Xamarin.Forms DependencyService Introduction
The DependencyService class is a service locator that enables Xamarin.Forms applications to invoke native platform functionality from shared code.
The process for using the DependencyService to invoke native platform functionality is to:
- Create an interface for the native platform functionality, in shared code. For more information, see Create an interface.
- Implement the interface in the required platform projects. For more information, see Implement the interface on each platform.
- Register the platform implementations with the
DependencyService. This enables Xamarin.Forms to locate the platform implementations at runtime. For more information, see Register the platform implementations. - Resolve the platform implementations from shared code, and invoke them. For more information, see Resolve the platform implementations.
The following diagram shows how native platform functionality is invoked in a Xamarin.Forms application:
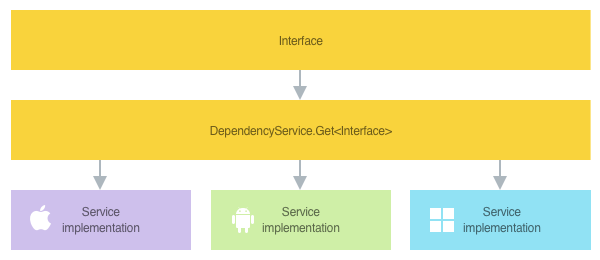
Create an interface
The first step in being able to invoke native platform functionality from shared code, is to create an interface that defines the API for interacting with the native platform functionality. This interface should be placed in your shared code project.
The following example shows an interface for an API that can be used to retrieve the orientation of a device:
public interface IDeviceOrientationService
{
DeviceOrientation GetOrientation();
}
Implement the interface on each platform
After creating the interface that defines the API for interacting with the native platform functionality, the interface must be implemented in each platform project.
iOS
The following code example shows the implementation of the IDeviceOrientationService interface on iOS:
namespace DependencyServiceDemos.iOS
{
public class DeviceOrientationService : IDeviceOrientationService
{
public DeviceOrientation GetOrientation()
{
UIInterfaceOrientation orientation = UIApplication.SharedApplication.StatusBarOrientation;
bool isPortrait = orientation == UIInterfaceOrientation.Portrait ||
orientation == UIInterfaceOrientation.PortraitUpsideDown;
return isPortrait ? DeviceOrientation.Portrait : DeviceOrientation.Landscape;
}
}
}
Android
The following code example shows the implementation of the IDeviceOrientationService interface on Android:
namespace DependencyServiceDemos.Droid
{
public class DeviceOrientationService : IDeviceOrientationService
{
public DeviceOrientation GetOrientation()
{
IWindowManager windowManager = Android.App.Application.Context.GetSystemService(Context.WindowService).JavaCast<IWindowManager>();
SurfaceOrientation orientation = windowManager.DefaultDisplay.Rotation;
bool isLandscape = orientation == SurfaceOrientation.Rotation90 ||
orientation == SurfaceOrientation.Rotation270;
return isLandscape ? DeviceOrientation.Landscape : DeviceOrientation.Portrait;
}
}
}
Universal Windows Platform
The following code example shows the implementation of the IDeviceOrientationService interface on the Universal Windows Platform (UWP):
namespace DependencyServiceDemos.UWP
{
public class DeviceOrientationService : IDeviceOrientationService
{
public DeviceOrientation GetOrientation()
{
ApplicationViewOrientation orientation = ApplicationView.GetForCurrentView().Orientation;
return orientation == ApplicationViewOrientation.Landscape ? DeviceOrientation.Landscape : DeviceOrientation.Portrait;
}
}
}
Register the platform implementations
After implementing the interface in each platform project, the platform implementations must be registered with the DependencyService, so that Xamarin.Forms can locate them at runtime. This is typically performed with the DependencyAttribute, which indicates that the specified type provides an implementation of the interface.
The following example shows using the DependencyAttribute to register the iOS implementation of the IDeviceOrientationService interface:
using Xamarin.Forms;
[assembly: Dependency(typeof(DependencyServiceDemos.iOS.DeviceOrientationService))]
namespace DependencyServiceDemos.iOS
{
public class DeviceOrientationService : IDeviceOrientationService
{
public DeviceOrientation GetOrientation()
{
...
}
}
}
In this example, the DependencyAttribute registers the DeviceOrientationService with the DependencyService. Similarly, the implementations of the IDeviceOrientationService interface on other platforms should be registered with the DependencyAttribute.
For more information about registering platform implementations with the DependencyService, see Xamarin.Forms DependencyService Registration and Resolution.
Resolve the platform implementations
Following registration of platform implementations with the DependencyService, the implementations must be resolved before being invoked. This is typically performed in shared code using the DependencyService.Get<T> method.
The following code shows an example of calling the Get<T> method to resolve the IDeviceOrientationService interface, and then invoking its GetOrientation method:
IDeviceOrientationService service = DependencyService.Get<IDeviceOrientationService>();
DeviceOrientation orientation = service.GetOrientation();
Alternatively, this code can be condensed into a single line:
DeviceOrientation orientation = DependencyService.Get<IDeviceOrientationService>().GetOrientation();
For more information about resolving platform implementations with the DependencyService, see Xamarin.Forms DependencyService Registration and Resolution.