Capture data from Event Hubs in Parquet format
This article explains how to use the no code editor to automatically capture streaming data in Event Hubs in an Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 account in the Parquet format.
Prerequisites
An Azure Event Hubs namespace with an event hub and an Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 account with a container to store the captured data. These resources must be publicly accessible and can't be behind a firewall or secured in an Azure virtual network.
If you don't have an event hub, create one by following instructions from Quickstart: Create an event hub.
If you don't have a Data Lake Storage Gen2 account, create one by following instructions from Create a storage account
The data in your Event Hubs instance (event hub) must be serialized in either JSON, CSV, or Avro format. On the Event Hubs Instance page for your event hub, follow these steps:
Configure a job to capture data
Use the following steps to configure a Stream Analytics job to capture data in Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2.
In the Azure portal, navigate to your event hub.
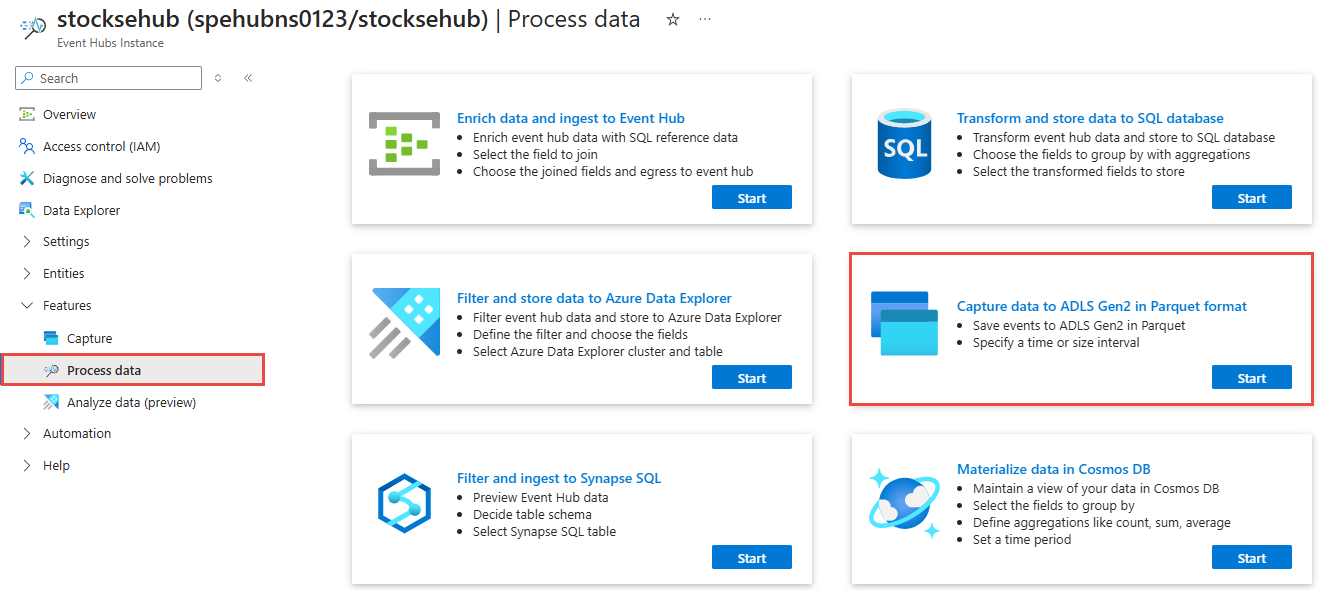
On the left menu, select Process Data under Features. Then, select Start on the Capture data to ADLS Gen2 in Parquet format card.
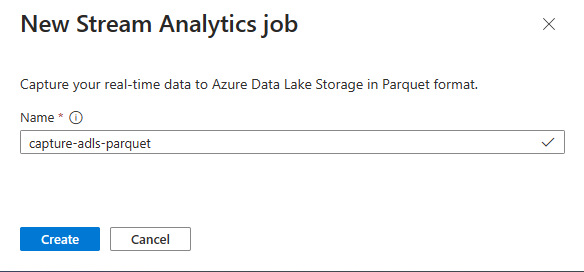
Enter a name for your Stream Analytics job, and then select Create.
