Add a custom endpoint or custom app source to an eventstream
If you want to connect your own application with an eventstream, you can add a custom endpoint or a custom app as a source. Then you can send real-time events to the eventstream from your own application with the connection endpoint exposed on the custom endpoint or custom app. Also, with the Apache Kafka protocol available as an option for custom endpoints or custom apps, you can send real-time events by using the Apache Kafka protocol.
This article shows you how to add a custom endpoint source or a custom app source to an eventstream in Microsoft Fabric event streams.
Note
Enhanced capabilities are enabled by default when you create eventstreams now. If you have eventstreams that were created using standard capabilities, those eventstreams will continue to work. You can still edit and use them as usual. We recommend that you create a new eventstream to replace standard eventstreams so that you can take advantage of additional capabilities and benefits of enhanced eventstreams.
Prerequisites
- Access to a workspace in the Fabric capacity license mode (or) the Trial license mode with Contributor or higher permissions.
- If you don't have an eventstream, create an eventstream.
Add custom endpoint data as a source
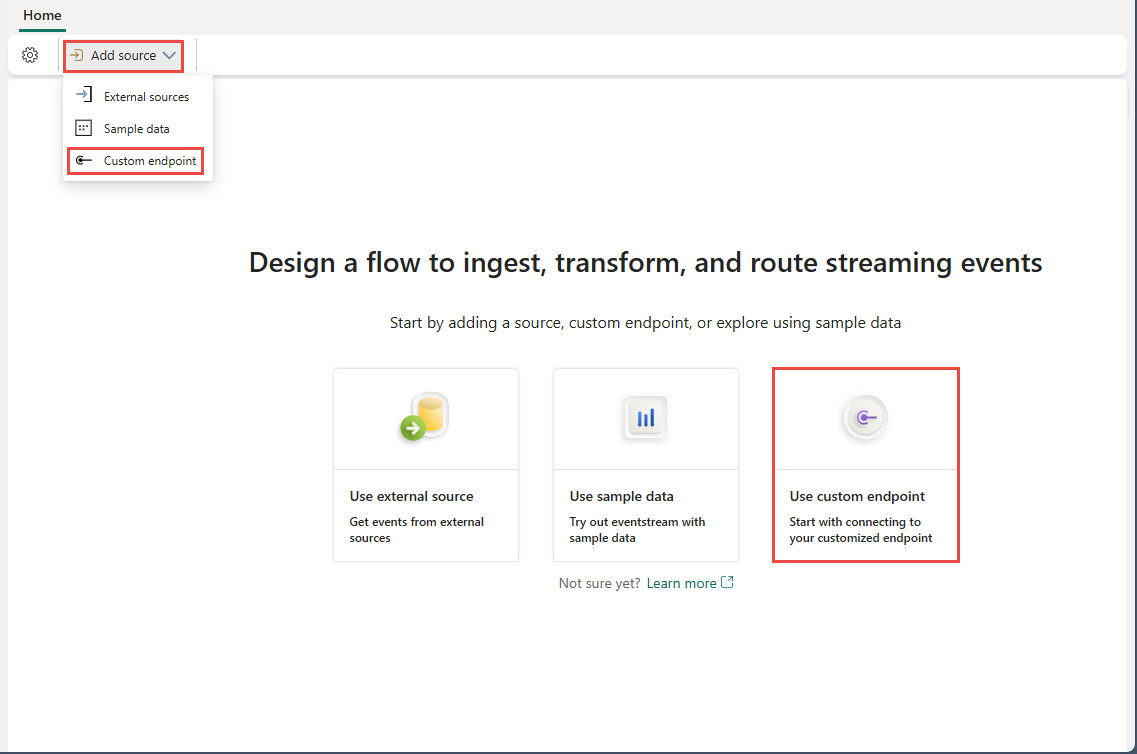
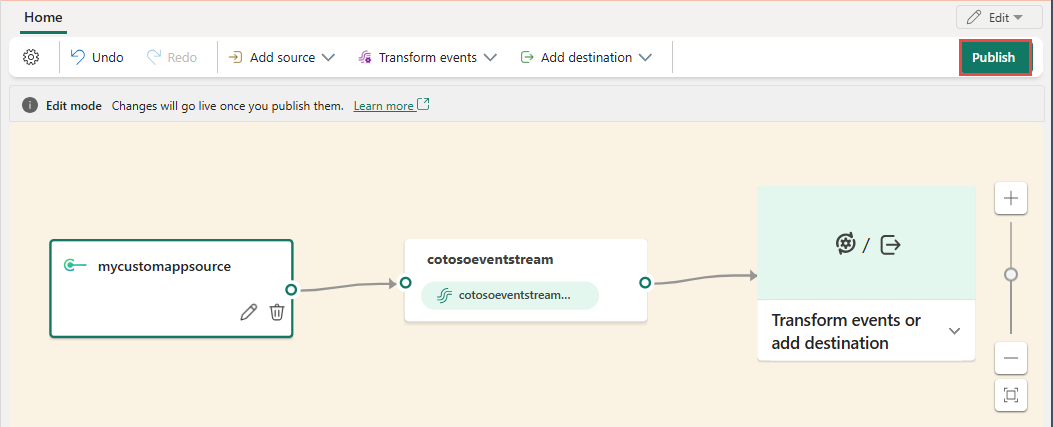
To add a custom endpoint source, on the get-started page, select Use custom endpoint. Or, if you already have a published eventstream and you want to add custom endpoint data as a source, switch to edit mode. On the ribbon, select Add source > Custom endpoint.
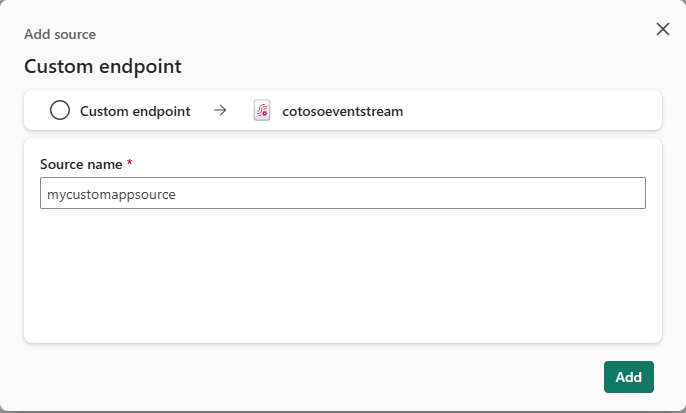
In the Custom endpoint dialog, enter a name for the custom source under Source name, and then select Add.
After you create the custom endpoint source, it's added to your eventstream on the canvas in edit mode. To implement the newly added data from the custom app source, select Publish.
Note
The maximum number of sources and destinations for one eventstream is 11.
Get endpoint details on the Details pane
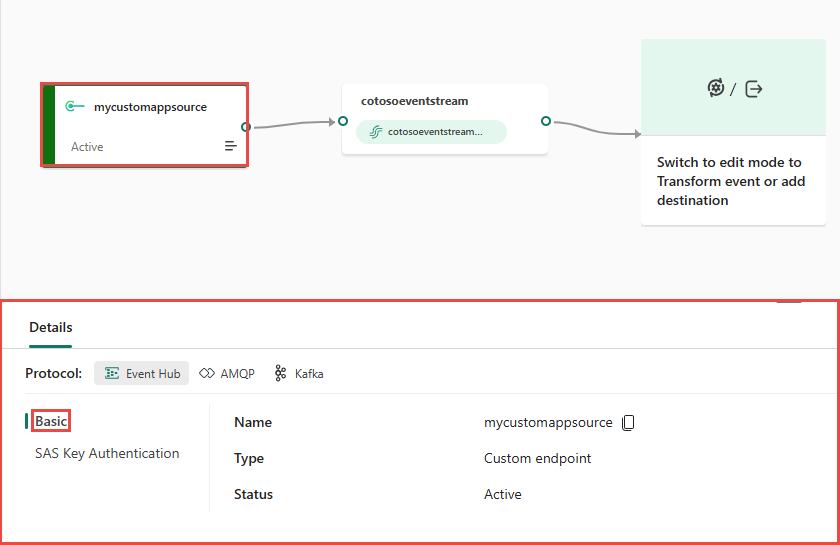
After you create a custom endpoint source, its data is available for visualization in the live view.
