Enable Azure Arc on Kubernetes cluster on your Azure Stack Edge Pro GPU device
APPLIES TO:  Azure Stack Edge Pro - GPU
Azure Stack Edge Pro - GPU Azure Stack Edge Pro 2
Azure Stack Edge Pro 2 Azure Stack Edge Pro R
Azure Stack Edge Pro R Azure Stack Edge Mini R
Azure Stack Edge Mini R
This article shows you how to enable Azure Arc on an existing Kubernetes cluster on your Azure Stack Edge Pro device.
This procedure assumes that you have read and understood the following articles:
Prerequisites
Make sure that you've completed the following prerequisites on your Azure Stack Edge Pro device and the client that you use to access the device:
For device
You have sign-in credentials to a 1-node Azure Stack Edge Pro device.
- The device is activated. See Activate the device.
- The device has the compute role configured via Azure portal and has a Kubernetes cluster. See Configure compute.
You've owner access to the subscription. You would need this access during the role assignment step for your service principal.
For client accessing the device
You have a Windows client system that is used to access the Azure Stack Edge Pro device.
The client is running Windows PowerShell 5.0 or later. To download the latest version of Windows PowerShell, go to Install Windows PowerShell.
You can have any other client with a Supported operating system as well. This article describes the procedure when using a Windows client.
You've completed the procedure described in Access the Kubernetes cluster on Azure Stack Edge Pro device. You have:
- Installed
kubectlon the client. - Make sure that the
kubectlclient version is skewed no more than one version from the Kubernetes master version running on your Azure Stack Edge Pro device.Use
kubectl versionto check the version of kubectl running on the client. Make a note of the full version.In the local UI of your Azure Stack Edge Pro device, go to Software update and note the Kubernetes server version number.