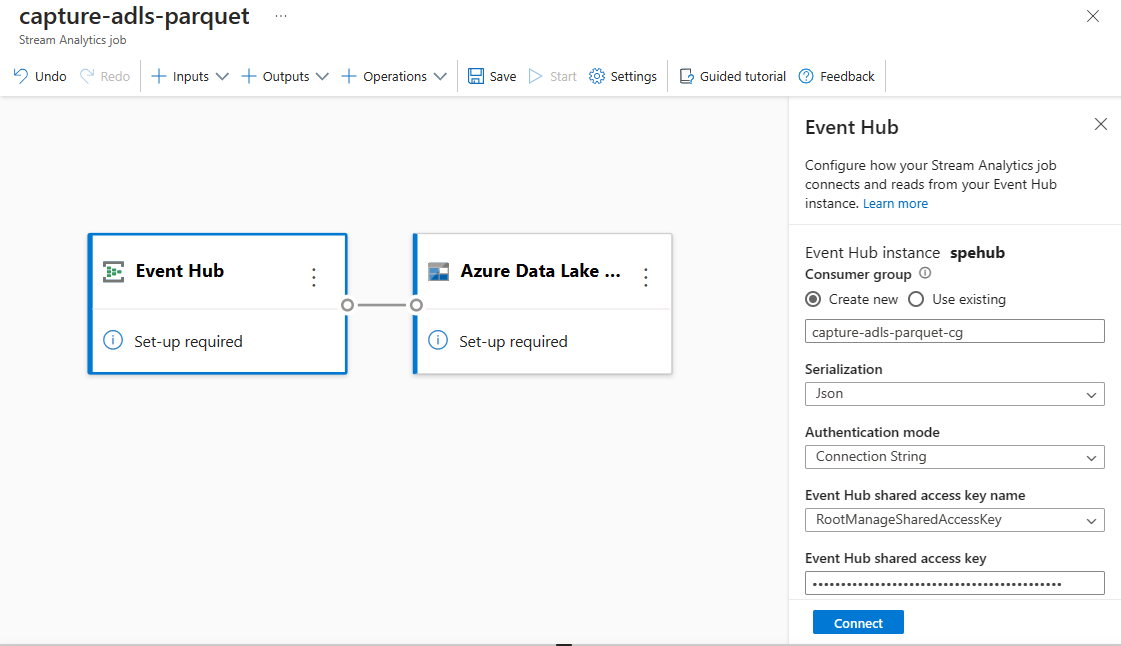
Specify the Serialization type of your data in the Event Hubs and the Authentication method that the job uses to connect to Event Hubs. For this tutorial, keep the default settings. Then select Connect.
When the connection is established successfully, you see:
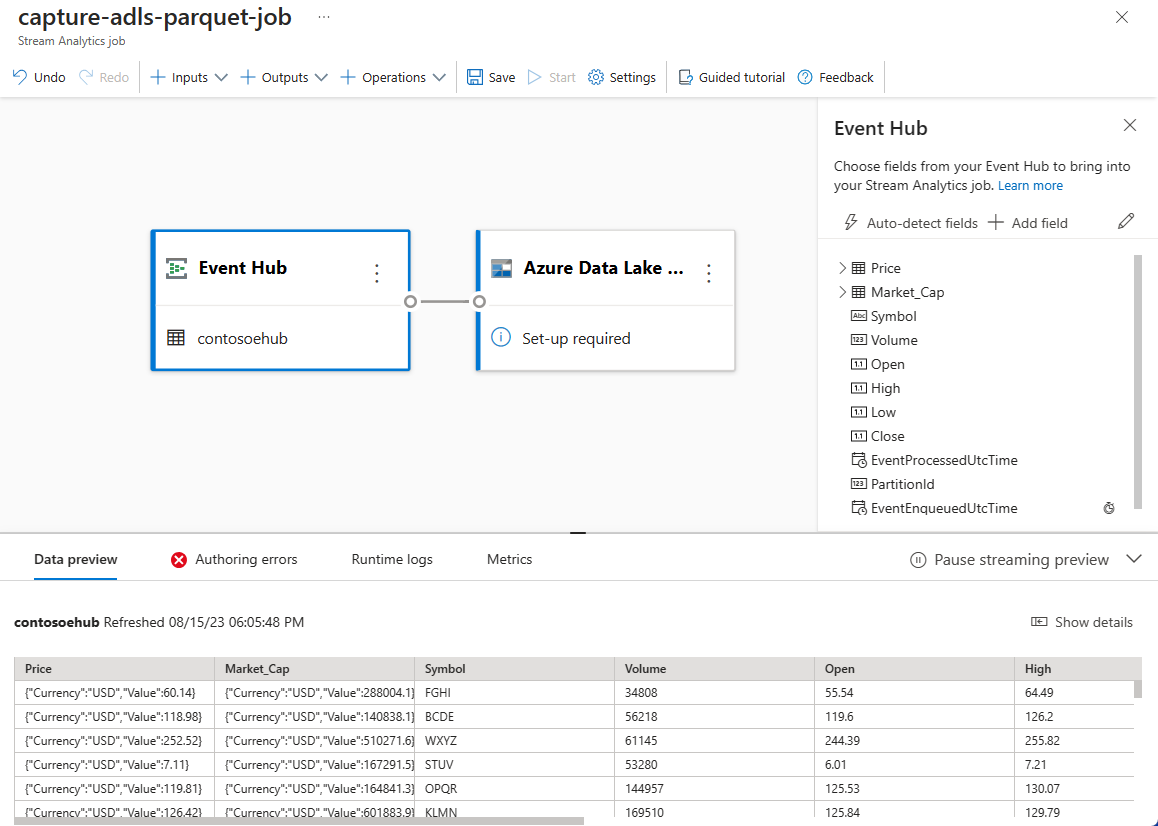
Fields that are present in the input data. You can choose Add field or you can