Integrate your ILB App Service Environment with the Azure Application Gateway
The App Service Environment is a deployment of Azure App Service in the subnet of a customer's Azure virtual network. It can be deployed with an external or internal endpoint for app access. The deployment of the App Service Environment with an internal endpoint is called an internal load balancer (ILB) App Service Environment.
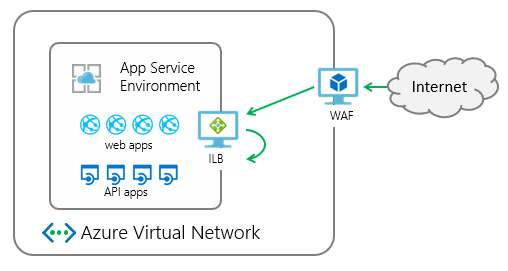
Web application firewalls help secure your web applications by inspecting inbound web traffic to block SQL injections, Cross-Site Scripting, malware uploads & application DDoS and other attacks. You can get a WAF device from Azure Marketplace or you can use the Azure Application Gateway.
The Azure Application Gateway is a virtual appliance that provides layer 7 load balancing, TLS offloading, and web application firewall (WAF) protection. It can listen on a public IP address and route traffic to your application endpoint. The following information describes how to integrate a WAF-configured application gateway with an app in an ILB App Service Environment.
The integration of the application gateway with the ILB App Service Environment is at an app level. When you configure the application gateway with your ILB App Service Environment, you're doing it for specific apps in your ILB App Service Environment.
In this walkthrough, you will:
- Create an Azure Application Gateway.
- Configure the application gateway to point to an app in your ILB App Service Environment.
- Edit the public DNS host name that points to your application gateway.
Prerequisites
To integrate your application gateway with your ILB App Service Environment, you need:
- An ILB App Service Environment.
- A private DNS zone for ILB App Service Environment.
- An app running in the ILB App Service Environment.
- A public DNS name for your application gateway.
- If you need to use TLS encryption to the application gateway, a valid public certificate that's used to bind to your application gateway is required.
ILB App Service Environment
For details on how to create an ILB App Service Environment, see Create an App Service Environment in the Azure portal and Create an App Service Environment with Azure Resource Manager template.
After ILB App Service Environment is created, the default domain is
<YourAseName>.appserviceenvironment.net.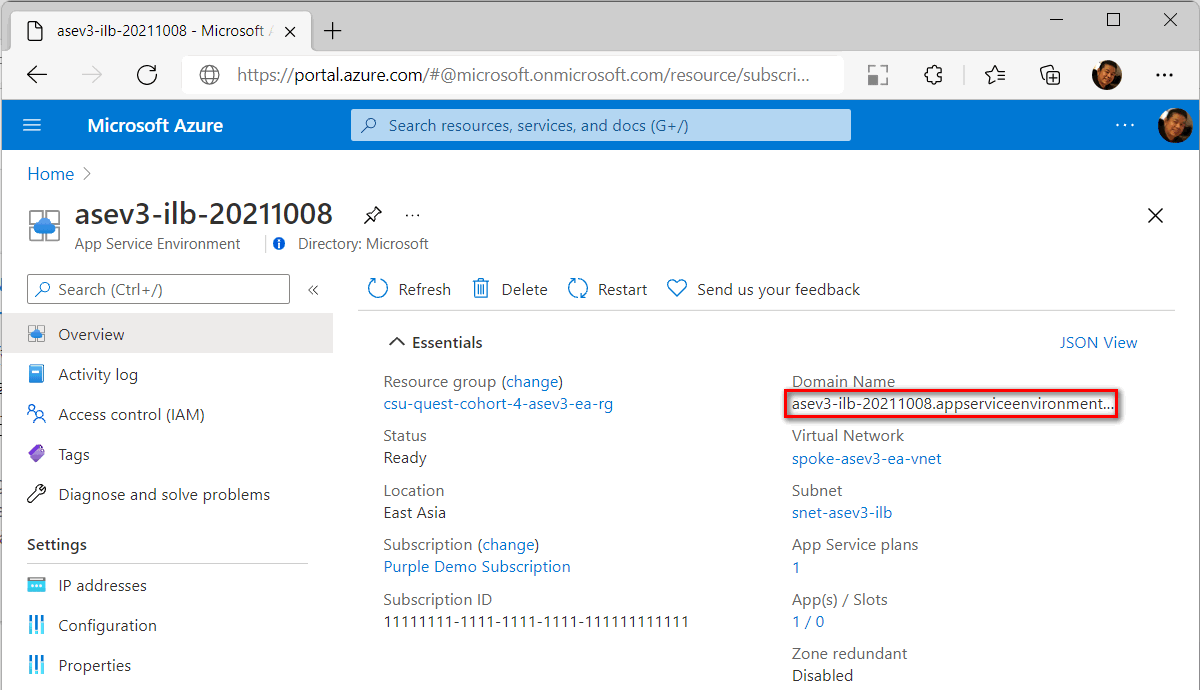
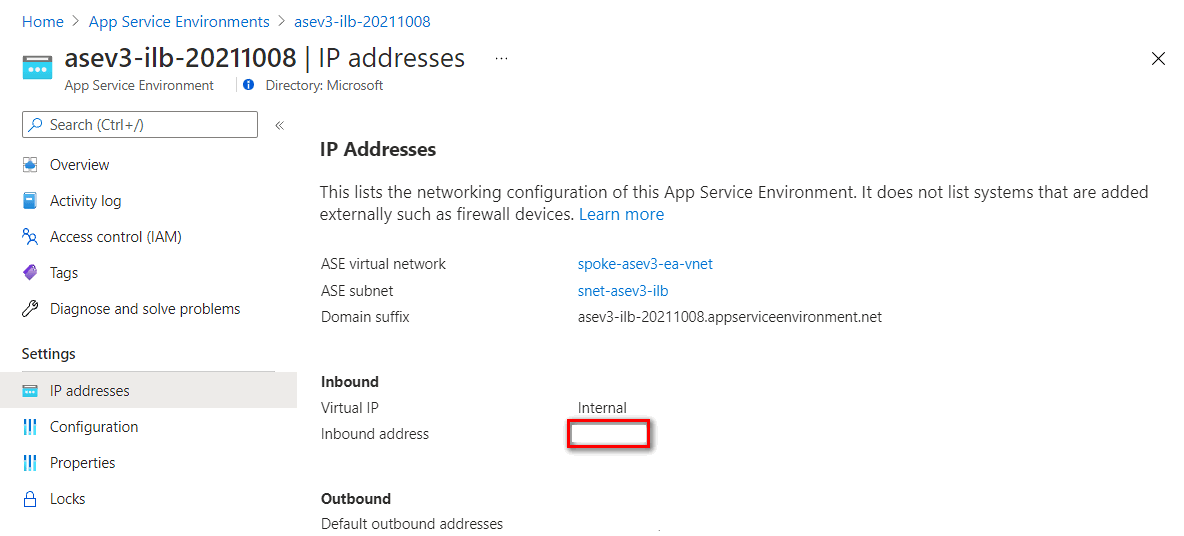
An internal load balancer is provisioned for inbound access. You can check the Inbound address in the IP addresses under App Service Environment Settings. You can create a private DNS zone mapped to this IP address later.
A private DNS zone
You need a private DNS zone for internal name resolution. Create it using the App Service Environment name using the record sets shown in the following table (for instructions, see Quickstart - Create an Azure private DNS zone using the Azure portal).
| Name | Type | Value |
|---|---|---|