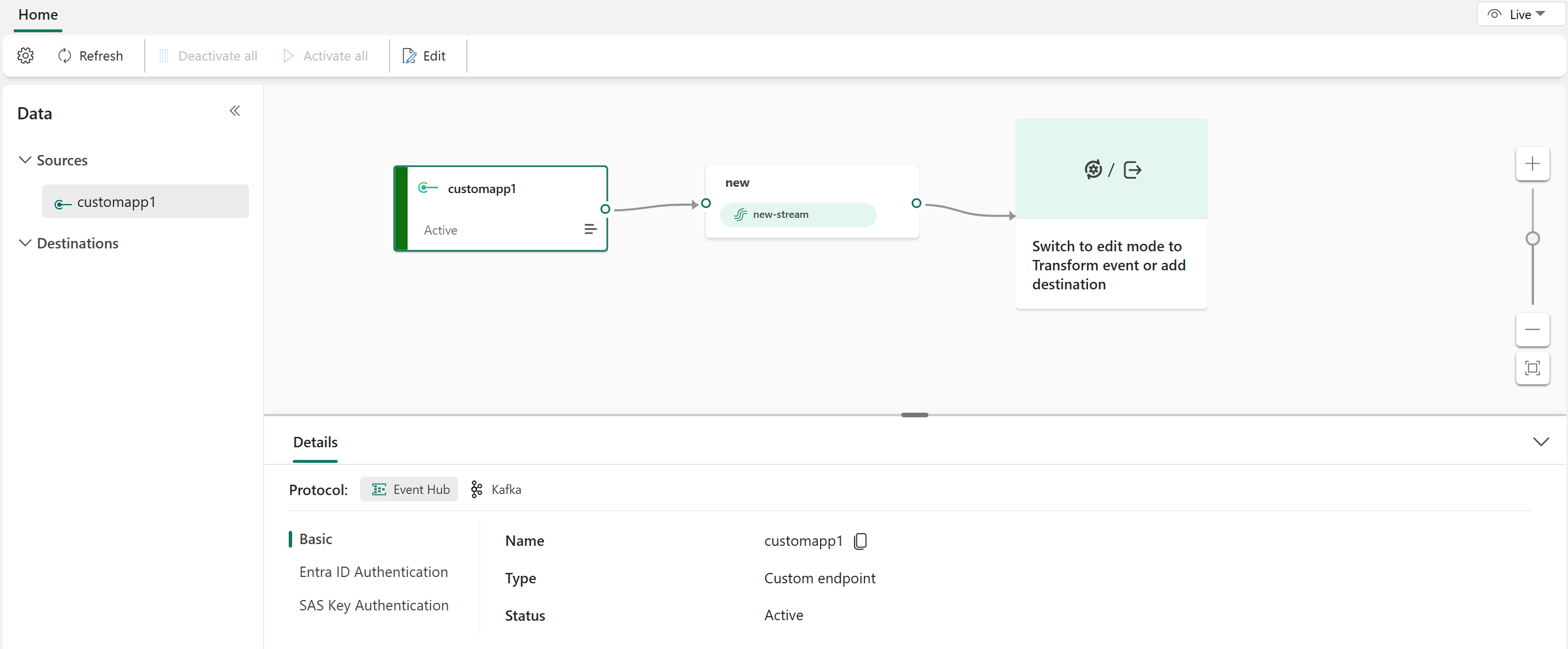
The Details pane has three protocol tabs: Event Hub, AMQP, and Kafka. Each protocol tab has three pages: Basic and SAS Key Authentication. These pages offer the endpoint details with the corresponding protocol for connecting.
Basic shows the name, type, and status of your custom endpoint.
SAS Key Authentication page provides information about connection keys and also a link to the sample code, with the corresponding keys embedded, that you can use to stream the events to your eventstream. The information on the Keys page varies by protocol.
Event hub
The SAS Key Authentication page on the Event Hub tab contains information related to an event hub's connection string. The information includes Event hub name, Shared access key name, Primary key, Secondary key, Connection string-primary key, Connection string-secondary key.