select the three dot symbol next to a field to optionally remove, rename, or change its name.
A live sample of incoming data in the Data preview table under the diagram view. It refreshes periodically. You can select Pause streaming preview to view a static view of the sample input.
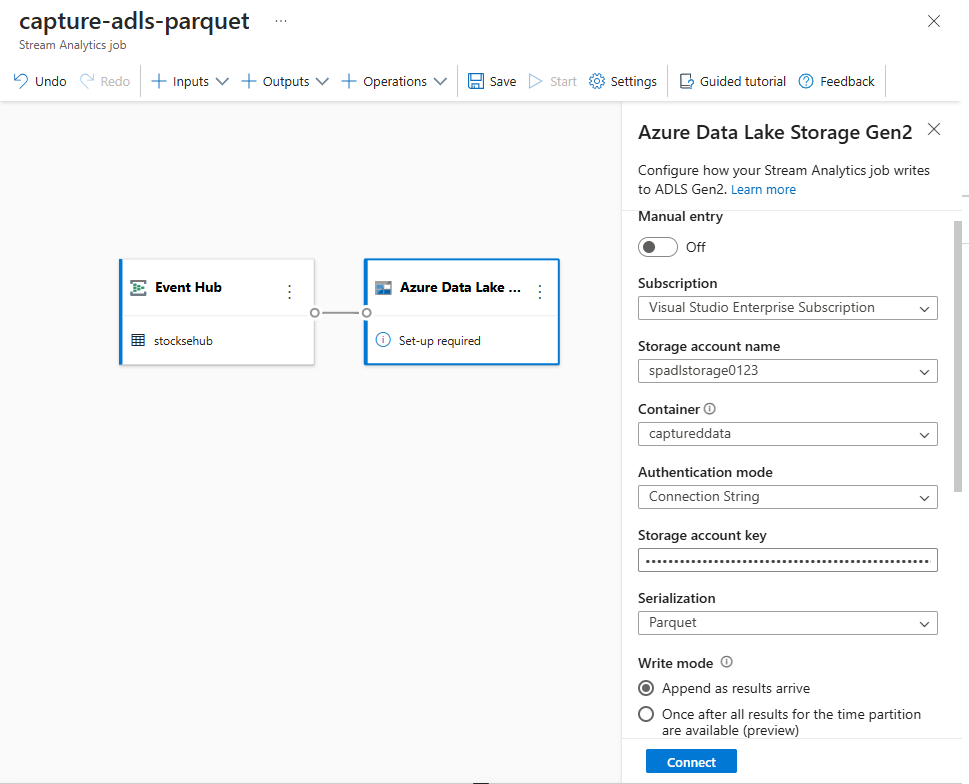
Select the Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 tile to edit the configuration.
