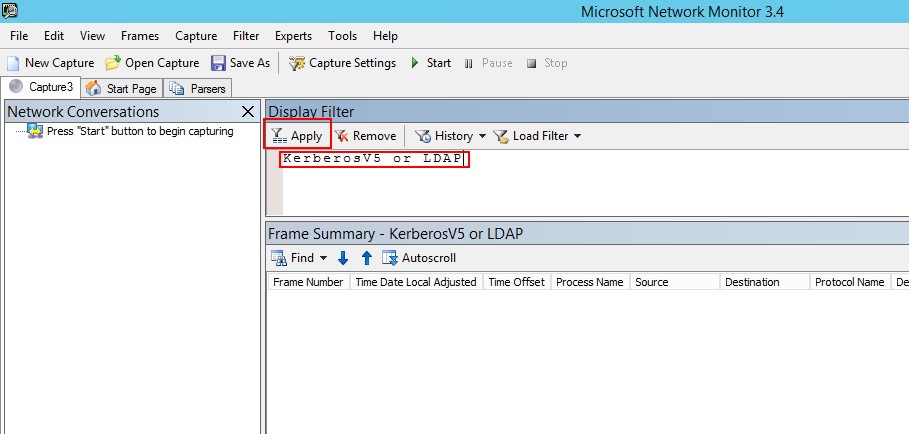
V okně Filtr zobrazení zadejte následující filtr: KerberosV5 NEBO LDAP a potom klikněte na Použít.
Kliknutím na Start spusťte relaci zachycení. Pokud nevidíte provoz do a z řadiče domény, zkontrolujte konfiguraci zrcadlení portů.
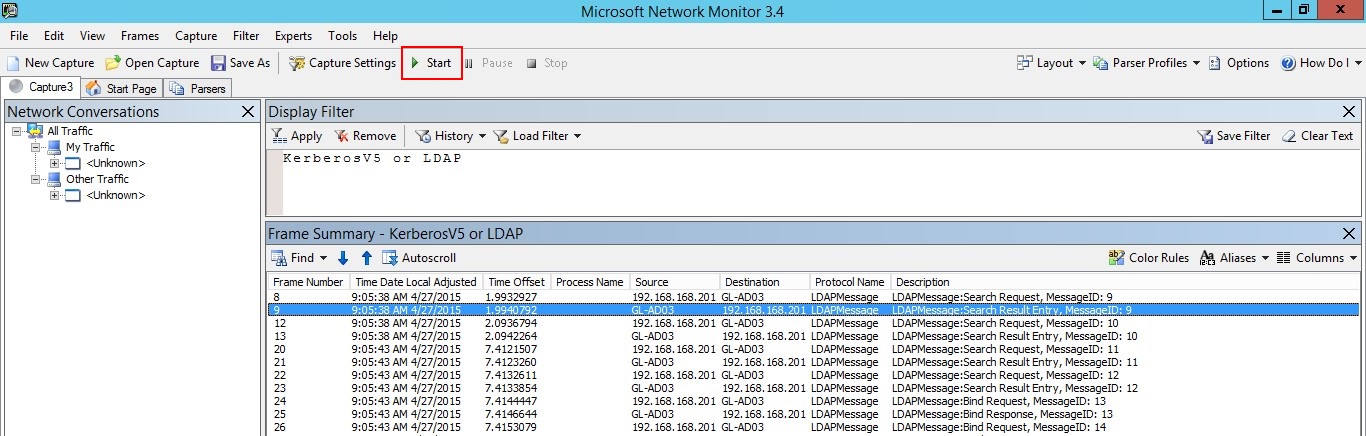
Poznámka
Je důležité zajistit, abyste viděli provoz do a z řadičů domény.
Pokud se provoz zobrazuje jenom v jednom směru, měli byste spolupracovat se síťovými nebo virtualizačními týmy, které vám pomůžou s řešením potíží s konfigurací zrcadlení portů.