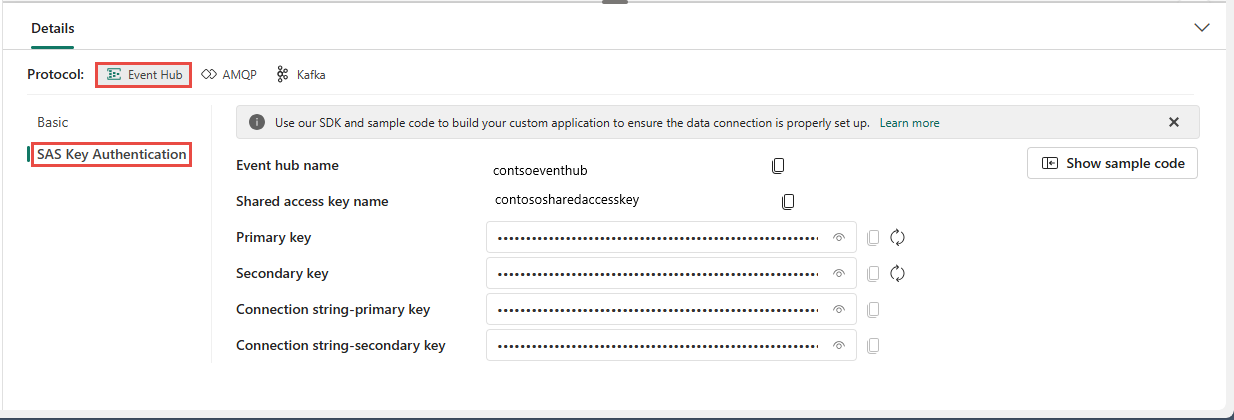
The event hub format is the default for the connection string, and it works with the Azure Event Hubs SDK. This format allows you to connect to your eventstream via the Event Hubs protocol.
The following example shows what the connection string looks like in event hub format:
Endpoint=sb://eventstream-xxxxxxxx.servicebus.windows.net/;SharedAccessKeyName=key_xxxxxxxx;SharedAccessKey=xxxxxxxx;EntityPath=es_xxxxxxx
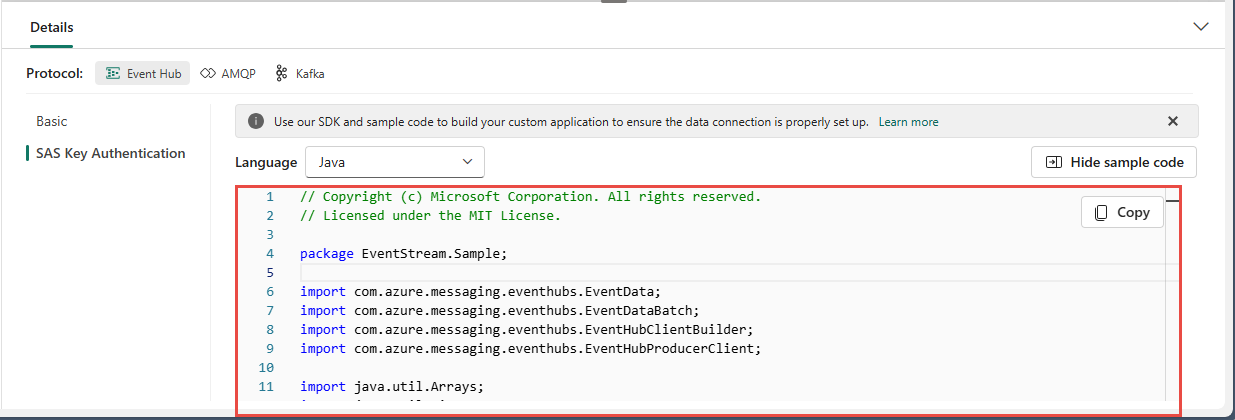
If you select the Show sample code button, you see the ready-to-use Java code that includes the required information about connection keys in the event hub. Copy and paste it into your application for use.
Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP)
The AMQP format is compatible with the AMQP 1.0 protocol, which is a standard messaging protocol that supports interoperability between various platforms and languages. You can use this format to connect to your eventstream by using the AMQP protocol.