On the Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 configuration page, follow these steps:
Select the subscription, storage account name, and container from the drop-down menu.
Once the subscription is selected, the authentication method and storage account key should be automatically filled in.
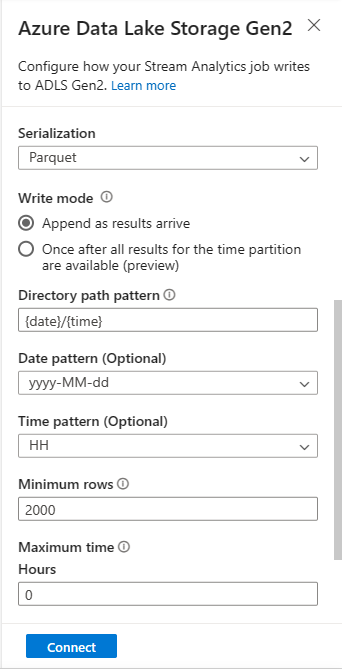
Select Parquet for Serialization format.
For streaming blobs, the directory path pattern is expected to be a dynamic value. It's required for the date to be a part of the file path for the blob – referenced as
{date}. To learn about custom path patterns, see to Azure Stream Analytics custom blob output partitioning.Select Connect
When the connection is established, you see fields that are present in the output data.
Select Save on the command bar to save your configuration.
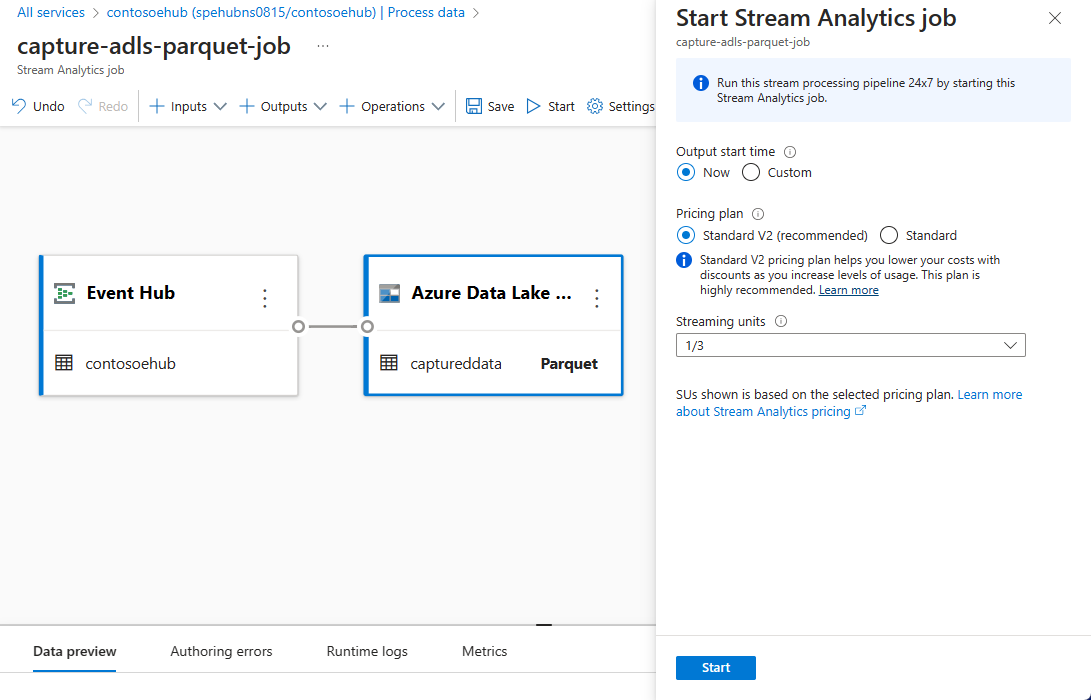
Select Start on the command bar to start the streaming flow to capture data. Then in the Start Stream Analytics job window:
Choose the output start time.