| * | A | App Service Environment inbound address |
| @ | A | App Service Environment inbound address |
| @ | SOA | App Service Environment DNS name |
| *.scm | A | App Service Environment inbound address |
App Service on ILB App Service Environment
You need to create an App Service plan and an app in your ILB App Service Environment. When creating the app in the portal, select your ILB App Service Environment as the Region.
A public DNS name to the application gateway
To connect to the application gateway from internet, you need a routable domain name. In this case, I used a routable domain name asabuludemo.com and planning to connect to an App Service with this domain name app.asabuludemo.com. The IP address mapped to this app domain name needs to be set to the Application Gateway Public IP address after the application gateway is created.
With a public domain mapped to the application gateway, you don't need to configure a custom domain in App Service. You can buy a custom domain name with App Service Domains.
A valid public certificate
For security enhancement, bind a TLS certificate for session encryption. To bind TLS certificate to the application gateway, a valid public certificate with following information is required. With App Service certificates, you can buy a TLS certificate and export it in .pfx format.
| Name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Common Name | <yourappname>.<yourdomainname>, for example: app.asabuludemo.com or *.<yourdomainname>, for example: *.asabuludemo.com |
A standard certificate or a wildcard certificate for the application gateway |
| Subject Alternative Name | <yourappname>.scm.<yourdomainname>, for example: app.scm.asabuludemo.com or *.scm.<yourdomainname>, for example: *.scm.asabuludemo.com |
The SAN that allowing to connect to App Service kudu service. It's an optional setting, if you don't want to publish the App Service kudu service to the internet. |
The certificate file should have a private key and save in .pfx format. The certificate is imported to the application gateway later.
Create an application gateway
For the basic application gateway creation, refer to Tutorial: Create an application gateway with a Web Application Firewall using the Azure portal.
In this tutorial, we use Azure portal to create an application gateway with ILB App Service Environment.
In the Azure portal, select New > Network > Application Gateway to create an application gateway.
Basics setting
In Tier dropdown list, you can select Standard V2 or WAF V2 to enable WAF feature on the application gateway.
Frontends setting
Select Frontend IP address type to Public, Private or Both . If you set to Private or Both, you need to assign a static IP address in the application gateway subnet range. In this case, we set to Public IP for public endpoint only.
Public IP address - You need to associate a public IP address for the application gateway public access. Record this IP address, you need to add a record in your DNS service later.