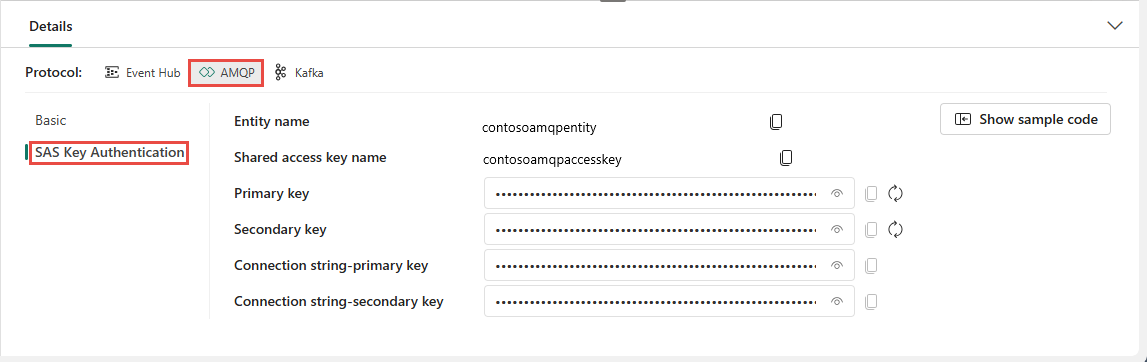
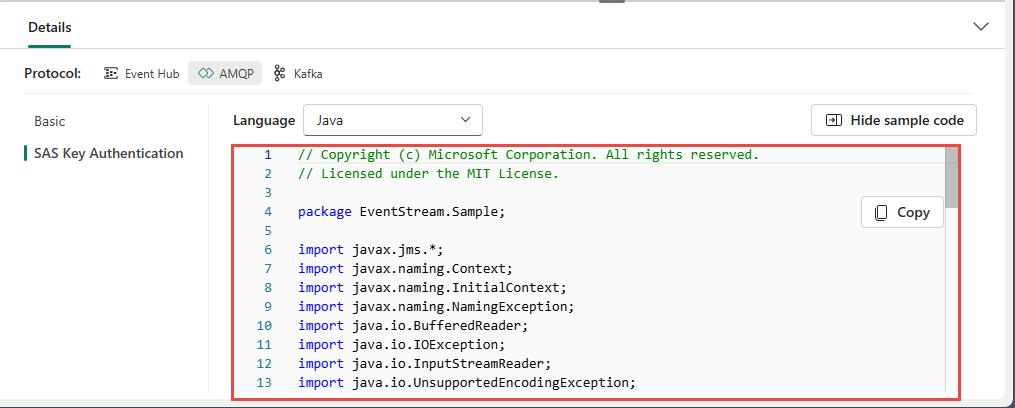
When you select Show sample code button, you see the ready-to-use Java code with connection key information in AMQP format.
Kafka
The Kafka format is compatible with the Apache Kafka protocol, which is a popular distributed streaming platform that supports high-throughput and low-latency data processing. You can use the SAS Key Authentication information for the Kafka protocol format to connect to your eventstream and stream the events.
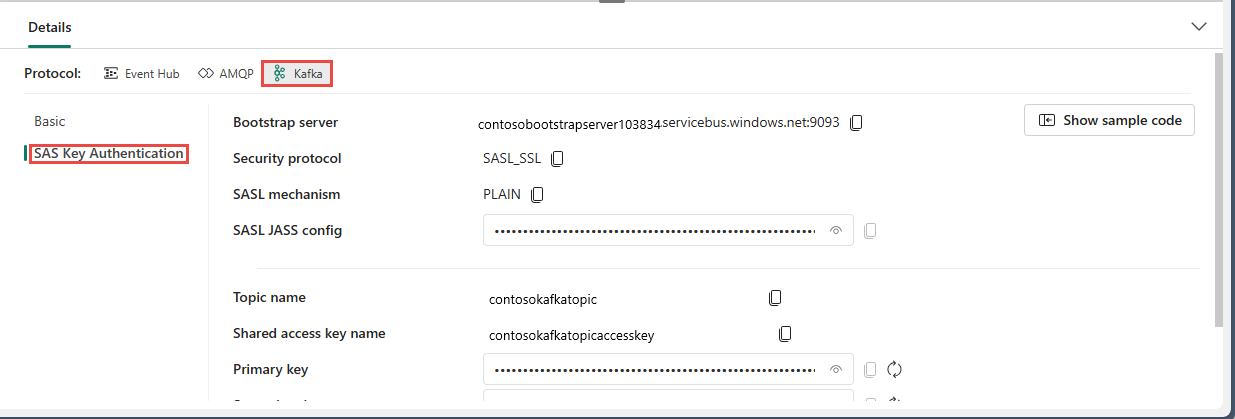
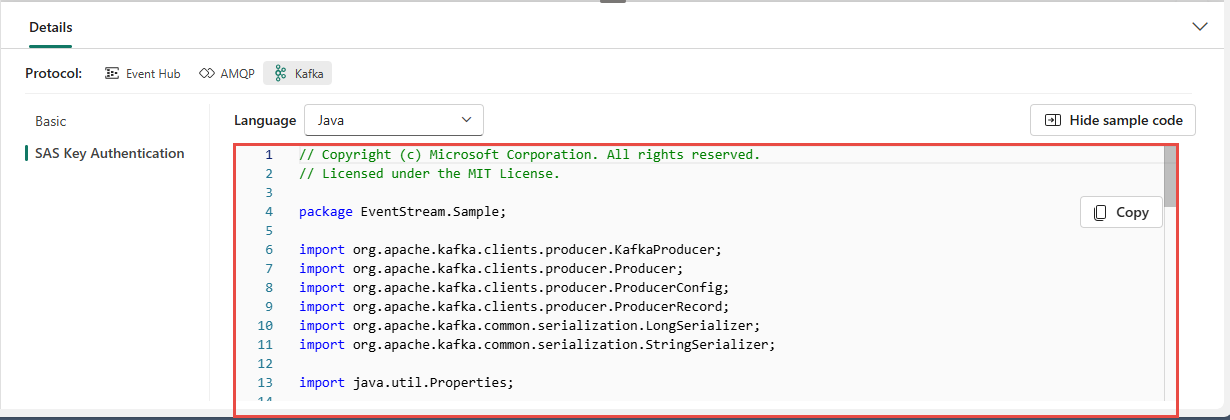
When you select the Show sample code button, you see the ready-to-use Java code, including the necessary connection keys in Kafka format. Copy it for your use.
Note
- You can choose the protocol format that suits your application needs and preferences, and then copy and paste the connection string into your application. You can also refer to or copy the sample code, which shows how to send or receive events by using various protocols.