Select the pricing plan.
Select the number of Streaming Units (SU) that the job runs with. SU represents the computing resources that are allocated to execute a Stream Analytics job. For more information, see Streaming Units in Azure Stream Analytics.
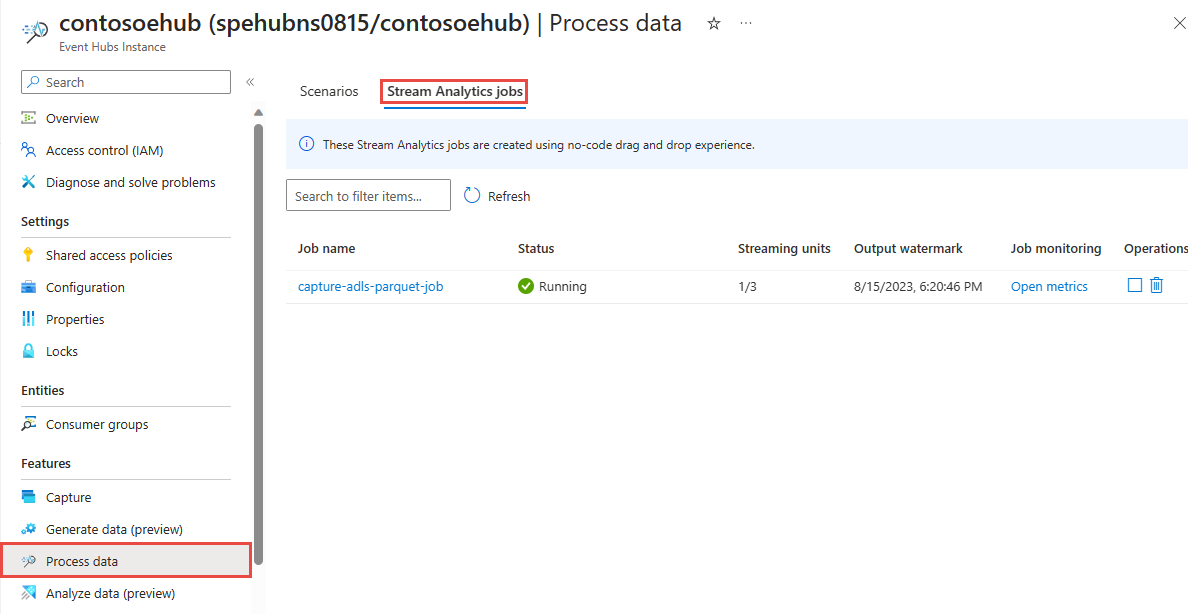
You should see the Stream Analytic job in the Stream Analytics job tab of the Process data page for your event hub.