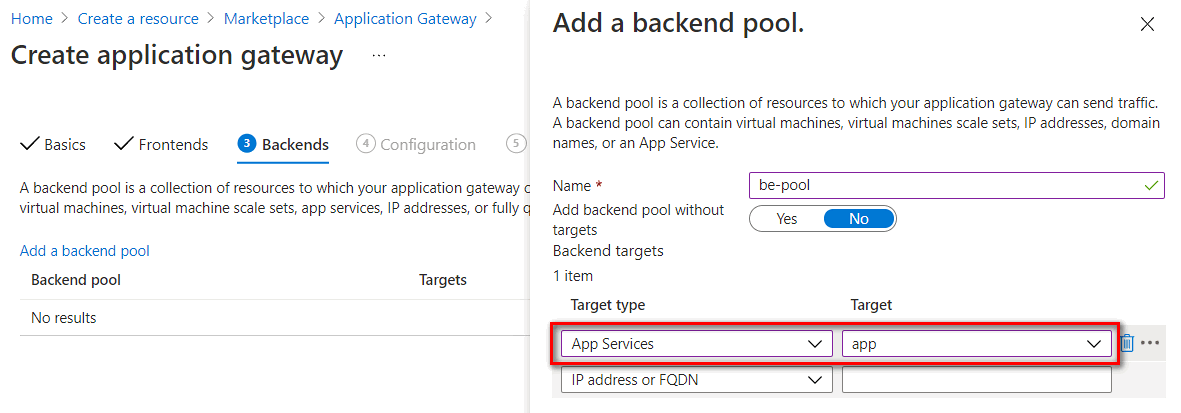
Backends setting
Input a backend pool name and select the App Services or IP address or FQDN in Target type. In this case, we set to App services and select App Service name from the target dropdown list.
Configuration setting
In Configuration setting, you need to add a routing rule by selecting Add a routing rule icon.
You need to configure a Listener and Backend targets in a routing rule. You can add an HTTP listener for proof of concept deployment or add an HTTPS listener for security enhancement.
To connect to the application gateway with HTTP protocol, you can create a listener with following settings,
Parameter Value Description Rule name For example: http-routingruleRouting name Listener name For example: http-listenerListener name Frontend IP Public For internet access, set to Public Protocol HTTP Don't use TLS encryption Port 80 Default HTTP Port Listener type Multisite Allow to listen multi-sites on the application gateway Host type Multiple/Wildcard Set to multiple or wildcard website name if listener type is set to multi-sites. Host name For example: app.asabuludemo.comSet to a routable domain name for App Service 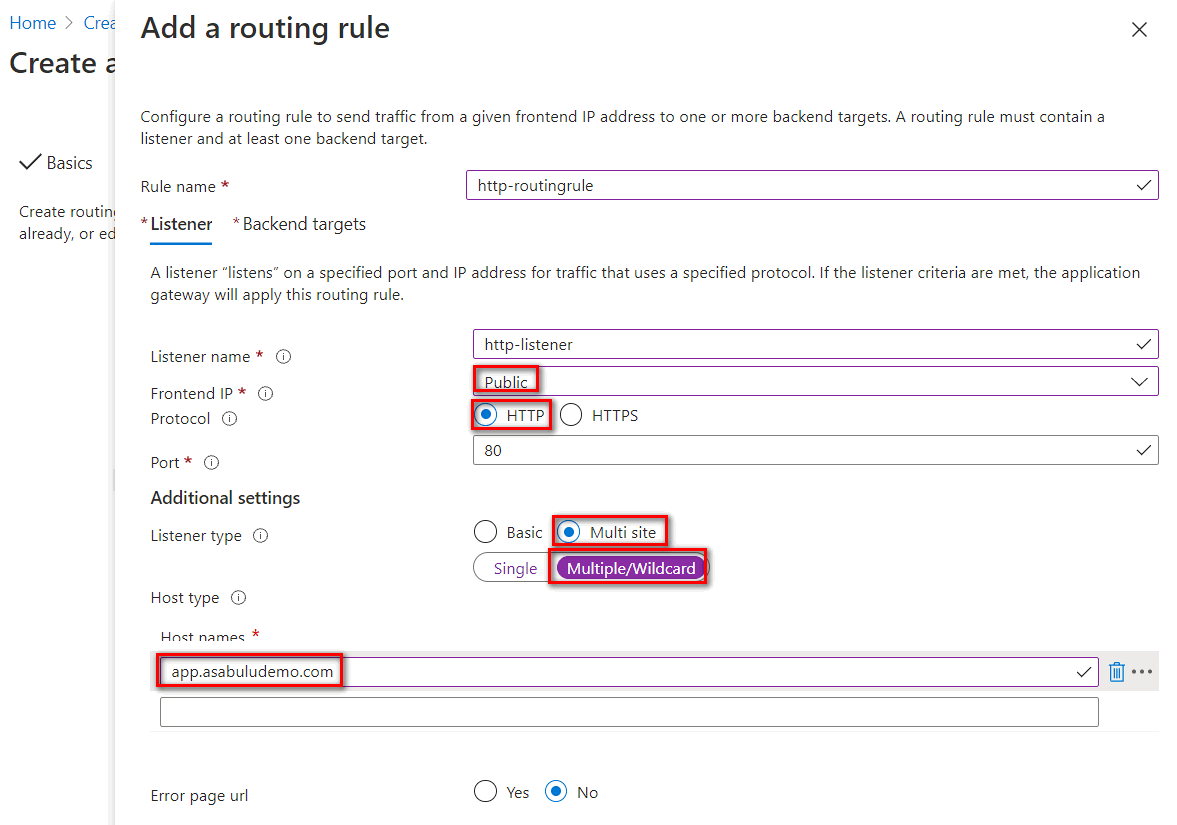