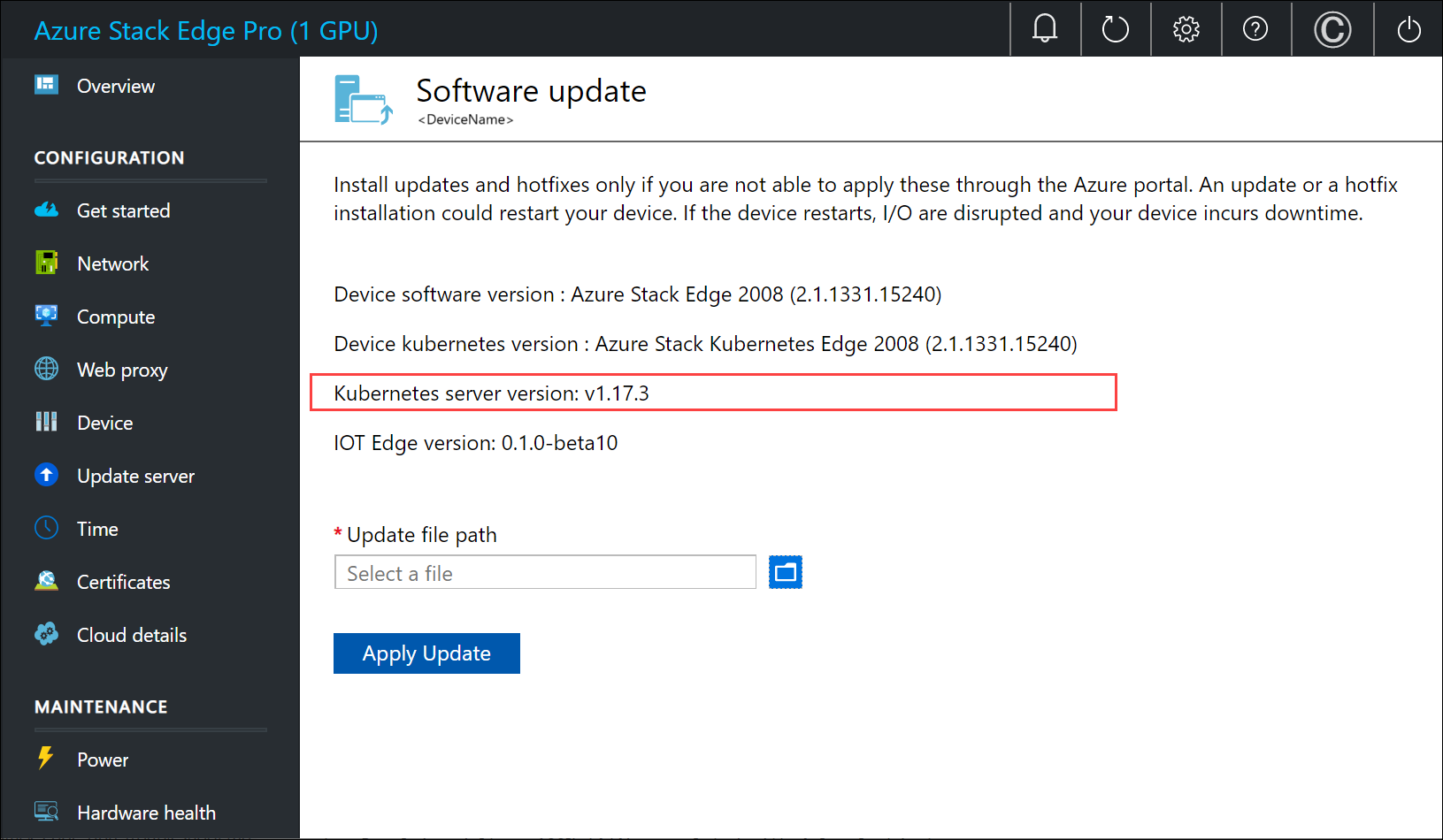
Verify these two versions are compatible.
- Installed
Register Kubernetes resource providers
Before you enable Azure Arc on the Kubernetes cluster, you need to enable and register Microsoft.Kubernetes and Microsoft.KubernetesConfiguration against your subscription.
To enable a resource provider, in the Azure portal, go to the subscription that you're planning to use for the deployment. Go to Resource Providers.
In the right-pane, search for the providers you want to add. In this example,
Microsoft.KubernetesandMicrosoft.KubernetesConfiguration.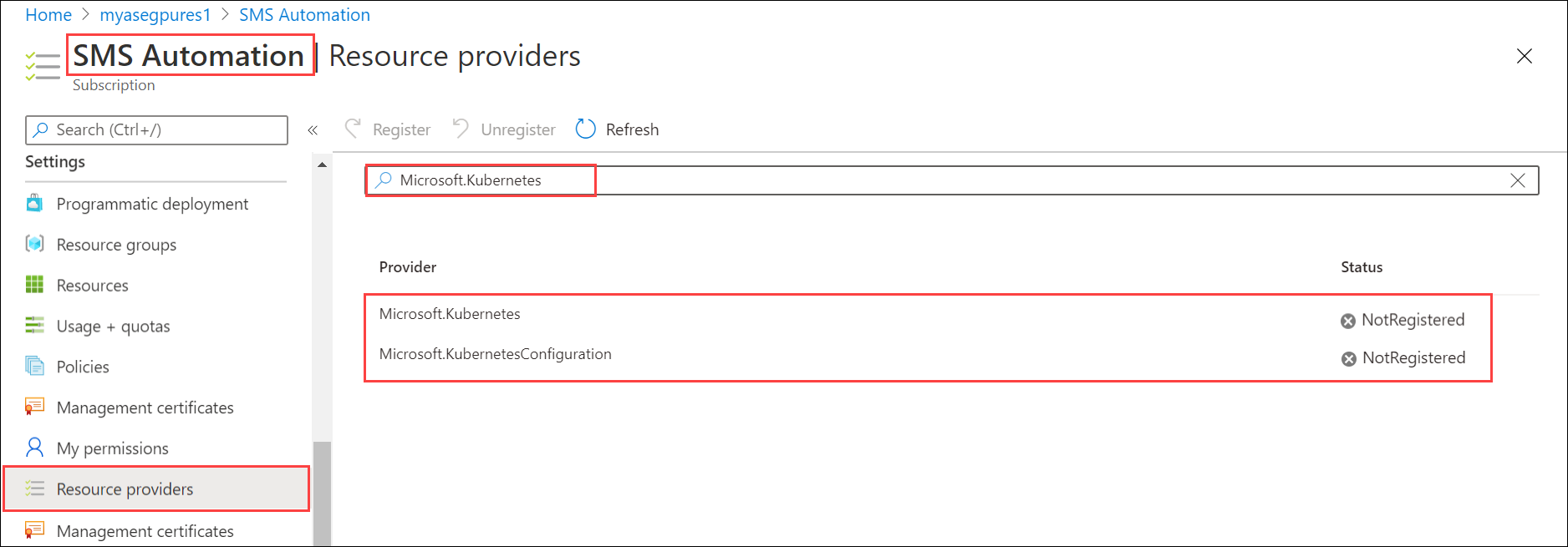
Select a resource provider and from the top of the command bar, select Register. Registration takes several minutes.
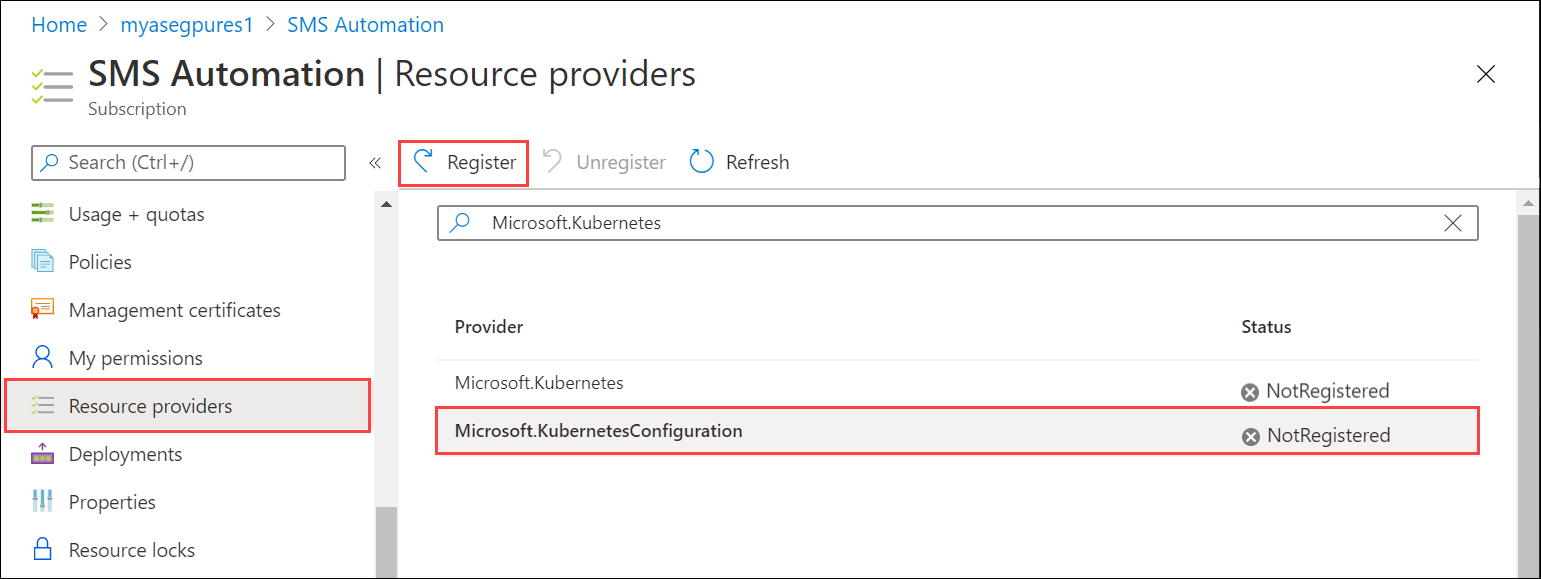
Refresh the UI until you see that the resource provider is registered. Repeat the process for both resource providers.