- To exit out of the sample code view, select Hide sample code.
Related content
For a list of supported sources, see Add an event source in an eventstream
Prerequisites
Before you start, you must get access to a workspace with Contributor or higher permissions where your eventstream is located.
Note
The maximum number of sources and destinations for one eventstream is 11.
Add a custom app as a source
If you want to connect your own application with an eventstream, you can add a custom app source. Then, send data to the eventstream from your own application with the connection endpoint exposed in the custom app.
To add a custom app source:
Select New source on the ribbon or the plus sign (+) in the main editor canvas, and then select Custom App.
On the Custom App pane, enter a source name for the custom app, and then select Add.
Get endpoint details on the Details pane to send events
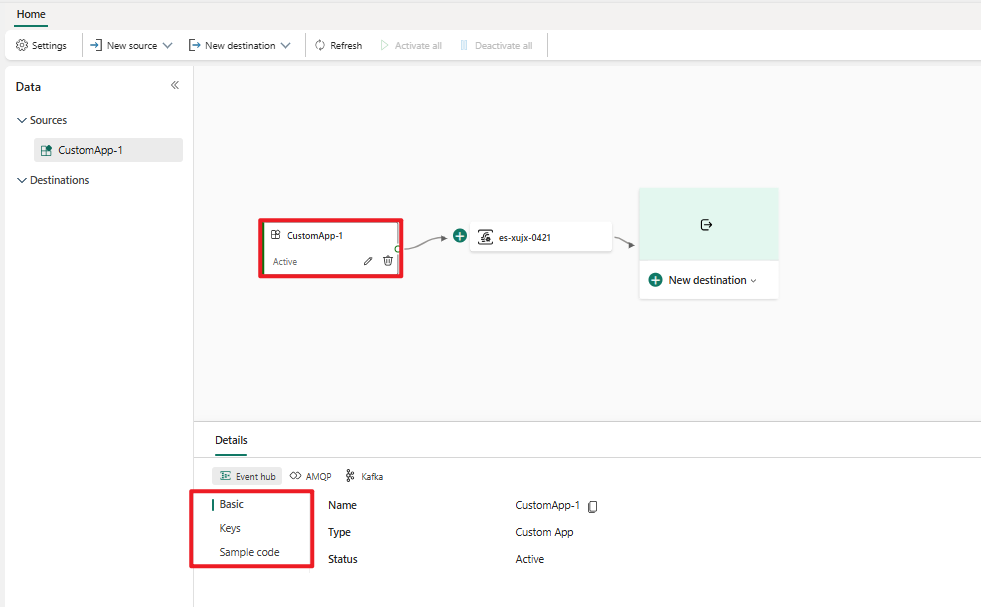
After you successfully create the custom application as a source, you can view the information on the Details pane.