To connect to the application gateway with TLS encryption, you can create a listener with following settings:
Parameter Value Description Rule name For example: https-routingruleRouting name Listener name For example: https-listenerListener name Frontend IP Public For internet access, set to Public Protocol HTTPS Use TLS encryption Port 443 Default HTTPS Port Https Settings Upload a certificate Upload a certificate contains the CN and the private key with .pfx format. Listener type Multisite Allow to listen multi-sites on the application gateway Host type Multiple/Wildcard Set to multiple or wildcard website name if listener type is set to multi-sites. Host name For example: app.asabuludemo.comSet to a routable domain name for App Service 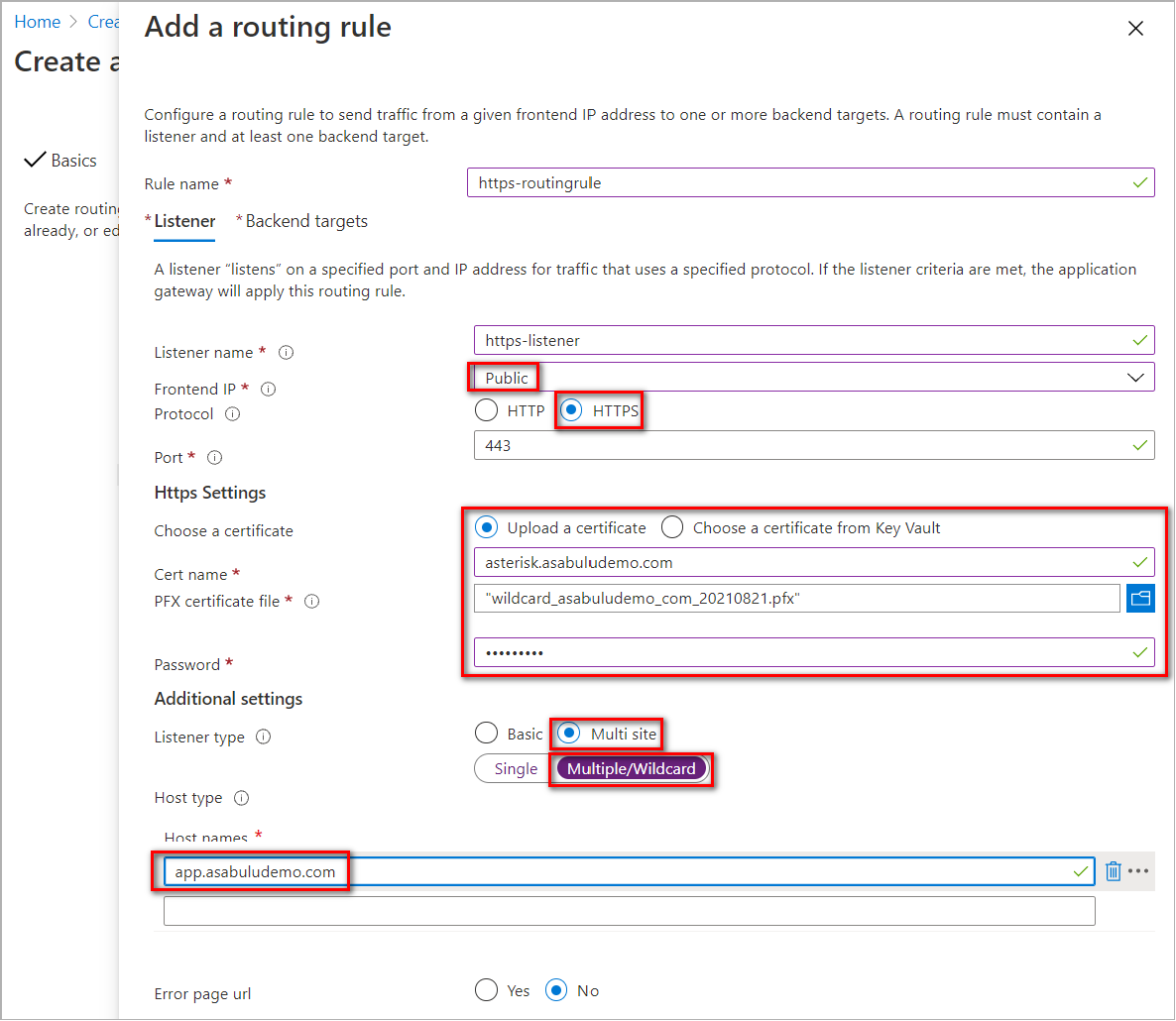
You have to configure a Backend Pool and HTTP setting in Backend targets. The Backend pool was configured in previously steps. Select Add new link to add an HTTP setting.