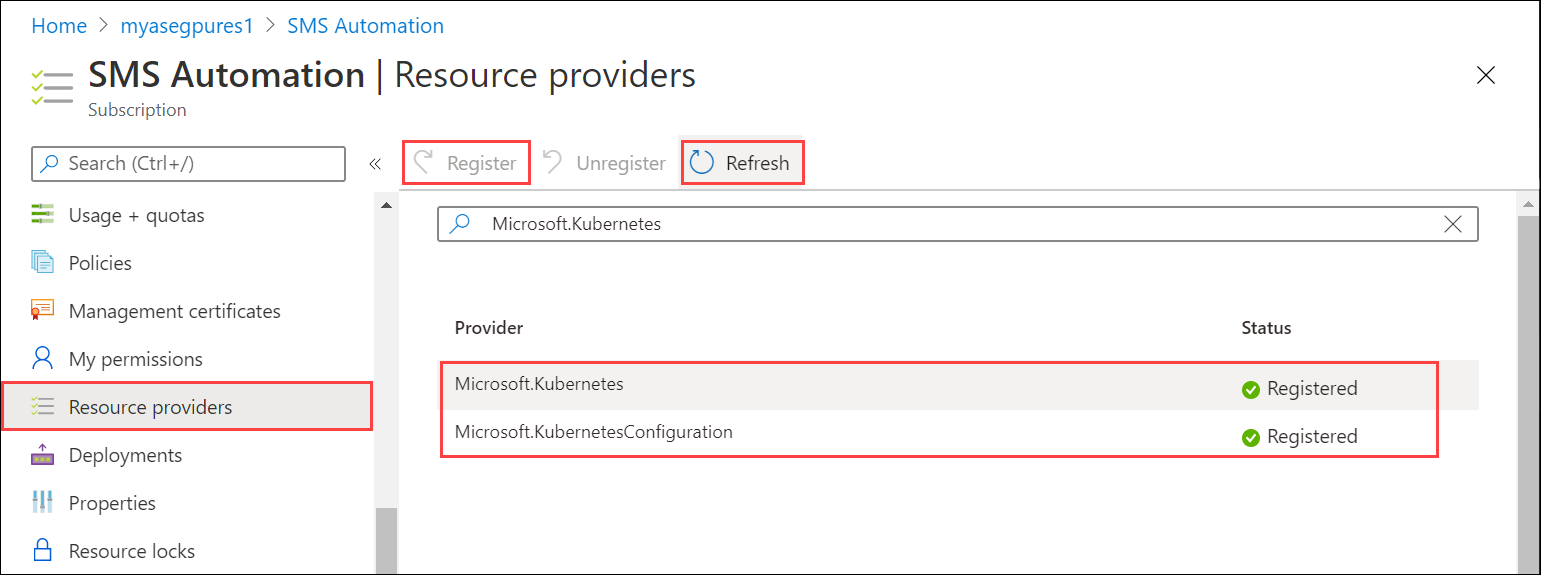
You can also register resource providers via the az cli. For more information, see Register the two providers for Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes.
