Create a site-to-site VPN connection - Azure PowerShell
This article shows you how to use PowerShell to create a site-to-site VPN gateway connection from your on-premises network to a virtual network (VNet).
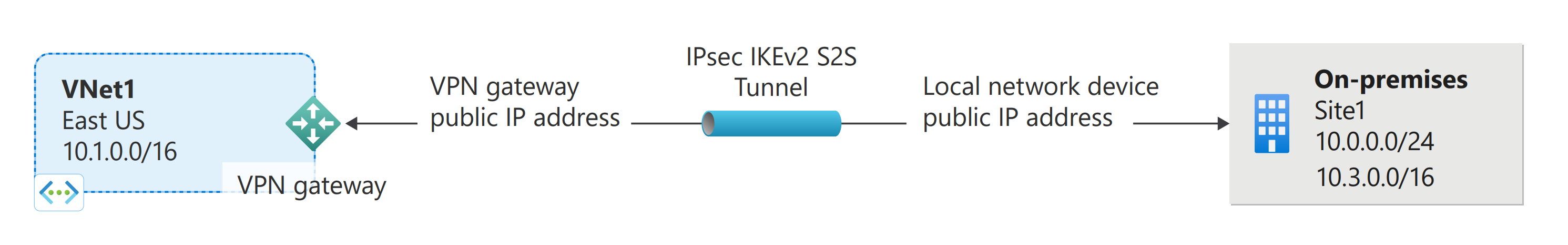
A site-to-site VPN gateway connection is used to connect your on-premises network to an Azure virtual network over an IPsec/IKE (IKEv1 or IKEv2) VPN tunnel. This type of connection requires a VPN device located on-premises that has an externally facing public IP address assigned to it. The steps in this article create a connection between the VPN gateway and the on-premises VPN device using a shared key. For more information about VPN gateways, see About VPN gateway.
Before you begin
Verify that your environment meets the following criteria before beginning configuration:
Verify that you have a functioning route-based VPN gateway. To create a VPN gateway, see Create a VPN gateway.
If you're unfamiliar with the IP address ranges located in your on-premises network configuration, you need to coordinate with someone who can provide those details for you. When you create this configuration, you must specify the IP address range prefixes that Azure routes to your on-premises location. None of the subnets of your on-premises network can overlap with the virtual network subnets that you want to connect to.
VPN devices:
- Make sure you have a compatible VPN device and someone who can configure it. For more information about compatible VPN devices and device configuration, see About VPN devices.
- Determine if your VPN device supports active-active mode gateways. This article creates an active-active mode VPN gateway, which is recommended for highly available connectivity. Active-active mode specifies that both gateway VM instances are active. This mode requires two public IP addresses, one for each gateway VM instance. You configure your VPN device to connect to the IP address for each gateway VM instance.
If your VPN device doesn't support this mode, don't enable this mode for your gateway. For more information, see Design highly available connectivity for cross-premises and VNet-to-VNet connections and About active-active mode VPN gateways.
Azure PowerShell
This article uses PowerShell cmdlets. To run the cmdlets, you can use Azure Cloud Shell. Cloud Shell is a free interactive shell that you can use to run the steps in this article. It has common Azure tools preinstalled and configured to use with your account.
To open Cloud Shell, just select Open Cloudshell from the upper-right corner of a code block. You can also open Cloud Shell on a separate browser tab by going to https://shell.azure.com/powershell. Select Copy to copy the blocks of code, paste them into Cloud Shell, and select the Enter key to run them.
You can also install and run the Azure PowerShell cmdlets locally on your computer. PowerShell cmdlets are updated frequently. If you haven't installed the latest version, the values specified in the instructions may fail. To find the versions of Azure PowerShell installed on your computer, use the Get-Module -ListAvailable Az cmdlet. To install or update, see Install the Azure PowerShell module.
Create a local network gateway
The local network gateway (LNG) typically refers to your on-premises location. It isn't the same as a virtual network gateway. You give the site a name by which Azure can refer to it, then specify the IP address of the on-premises VPN device to which you'll create a connection. You also specify the IP address prefixes that are routed through the VPN gateway to the VPN device. The address prefixes you specify are the prefixes located on your on-premises network. If your on-premises network changes, you can easily update the prefixes.
Select one of the following examples. The values used in the examples are:
- The GatewayIPAddress is the IP address of your on-premises VPN device, not your Azure VPN gateway.
- The AddressPrefix is your on-premises address space.
Single address prefix example
New-AzLocalNetworkGateway -Name Site1 -ResourceGroupName TestRG1 `
-Location 'East US' -GatewayIpAddress '[IP address of your on-premises VPN device]' -AddressPrefix '10.0.0.0/24'
Multiple address prefix example
New-AzLocalNetworkGateway -Name Site1 -ResourceGroupName TestRG1 `
-Location 'East US' -GatewayIpAddress '[IP address of your on-premises VPN device]' -AddressPrefix @('10.3.0.0/16','10.0.0.0/24')
Configure your VPN device
Site-to-site connections to an on-premises network require a VPN device. In this step, you configure your VPN device. When configuring your VPN device, you need the following items:
Shared key: This shared key is the same one that you specify when you create your site-to-site VPN connection. In our examples, we use a simple shared key. We recommend that you generate a more complex key to use.
Public IP addresses of your virtual network gateway instances: Obtain the IP address for each VM instance. If your gateway is in active-active mode, you'll have an IP address for each gateway VM instance. Be sure to configure your device with both IP addresses, one for each active gateway VM. Active-standby mode gateways have only one IP address. In the example, VNet1GWpip1 is the name of the public IP address resource.