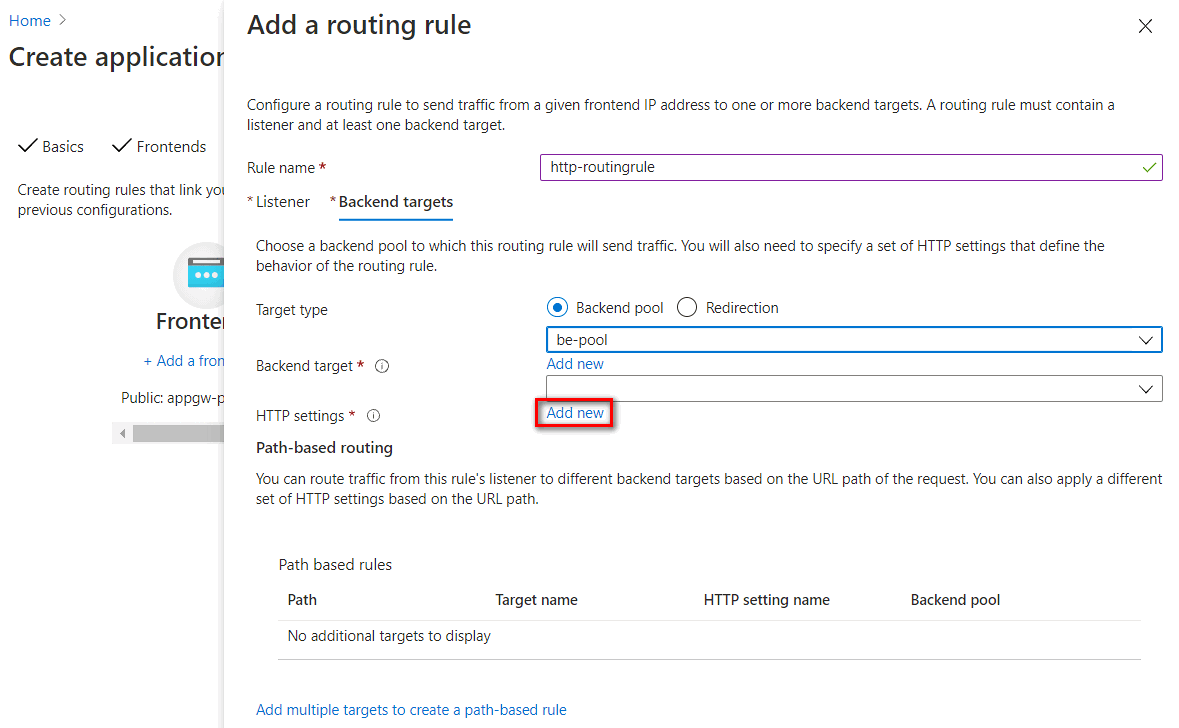
HTTP settings listed in the following table:
Parameter Value Description HTTP setting name For example: https-settingHTTP setting name Backend protocol HTTPS Use TLS encryption Backend port 443 Default HTTPS Port Use well known CA certificate Yes The default domain name of ILB App Service Environment is .appserviceenvironment.net. The certificate of this domain is issued by a public trusted root authority. In the Trusted root certificate setting, you can set to use well known CA trusted root certificate.Override with new host name Yes The host name header is overwritten on connecting to the app on ILB App Service Environment Host name override Pick host name from backend target When setting backend pool to App Service, you can pick host from backend target Create custom probes No Use default health probe 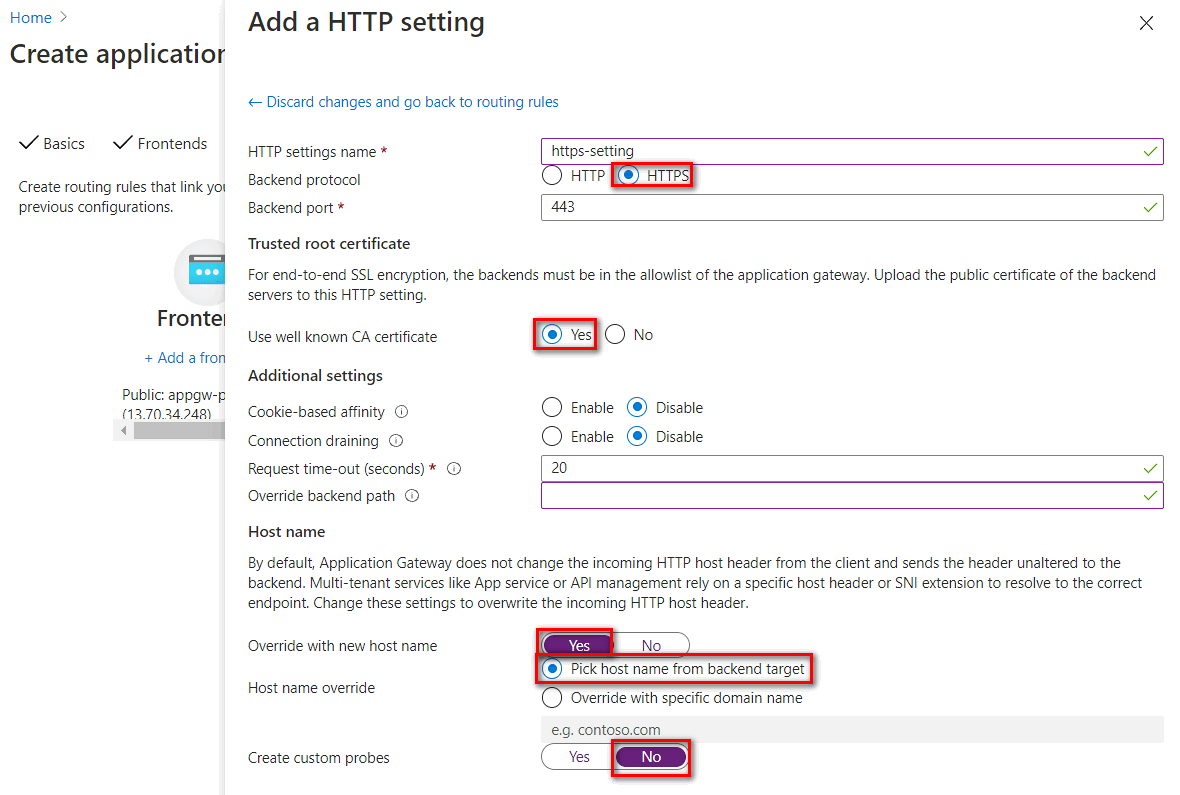