Create service principal, assign role
Make sure that you have
Subscription IDand the name of the resource group you used for the resource deployment for your Azure Stack Edge service. To get the subscription ID, go to your Azure Stack Edge resource in the Azure portal. Navigate to Overview > Essentials.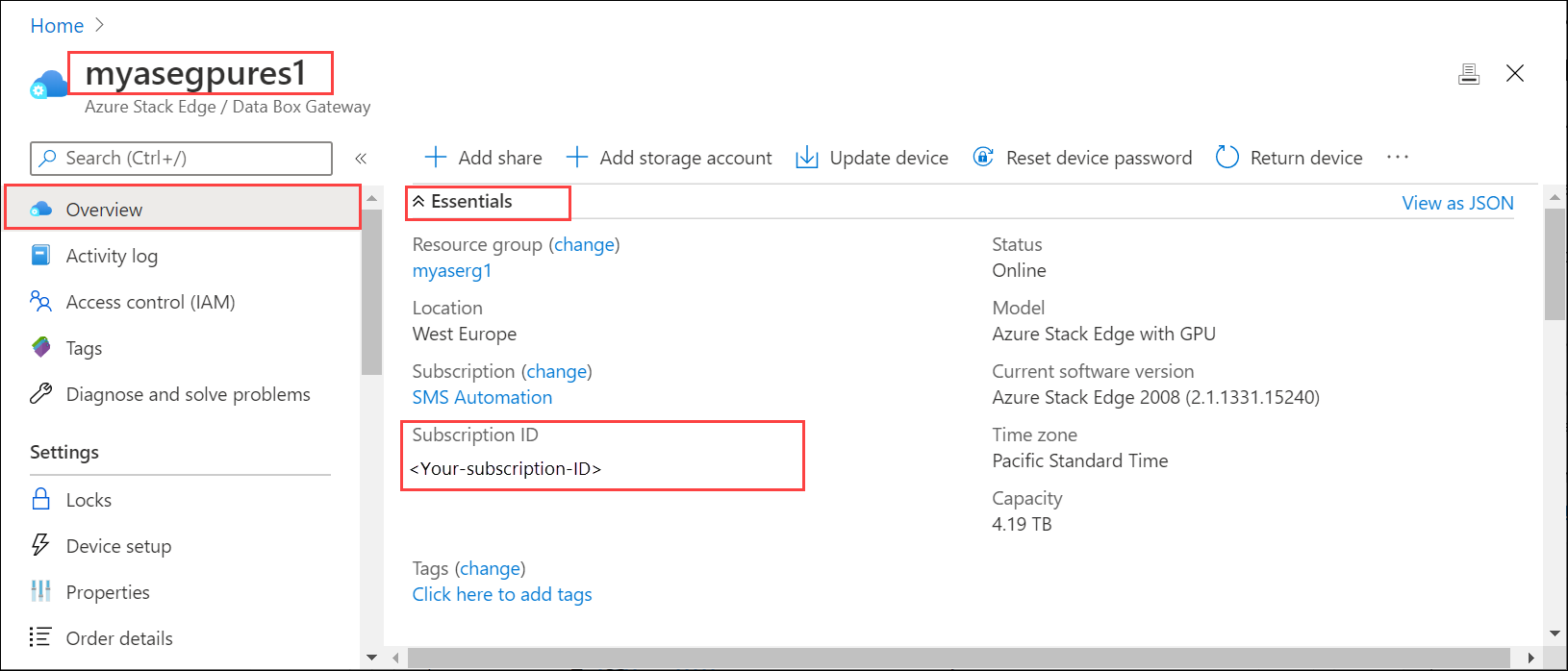
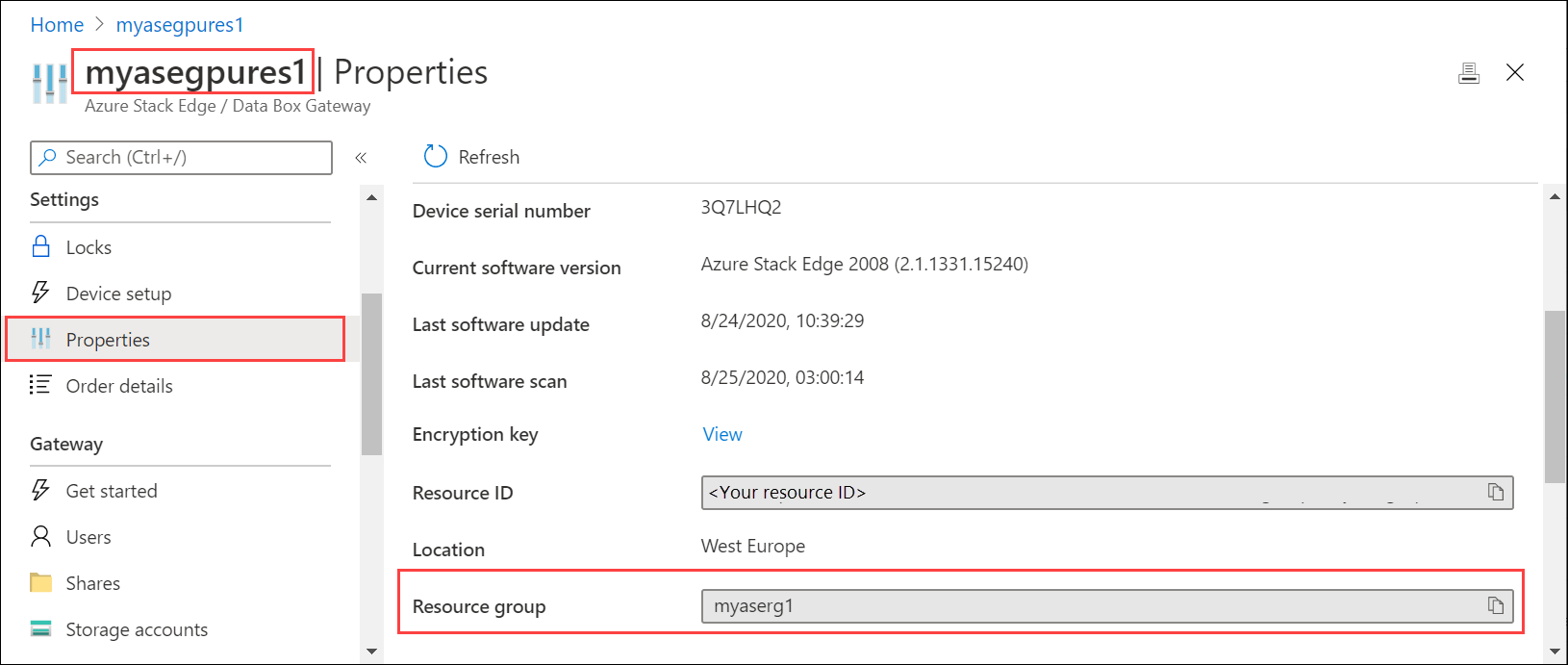
To get the resource group name, go to Properties.
To create a service principal, use the following command via the
az cli.az ad sp create-for-rbac --name "<Informative name for service principal>"For information on how to log into the
az cli, Start Cloud Shell in Azure portal. If usingaz clion a local client to create the service principal, make sure that you're running version 2.25 or later.Here's an example.
PS /home/user> az ad sp create-for-rbac --name "https://azure-arc-for-ase-k8s" { "appId": "xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx", "displayName": "azure-arc-for-ase-k8s", "name": "https://azure-arc-for-ase-k8s", "password": "<password>", "tenant": "xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx" } PS /home/user>Make a note of the
appID,name,password, andtenantIDas you'll use these values as input to the next command.After creating the new service principal, assign the
Kubernetes Cluster - Azure Arc Onboardingrole to the newly created principal. This is a built-in Azure role (use the role ID in the command) with limited permissions. Use the following command:az role assignment create --role 34e09817-6cbe-4d01-b1a2-e0eac5743d41 --assignee <appId-from-service-principal> --scope /subscriptions/<SubscriptionID>/resourceGroups/<Resource-group-name>Here's an example.