Verify output
On the Event Hubs instance page for your event hub, follow these steps:
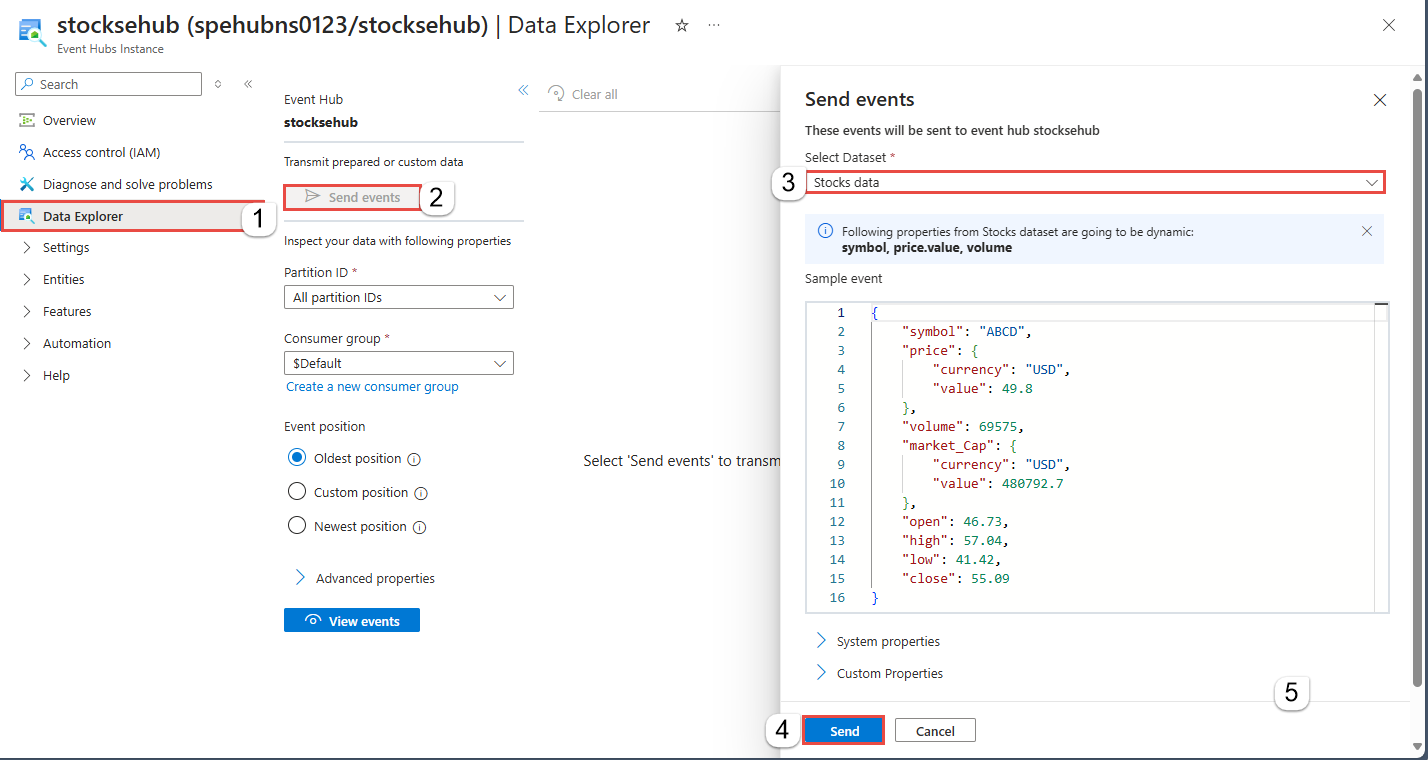
- On the left menu, select Data Explorer.
- In the middle pane, select Send events.
- In the Send events pane, for Select dataset, select Stocks data.
- Select Send.
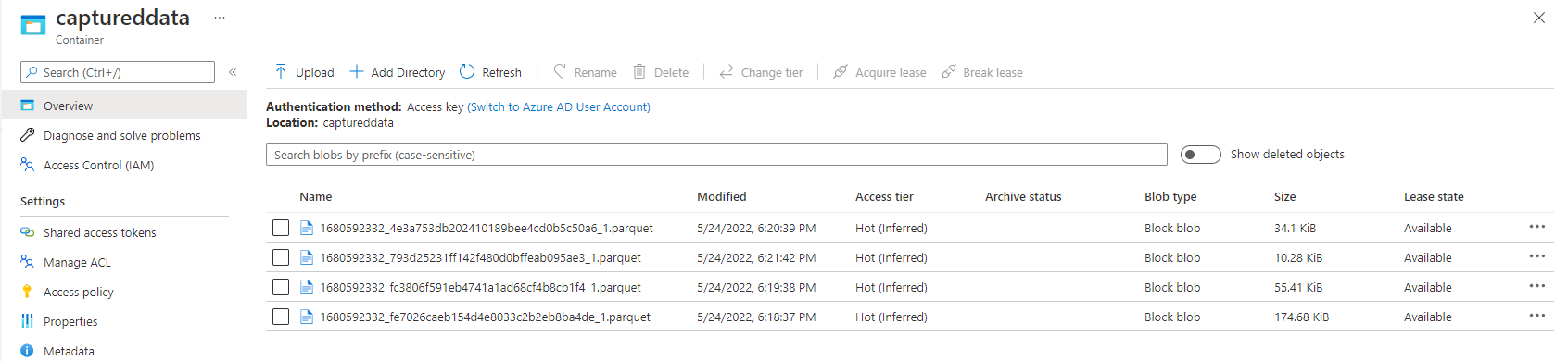
Verify that the Parquet files are generated in the Azure Data Lake Storage container.