Get-AzPublicIpAddress -Name VNet1GWpip1 -ResourceGroupName TestRG1
Depending on the VPN device that you have, you might be able to download a VPN device configuration script. For more information, see Download VPN device configuration scripts.
The following links provide more configuration information:
For information about compatible VPN devices, see About VPN devices.
Before you configure your VPN device, check for any known device compatibility issues.
For links to device configuration settings, see Validated VPN devices. We provide the device configuration links on a best-effort basis, but it's always best to check with your device manufacturer for the latest configuration information.
The list shows the versions that we tested. If the OS version for your VPN device isn't on the list, it still might be compatible. Check with your device manufacturer.
For basic information about VPN device configuration, see Overview of partner VPN device configurations.
For information about editing device configuration samples, see Editing samples.
For cryptographic requirements, see About cryptographic requirements and Azure VPN gateways.
For information about parameters that you need to complete your configuration, see Default IPsec/IKE parameters. The information includes IKE version, Diffie-Hellman (DH) group, authentication method, encryption and hashing algorithms, security association (SA) lifetime, perfect forward secrecy (PFS), and Dead Peer Detection (DPD).
For IPsec/IKE policy configuration steps, see Configure custom IPsec/IKE connection policies for S2S VPN and VNet-to-VNet.
To connect multiple policy-based VPN devices, see Connect a VPN gateway to multiple on-premises policy-based VPN devices.
Create the VPN connection
Create a site-to-site VPN connection between your virtual network gateway and your on-premises VPN device. If you're using an active-active mode gateway (recommended), each gateway VM instance has a separate IP address. To properly configure highly available connectivity, you must establish a tunnel between each VM instance and your VPN device. Both tunnels are part of the same connection.
The shared key must match the value you used for your VPN device configuration. Notice that the '-ConnectionType' for site-to-site is IPsec.
Set the variables.
$gateway1 = Get-AzVirtualNetworkGateway -Name VNet1GW -ResourceGroupName TestRG1 $local = Get-AzLocalNetworkGateway -Name Site1 -ResourceGroupName TestRG1Create the connection.
New-AzVirtualNetworkGatewayConnection -Name VNet1toSite1 -ResourceGroupName TestRG1 ` -Location 'East US' -VirtualNetworkGateway1 $gateway1 -LocalNetworkGateway2 $local ` -ConnectionType IPsec -SharedKey 'abc123'
Verify the VPN connection
There are a few different ways to verify your VPN connection.
You can verify that your connection succeeded by using the 'Get-AzVirtualNetworkGatewayConnection' cmdlet, with or without '-Debug'.
Use the following cmdlet example, configuring the values to match your own. If prompted, select 'A' in order to run 'All'. In the example, '-Name' refers to the name of the connection that you want to test.
Get-AzVirtualNetworkGatewayConnection -Name VNet1toSite1 -ResourceGroupName TestRG1After the cmdlet has finished, view the values. In the example below, the connection status shows as 'Connected' and you can see ingress and egress bytes.
"connectionStatus": "Connected", "ingressBytesTransferred": 33509044, "egressBytesTransferred": 4142431
To modify IP address prefixes for a local network gateway
If the IP address prefixes that you want routed to your on-premises location change, you can modify the local network gateway. When using these examples, modify the values to match your environment.
To add more address prefixes:
Set the variable for the LocalNetworkGateway.
$local = Get-AzLocalNetworkGateway -Name Site1 -ResourceGroupName TestRG1Modify the prefixes. The values you specify overwrite the previous values.
Set-AzLocalNetworkGateway -LocalNetworkGateway $local ` -AddressPrefix @('10.101.0.0/24','10.101.1.0/24','10.101.2.0/24')
To remove address prefixes:
Leave out the prefixes that you no longer need. In this example, we no longer need prefix 10.101.2.0/24 (from the previous example), so we update the local network gateway and exclude that prefix.
Set the variable for the LocalNetworkGateway.
$local = Get-AzLocalNetworkGateway -Name Site1 -ResourceGroupName TestRG1Set the gateway with the updated prefixes.
Set-AzLocalNetworkGateway -LocalNetworkGateway $local ` -AddressPrefix @('10.101.0.0/24','10.101.1.0/24')
To modify the gateway IP address for a local network gateway
If you change the public IP address for your VPN device, you need to modify the local network gateway with the updated IP address. When modifying this value, you can also modify the address prefixes at the same time. When modifying, be sure to use the existing name of your local network gateway. If you use a different name, you create a new local network gateway, instead of overwriting the existing gateway information.
New-AzLocalNetworkGateway -Name Site1 `
-Location "East US" -AddressPrefix @('10.101.0.0/24','10.101.1.0/24') `
-GatewayIpAddress "5.4.3.2" -ResourceGroupName TestRG1
To delete a gateway connection
If you don't know the name of your connection, you can find it by using the 'Get-AzVirtualNetworkGatewayConnection' cmdlet.
Remove-AzVirtualNetworkGatewayConnection -Name VNet1toSite1 `
-ResourceGroupName TestRG1
Next steps
- Once your connection is complete, you can add virtual machines to your virtual networks. For more information, see Virtual Machines.
- For information about BGP, see the BGP Overview and How to configure BGP.
- For information about creating a site-to-site VPN connection using Azure Resource Manager template, see Create a site-to-site VPN Connection.
- For information about creating a vnet-to-vnet VPN connection using Azure Resource Manager template, see Deploy HBase geo replication.