PS /home/user> az role assignment create --role 34e09817-6cbe-4d01-b1a2-e0eac5743d41 --assignee xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx --scope /subscriptions/xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx/resourceGroups/myaserg1 { "canDelegate": null, "id": "/subscriptions/xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx/resourceGroups/myaserg1/providers/Microsoft.Authorization/roleAssignments/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000", "name": "xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx", "principalId": "xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx", "principalType": "ServicePrincipal", "resourceGroup": "myaserg1", "roleDefinitionId": "/subscriptions/xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx/providers/Microsoft.Authorization/roleDefinitions/34e09817-6cbe-4d01-b1a2-e0eac5743d41", "scope": "/subscriptions/xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx/resourceGroups/myaserg1", "type": "Microsoft.Authorization/roleAssignments" } PS /home/user>
Enable Arc on Kubernetes cluster
Follow these steps to configure the Kubernetes cluster for Azure Arc management:
Connect to the PowerShell interface of your device.
Type:
Set-HcsKubernetesAzureArcAgent -SubscriptionId "<Your Azure Subscription Id>" -ResourceGroupName "<Resource Group Name>" -ResourceName "<Azure Arc resource name (shouldn't exist already)>" -Location "<Region associated with resource group>" -TenantId "<Tenant Id of service principal>" -ClientId "<App id of service principal>"When this command is run, there's a follow-up prompt to enter the
ClientSecret. Provide the service principal password.Add the
CloudEnvironmentparameter if you're using a cloud other than Azure public. You can set this parameter toAZUREPUBLICCLOUD,AZURECHINACLOUD,AZUREGERMANCLOUD, andAZUREUSGOVERNMENTCLOUD.Note
- To deploy Azure Arc on your device, make sure that you are using a Supported region for Azure Arc.
- Use the
az account list-locationscommand to figure out the exact location name to pass in theSet-HcsKubernetesAzureArcAgentcmdlet. Location names are typically formatted without any spaces. ClientIdandClientSecretare required.
Here's an example:
[10.100.10.10]: PS>Set-HcsKubernetesAzureArcAgent -SubscriptionId "xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx" -ResourceGroupName "myaserg1" -ResourceName "myasetestresarc" -Location "westeurope" -TenantId "xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx" -ClientId "xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx" WARNING: A script or application on the remote computer 10.126.76.0 is sending a prompt request. When you are prompted, enter sensitive information, such