Configure an application gateway integration with ILB App Service Environment
To access ILB App Service Environment from the application gateway, you need to check if a virtual network link to private DNS zone. If there's no virtual network linked to your application gateway's virtual network, add a virtual network link with following steps.
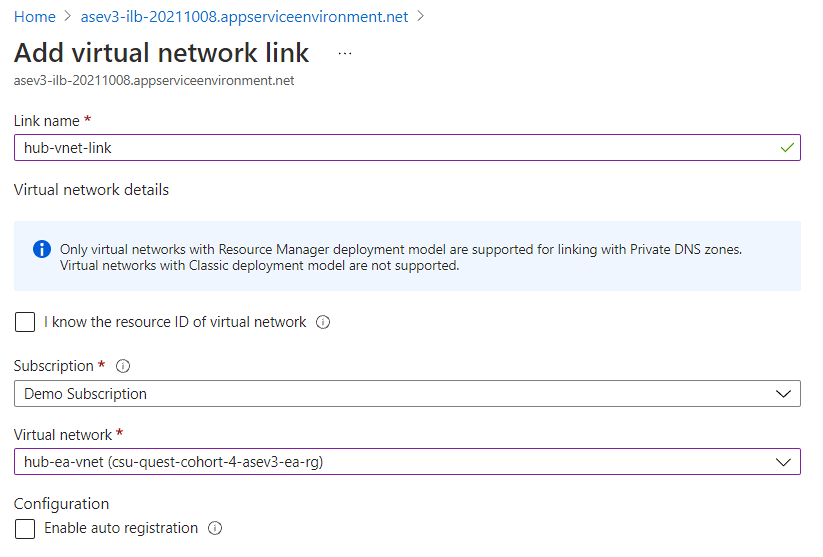
Configure virtual network links with a private DNS zone
- To configure virtual network link with private DNS zone, go to the private DNS zone configuration plane. Select the Virtual network links > Add
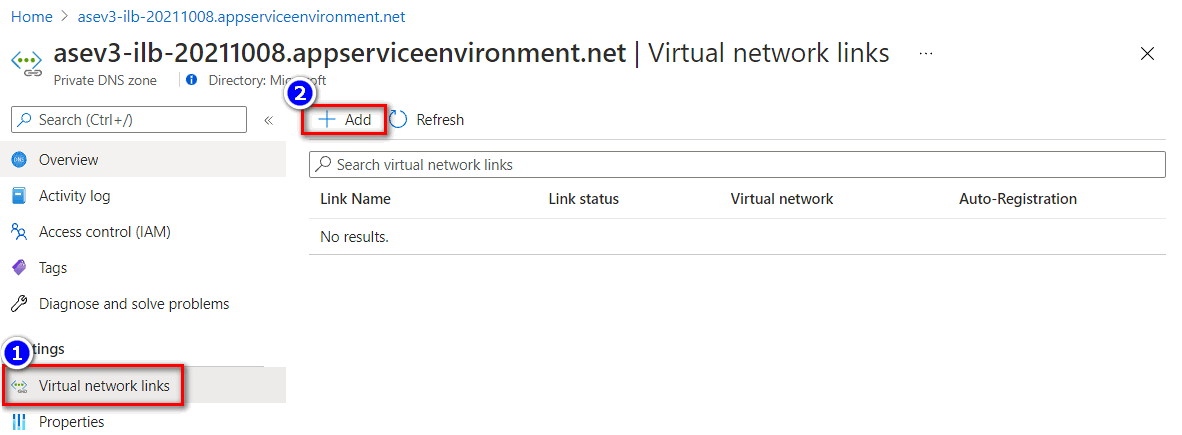
- Input the Link name and select the respective subscription and virtual network where the application gateway resides in.