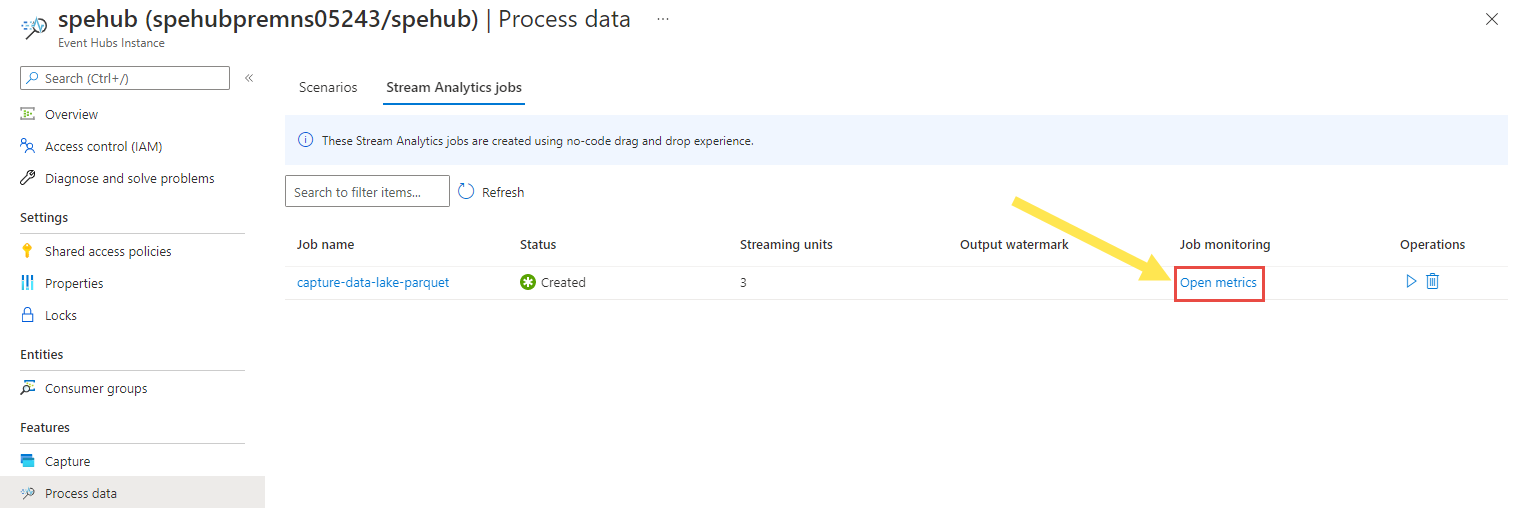
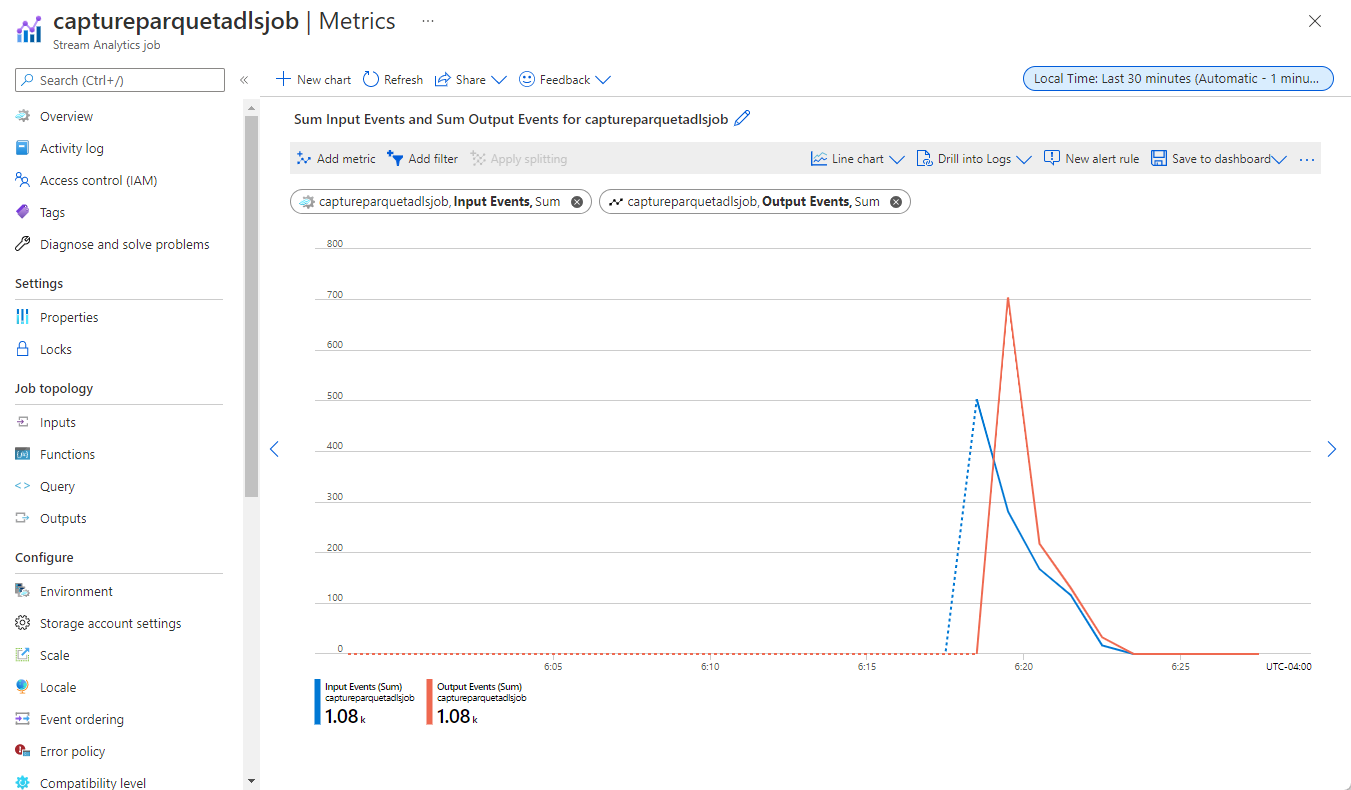
Back on the Event Hubs instance page, select Process data on the left menu. Switch to the Stream Analytics jobs tab. Select Open metrics to monitor it. Add Input metrics to the chart using the Add metric on the toolbar. If you don't see the metrics in the chart, wait for a few minutes, and refresh the page.
Here's an example screenshot of metrics showing input and output events.
Considerations when using the Event Hubs Geo-replication feature
Azure Event Hubs recently launched the Geo-Replication feature in public preview. This feature is different from the Geo Disaster Recovery feature of Azure Event Hubs.
When the failover type is Forced and replication consistency is Asynchronous, Stream Analytics job doesn't guarantee exactly once output to an Azure Event Hubs output.
Azure Stream Analytics, as producer with an event hub an output, might observe watermark delay on the job during failover duration and during throttling by Event Hubs in case replication lag between primary and secondary reaches the maximum configured lag.
Azure Stream Analytics, as consumer with Event Hubs as Input, might observe watermark delay on the job during failover duration and might skip data or find duplicate data after failover is complete.
Due to these caveats, we recommend that you restart the Stream Analytics job with appropriate start time right after Event Hubs failover is complete. Also, since Event Hubs Geo-replication feature is in public preview, we don't recommend using this pattern for production Stream Analytics jobs at this point. The current Stream Analytics behavior will improve before the Event Hubs Geo-replication feature is generally available and can be used in Stream Analytics production jobs.
Related content
Now you know how to use the Stream Analytics no code editor to create a job that captures Event Hubs data to Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 in Parquet format. Next, you can learn more about Azure Stream Analytics and how to monitor the job that you created.