as credentials or passwords, only if you trust the remote computer and the application or script that is requesting the data. cmdlet Set-HcsKubernetesAzureArcAgent at command pipeline position 1 Supply values for the following parameters: ClientSecret: ********************************** [10.100.10.10]: PS>In the Azure portal, a resource should be created with the name you provided in the preceding command.
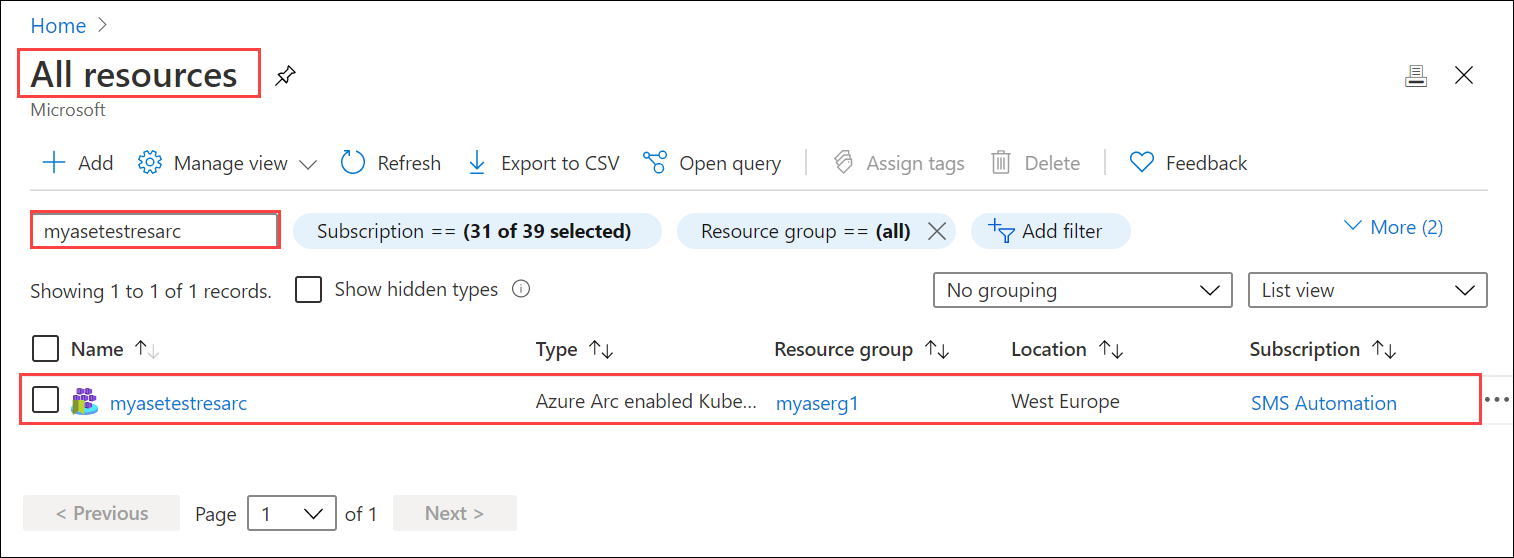
To verify that Azure Arc is enabled successfully, run the following command from PowerShell interface:
kubectl get deployments,pods -n azure-arcHere's a sample output that shows the Azure Arc agents that were deployed on your Kubernetes cluster in the
azure-arcnamespace.[10.128.44.240]: PS>kubectl get deployments,pods -n azure-arc NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE deployment.apps/cluster-metadata-operator 1/1 1 1 13d deployment.apps/clusterconnect-agent 1/1 1 1 13d deployment.apps/clusteridentityoperator 1/1 1 1 13d deployment.apps/config-agent 1/1 1 1 13d deployment.apps/controller-manager 1/1 1 1 13d deployment.apps/extension-manager 1/1 1 1 13d deployment.apps/flux-logs-agent 1/1 1 1 13d deployment.apps/kube-aad-proxy 1/1 1 1 13d deployment.apps/metrics-agent 1/1 1 1 13d deployment.apps/resource-sync-agent 1/1 1 1 13d NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod/cluster-metadata-operator-9568b899c-2stjn 2/2 Running 0 13d pod/clusterconnect-agent-576758886d-vggmv 3/3 Running 0 13d pod/clusteridentityoperator-6f59466c87-mm96j 2/2 Running 0 13d pod/config-agent-7cbd6cb89f-9fdnt 2/2 Running 0 13d pod/controller-manager-df6d56db5-kxmfj 2/2 Running 0 13d pod/extension-manager-58c94c5b89-c6q72 2/2 Running 0 13d pod/flux-logs-agent-6db9687fcb-rmxww 1/1 Running 0 13d pod/kube-aad-proxy-67b87b9f55-bthqv 2/2 Running 0 13d pod/metrics-agent-575c565fd9-k5j2t 2/2 Running 0 13d pod/resource-sync-agent-6bbd8bcd86-x5bk5 2/2 Running 0 13d [10.128.44.240]: PS>
A conceptual overview of these agents is available here.
Remove Arc from the Kubernetes cluster
To remove the Azure Arc management, follow these steps:
-
- Connect to the PowerShell interface of your device.
Type:
Remove-HcsKubernetesAzureArcAgent
Note
By default, when resource yamls are deleted from the Git repository, the corresponding resources are not deleted from the Kubernetes cluster. You need to set --sync-garbage-collection in Arc OperatorParams to allow the deletion of resources when deleted from git repository. For more information, see Delete a configuration
Next steps
To understand how to run an Azure Arc deployment, see
Deploy a stateless PHP Guestbook application with Redis via GitOps on an Azure Stack Edge Pro device