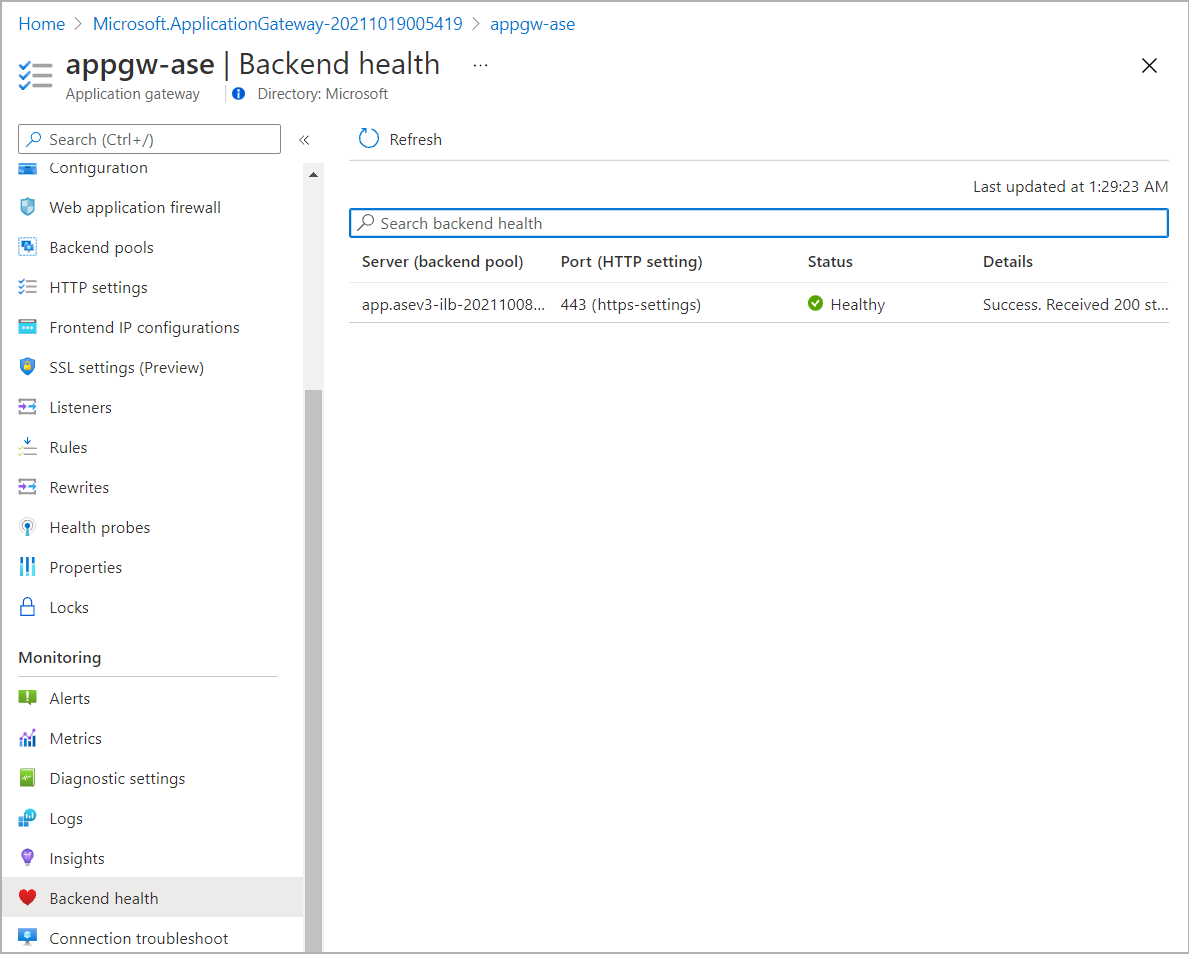
- You can confirm the backend health status from Backend health in the application gateway plane.
Add a public DNS record
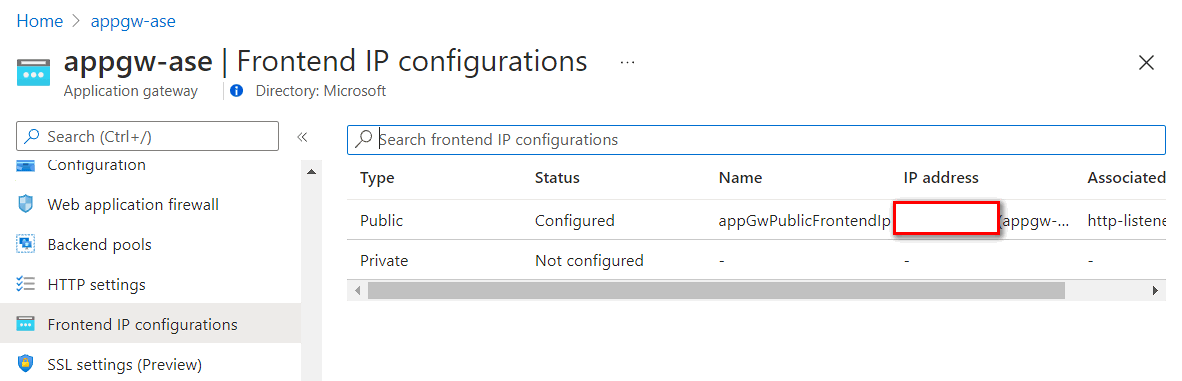
You need to configure a proper DNS mapping when access to the application gateway from internet.
- The public IP address of the application gateway can be found in Frontend IP configurations in the application gateway plane.
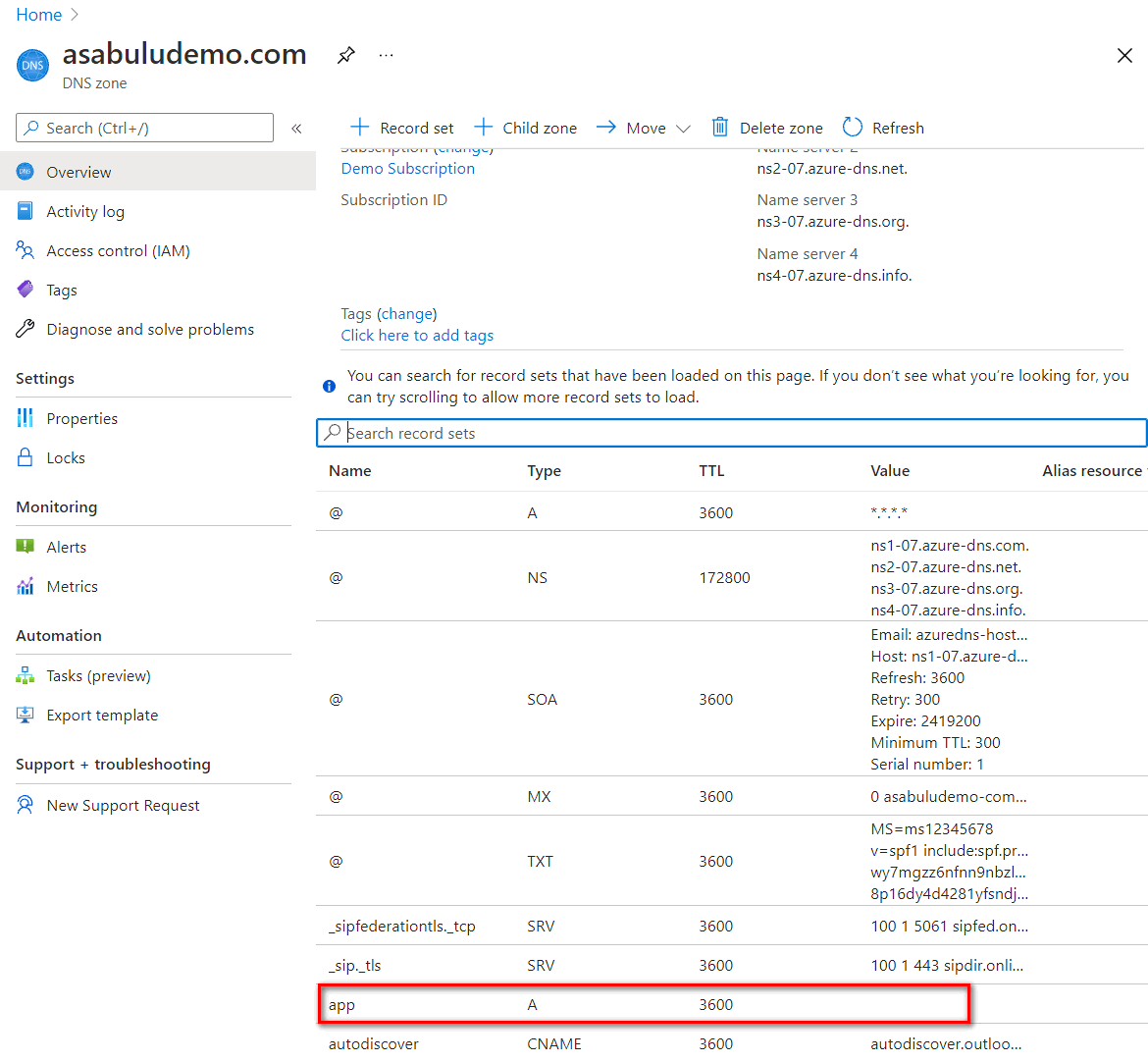
- Use Azure DNS service as example, you can add a record set to map the app domain name to the public IP address of the application gateway.
Validate connection
- On a machine access from internet, you can verify the name resolution for the app domain name to the application gateway public IP address.
- On a machine access from internet, test the web access from a browser.