The Details pane has three protocol tabs: Event Hub, AMQP, and Kafka. Each protocol tab has three pages: Basics, Keys, and Sample code. These pages offer the endpoint details with the corresponding protocol for connecting.
Basic shows the name, type, and status of your custom app.
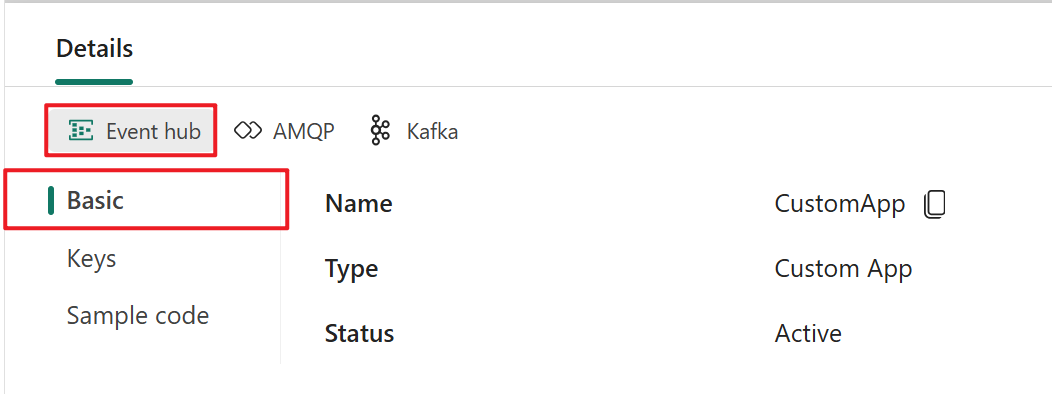
Keys provides information about connection keys. Sample code provides the sample code, with the corresponding keys embedded, that you can use to stream the events to your eventstream. The information on these pages varies by protocol.
Event hub
The Keys page on the Event Hub tab contains information related to an event hub's connection string. The information includes Event hub name, Shared access key name, Primary key, and Connection string-primary key.

The event hub format is the default for the connection string, and it works with the Azure Event Hubs SDK. This format allows you to connect to your eventstream via the Event Hubs protocol.
The following example shows what the connection string looks like in event hub format:
Endpoint=sb://eventstream-xxxxxxxx.servicebus.windows.net/;SharedAccessKeyName=key_xxxxxxxx;SharedAccessKey=xxxxxxxx;EntityPath=es_xxxxxxx
The Sample code page on the Event Hub tab offers ready-to-use code that includes the required information about connection keys in the event hub. Simply copy and paste it into your application for use.

Kafka
The Kafka format is compatible with the Apache Kafka protocol, which is a popular distributed streaming platform that supports high-throughput and low-latency data processing. You can use the Keys and Sample code information for the Kafka protocol format to connect to your eventstream and stream the events.

The Sample code page on the Kafka tab provides ready-made code, including the necessary connection keys in Kafka format. Simply copy it for your use.

AMQP
The AMQP format is compatible with the AMQP 1.0 protocol, which is a standard messaging protocol that supports interoperability between various platforms and languages. You can use this format to connect to your eventstream by using the AMQP protocol.

The Sample code page on the AMQP tab provides ready-to-use code with connection key information in AMQP format.

You can choose the protocol format that suits your application needs and preferences, and then copy and paste the connection string into your application. You can also refer to or copy the sample code on the Sample code page, which shows how to send or receive events by using various protocols.
Related content
To learn how to add other sources to an eventstream, see the following articles: